Updated July 10, 2023
Definition of Semi-Variable Cost
Semi-variable cost combines fixed and variable costs, considered fixed cost up to a certain production level. Once production surpasses this limit, the nature of the cost becomes variable. The fixed cost continues to apply even in the absence of production.
Explanation
The organization employs permanent laborers who receive a fixed salary regardless of work or production. However, when production exceeds capacity, the organization hires temporary laborers on a contract basis, resulting in variable costs for their wages. Therefore, the payment of wages is considered a semi-variable cost as it combines fixed and variable elements. In this case, the organization incurs a fixed portion of the cost regardless of earnings or income.
According to accounting principles, there is no requirement to bifurcate the cost into the semi-variable cost if it functions as a function of the activity volume. Determining the variable portion must be made for internal purposes only and must be paid.
The Formula for Semi Variable Cost
The formula for Semi Variable cost is defined as under:
In the concept of semi-variable cost, companies must incur fixed costs regardless of production or income, while variable costs depend on additional activity or income generation.
Examples of Semi Variable Cost
ABC Ltd is the manufacturer of bottles. The variable cost is the cost of maintenance and the additional labor charges in case of an export order. The fixed cost is the depreciation of the machinery and salaries of the certain permanent laborers involved in producing bottles. The details of the overall cost related to production are as follows-
| Particulars (Cost Incurred) | Amount ($) |
| Rent of Factory per month where production is done | 50000 |
| Repairs to Machinery p.a. | 40000 |
| Salaries fixed per month | 35000 |
| Depreciation of machinery (p.a.) | 32000 |
| Labor Charges Per Hour of Temporary Labors | $ 25 Per Hour |
The organization’s Production Capacity is 5,000 units. We estimate sales for the year 2019-20 at 4,500 units. The organization has received an export order of 1,000 units, and the selling price per bottle is $300. Determine whether to accept the export order and calculate the additional cost to be incurred if it is accepted.
In case of repairs, the company fixes $25,000 as a base amount, and additional costs depend on production. The company maintains a fixed depreciation rate, and the rent remains unchanged. If the export order is accepted, ten laborers will work 8 hours daily for 30 days.
Solution:
Calculation of Fixed Cost
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Rent Per Annum ($ 50,000 * 12) | 600000 |
| Repairs (Fixed in nature) | 25000 |
| Fixed Salaries p.a. (35000*12) | 420000 |
| Depreciation | 32000 |
| Total Fixed Cost | 1077000 |
Calculation of Variable Cost per unit
|
Particulars |
Amount ($) |
| Repairs (40000-25000) = 15000/ 4500 units | 3.3333 per unit |
| Additional Labor cost (10 Labors * 8 hours per day * 30 days * 25 per hour) | 60,000.00 |
Calculation of Profitability if no export order is accepted
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Sales (4500 units * $ 300 per unit) | 1,350,000.00 |
| Less: Variable Cost | |
| Repairs Cost | -15,000.00 |
| Less: Fixed Cost | |
| Salaries | -420,000.00 |
| Repairs Fixed | -25,000.00 |
| Rent | -600,000.00 |
| Depreciation | -32,000.00 |
| Profit | 258,000.00 |
Calculation of Profitability if export order is accepted
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Sales (5500 units * $ 300 per unit) | 1650000 |
| Less: Variable Cost | |
| Repairs Cost (for 5000 units) | -15000 |
| Repairs Cost (for 500 units) | -1666.67 |
| Labor charges (10 Labors * 8 hours per day * 30 days * 25 per hour) | -60000 |
| Less: Fixed Cost | |
| Salaries | -420000 |
| Repairs Fixed | -25000 |
| Rent | -600000 |
| Depreciation | -32000 |
| Profit | 496333.34 |
The organization should accept the Export Order as it will enable them to achieve a profit increase of approximately 92%. The additional costs to be incurred in the case of export include labor charges and repair costs for the additional units produced.
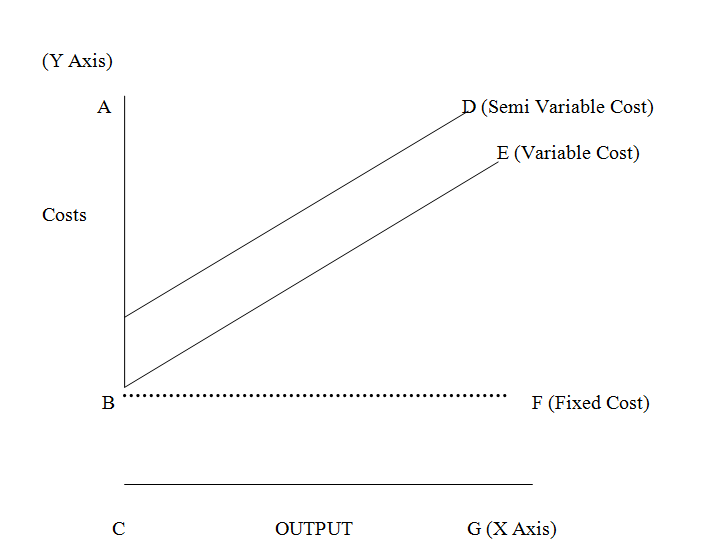
Semi Variable Cost Graph
Semi-variable cost graphs are given below:
The graph above depicts different output levels on the X-axis and the corresponding costs on the Y-axis. The line BD represents the semi-variable cost, which shows the total cost incurred by the company at different output levels. It is derived by adding the fixed cost and variable cost. The fixed cost, represented by line BF, is a cost that remains constant regardless of changes in output. Conversely, line CE represents the variable cost, which varies with the production level.
Advantages
The advantages of semi-variable cost are provided and discussed below-
- The cost contains a mixture of fixed and variable costs, and the variable cost component is to be incurred only as a function of activity volume.
- It can benefit businesses because of the lower breakeven point in case of lower fixed costs.
- The variable portion of the semi-variable cost is incurred only after a certain production or income generation level.
- The semi-variable cost need not be classified separately; an organization can show it as normal expenses.
- It is beneficial for organizations that rarely receive large orders.
- In the case of additional or large-scale production, the semi-variable cost may be beneficial in lowering the overall cost and increasing the organization’s profit.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Semi Variable costs are provided and discussed below-
- In case of production is lower, the fixed cost has to be incurred, which might increase the cost of production and decrease the profit.
- If the fixed cost increases, the breakeven might create a loss situation.
- The cost is used for internal purposes only; hence it is not important in the accounts.
- The readers of the financial statement won’t know how much portion is fixed cost or variable cost as it is reflected as a single cost in the income or profit and loss statement.
Conclusion
It is part of the expense comprising fixed and variable cost components. Up to a certain production level, the cost is to be considered fixed, and after the production increases or reaches a certain level, the variable cost has to be incurred. The main benefit of it is that it is beneficial if the fixed cost is lower, so the breakeven can be achieved easily. On the other hand, if the fixed cost is higher, it is difficult to achieve breakeven, and the organization may suffer a loss. But on the other hand, the fixed cost has to be incurred irrespective of income or production volume, which might increase the production cost.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Semi Variable Costs. Here we also discuss the definition and examples of semi-variable cost, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –