What is Semantic Search?
Have you ever searched for something online and got links that don’t exactly match what you were looking for? Before advancement in AI, you had to enter very specific and targeted keywords in search engines to get the information you wanted. That was the limitation of traditional keyword search. But today, your search engine can understand what you actually mean. How? Enter semantic search — a smart way to find the information you need.
Rather than just matching exact words like traditional keyword-based search systems, semantic search uses NLP and ML algorithms to understand the context and real meaning behind the search terms.
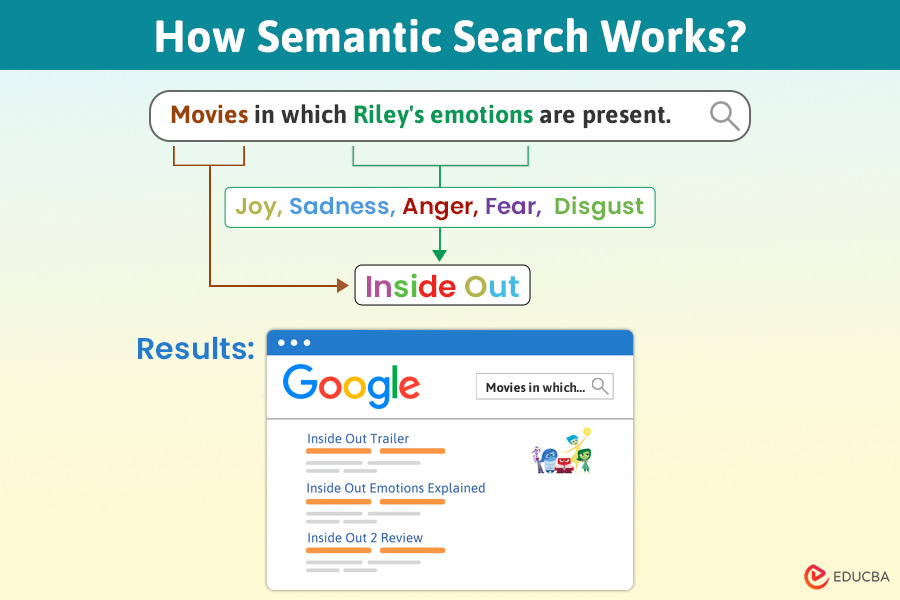
For example, if you search “Movies in which Riley’s emotions are present,” on Google, the semantic search algorithm will connect the words “Riley’s emotions” and “Movies” to the movie “Inside Out.” As a result, it will show results like the Inside Out trailer, review, or similar links.
Table of Contents
Is Semantic Search a Trend or Necessity?
According to a 2023 study by Grand View Research, the global semantic search market might grow at a CAGR of 18.4% from 2023 to 2030. It shows how the demand for more accurate and contextually relevant search results is increasing.
It is also enhancing user experiences and operational efficiency. For instance, major companies, including Google and Microsoft, are already using this to personalize user interactions.
How Does Semantic Search Work?
Here’s what goes on behind the scenes when you use a semantic search-based system.
1. Identifying the meaning behind the keywords in your search query
Instead of just matching keywords, semantic search technology analyzes the meaning behind the words in your query.
For example, if you search for “best pizzas near me,” the system understands that you are looking for nearby pizza places with good reviews, not just any web page with those specific words.
2. Understanding the context in which the user wants information
After analyzing the search query, the system tries to understand the context.
For instance, if you search for “Apple,” it considers factors like your search history and location to determine if you are referring to the fruit or the brand.
Some engines also use vectors, which are numerical representations for concepts or attributes, such as color, texture, and shape, in a multidimensional space. These types will find the nearest vector representing the concept most relevant to your search term and bring up the best results based on that.
3. Using meaning and context to rank relevant results
Once the system grasps the context, it ranks the results based on relevance. It identifies which results best match your query and moves them to the top of the list. Over time, the system learns from your behavior, personalizes your search results, and refines the ranking.
For example, if you consistently click on Italian food recipes when searching for “dinner ideas,” the system will start prioritizing these types of results for you.
Semantic Search Example
To understand how semantic search works, let’s use an example where a user wants to find the name of the movie featuring Riley’s emotions.
A) Core Components of Semantic Search at Work:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- It will understand the intent behind the query.
- It will interpret “Riley’s emotions” as characters from the movie “Inside Out.”
- Machine Learning
- It will identify patterns in previous similar queries.
- It will enhance the ability to return relevant results in the future.
- Knowledge Graphs
- They store information about entities (e.g., Riley, emotions, movies).
- They will understand the relationships between these entities.
B) User Query:
Query: “Name of the movie in which Riley’s emotions are present”.
C) Solution Process:
- NLP Processing:
- Recognizes “Riley’s emotions” are Joy, Sadness, Anger, Fear, and Disgust from “Inside Out.”
- Machine Learning:
- Recognizes patterns related to “Inside Out” and emotions.
- Knowledge Graph Connection:
- Knows “Inside Out” features Riley and her emotions.
- Links entities: Riley, emotions (Joy, Sadness, Anger, Fear, Disgust), and the movie “Inside Out.”
Role of Entities and Relationships:
| Entities | Relationships |
| Riley | Character in “Inside Out” |
| Emotions | Joy, Sadness, Anger, Fear, and Disgust are key elements of “Inside Out” |
| Movies | “Inside Out” |
How It All Comes Together:
- NLP: Understands user intent to find movies with Riley’s emotions.
- Machine Learning: Refines results based on similar past queries.
- Knowledge Graphs: Connects Riley, her emotions, and the movie “Inside Out.”
D) Result:
The search engine returns “Inside Out” and possibly other related content featuring Riley’s emotions, such as a sequel or related media.
Tips to Make the Most Out of Semantic Search
Here’s how you can optimize semantic search:
1. Be Specific and Use Natural Language Processing
Use complete sentences and natural language as if you are having a conversation. This approach gives the search system more context, leading to more accurate results.
Examples:
Instead of searching for “best restaurants,” you can type “What are the best restaurants near me for Indian food?”
| General Query | Specific Query |
| “weather” | “What’s the weather in Singapore tomorrow?” |
| “movie reviews” | “What are the reviews for the latest Deadpool movie?” |
2. Use Reliable Sources
Use or reference high-quality and credible sources to make a big difference in your results. Reliable sources enhance the relevance and credibility of your search results, whether you are conducting research or building a search engine from scratch.
When researching, prefer reliable sources and avoid unreliable sources.
| Reliable Sources | Unreliable Sources |
| Government publications | Unverified blogs |
| Reputable news organizations (e.g., BBC) | Social media rumors |
| Academic journals | Clickbait websites |
3. Understand and Leverage Semantic Markup
Use semantic markup (HTML techniques) to help search engines understand web content better. Developers can enhance the website’s performance on search engines.
Developers can use descriptive tags like <section> and <header> in the HTML code.
4. Be Aware of Geo-Location
It’s important to remember that many search algorithms consider your current location while generating results. If you are developing a semantic search engine, you will need to account for this feature. If you are a user, be aware that your location can affect your search results.
If you are searching for “best coffee shops,” results may vary if you are in New Jersey versus New York.
Benefits
Semantic search offers several benefits, such as:
1. Provides Relevant Results to Improve User Experience
Semantic search goes beyond exact keyword matching and understands the meaning behind the search query. It also looks for context clues by looking at the user’s previous searches, location, and preferences. By understanding this, it provides answers more quickly and accurately, leading to a better overall user experience.
2. Advanced Understanding Leads to Rich Snippets
It can handle complex and multi-faceted queries, breaking them down and understanding each part to provide comprehensive results. This way, it generates rich snippets, providing users with concise, direct answers and related information without requiring them to click through multiple links.
3. Enhances Search for Specific Domains and Information
In specialized fields like medicine, law, and academia, semantic search can greatly improve the accuracy and relevance of search results by understanding domain-specific terminology and concepts.
It also helps in resolving ambiguities in search queries by understanding the context. For example, it can differentiate between a search for “Apple,” the fruit, and “Apple,” the technology company. Due to this, content that may not rank well with keyword-based search can become more discoverable.
4. Voice Search Optimization
Semantic search is crucial for optimizing voice search, as it can understand conversational language and provide accurate responses to spoken queries.
Industrial Applications
1. E-commerce: By understanding user intent and context, semantic search can provide more accurate product recommendations. Helps customers find products more easily, even if they use different terms or phrases to describe what they are looking for.
2. Healthcare: Allows for efficient searching through patient records by understanding medical terminology and context. It also helps researchers find relevant studies and papers by understanding the specific medical concepts and relationships.
3. Legal: Enables lawyers and researchers to find relevant case laws and legal precedents by understanding the context and specific legal terms.
4. Human Resources: Improves the recruitment process by matching job descriptions with candidate profiles based on skills, experience, and job requirements.
5. Education: Offers personalized learning resources and recommendations based on students’ learning history and preferences.
6. Finance: Helps analysts and investors find relevant financial reports, news, and data by understanding financial terminology and context. Furthermore, it also assists in identifying relevant risk factors and trends by understanding complex financial relationships.
7. Marketing and Advertising: Helps marketers find relevant content ideas and topics by understanding the interests and preferences of their audience.
Final Thoughts
As we generate more data every day, the capability of finding the information we need becomes more vital. That is why the personalized and context-aware results of semantic search make it a powerful tool for users and developers alike. Moreover, the surge of AI technology and machine learning algorithms are improving the precision of semantic search.
The next time you are writing a query or developing a search algorithm, remember the power of semantic search. Utilize it, play around with it, and see how it empowers you to find the information you need, faster and more accurately.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive article provides you with complete information on what semantic search is. Here are other articles you may find useful.