Updated November 17, 2023
Difference Between Shares Outstanding vs Float
The outstanding shares comprise float stock and restricted stock. Outstanding shares refer to the shares (issued stocks) held by shareholders, company management, and investors in the public domain (Retail and Institutional investors). However, outstanding stocks do not include treasury stock. The term “float stock” refers to a company’s shares that have been issued to the public and are available for investors to trade in the stock market. Stock data, including the number of authorized shares and something called “float,” reflects the market’s sentiment about the company.
Share Outstanding (Issued Stock)
Outstanding shares are recorded on a company’s balance sheet under the head of “Capital Stock.” The number of outstanding shares is used in calculating key metrics such as a company’s market capitalization, as well as its earnings per share (EPS) and cash flow per share (CFPS).
Features of Outstanding Stock
- Outstanding stock numbers should not be greater than the number of authorized shares. Generally, the company authorizes more shares than the actual issuance size due to efficiency and practicality viability.
- If the company issues all its authorized shares but needs to grant more in the future, it has to authorize more shares at that point. It requires a board and stockholder vote and a document to be filed with regulatory bodies.
- Outstanding stock does not include treasury stock, which are stock shares that the company repurchases. It also does not include unissued shares.
- It can be held on a short, medium, or long-term basis.
Outstanding Shares Formula
Example
A Company has issued 25,000 shares, offered 3,000 shares to two partners, and retained 5,600 stocks in the treasury.
- Outstanding shares Formula: Shares issued – treasury shares
= 25,000 – 5,600 – (2 x 3,000) = 13,400.
- Suppose the stock is currently at $50.00. Therefore, the firm’s market capitalization is 13,400x $50.00 = $67,000.
- Company A has a net income of $15,500 per the latest financials. Therefore, the firm’s earnings per share are $15,500/ 13,400 = $1.16.
Float Stock
Float Stock means the number of shares available to buy and sell for the investors. It doesn’t count shares owned by company management and internals.
The float is derived by taking a company’s outstanding (total) shares and subtracting any restricted stock (stock under sales restriction) from it. Float stock is important for investors because it indicates how many shares are available for general investing public trading. The float value can change yearly if the company decides to repurchase shares from the market or sell more of its authorized shares internally instead of publicly.
A “low float” stock has a relatively low number of shares available for trading. Stocks with a low float and market cap tend to be volatile and can quickly move to the upside if they have a positive catalyst.
Features of the Stock Float
- Float stock includes a listed company’s share available to buy or sell to the general public.
- A company’s stock float can play an important factor in the price movement of its stock. A stock with a smaller float is more likely to feel the impact of volume change.
- Management and investors have a lot of confidence in the stock if they hold a large percentage.
- Stocks with smaller floats can become more volatile than those with larger floats.
- It can be held on a short or medium-term basis.
Float Stock Formula
Example: A company may have 6,000 outstanding shares and 1,000 restricted shares with its management and another internal body, then:
- Float stock: Shares outstanding – restricted shares = 6,000 – 1,000 = 5,000
- This is the number available number of available stocks for trading.
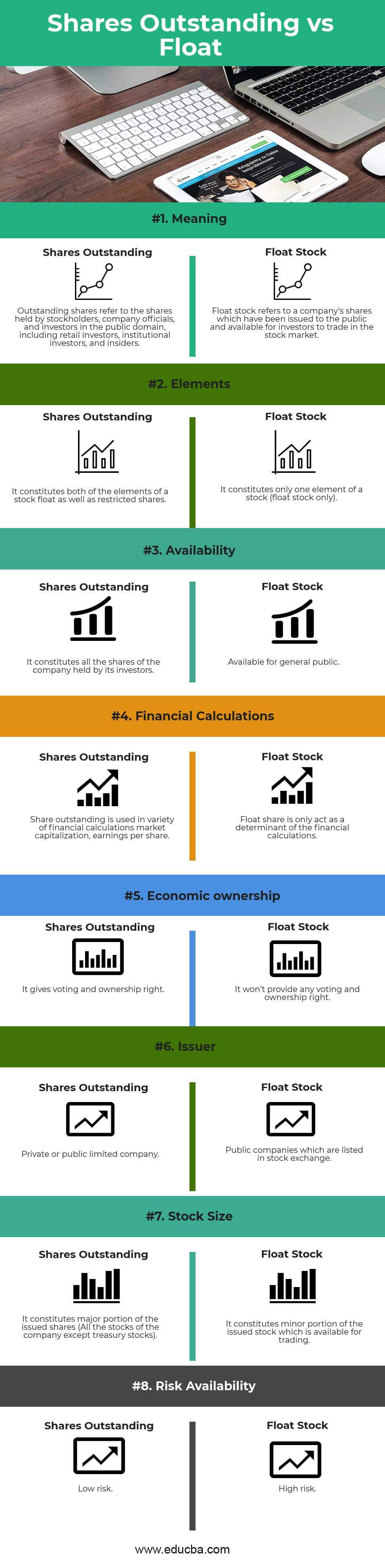
Head To Head Comparison Between Shares Outstanding vs Float (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 difference between Shares Outstanding vs Float
Key Differences Between Shares Outstanding vs Float
Both Shares Outstanding vs Float are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences between Shares Outstanding vs Float.
- Float constitutes one of two elements in the total number of outstanding shares. The float plus the number of restricted shares equals the total outstanding shares.
- Outstanding shares compromise various types of shares, while float shares are only those available for trading. Each company issuing restricted and public shares maintains outstanding shares and float.
- Float shares are only available for the general public, whereas share outstanding constitutes all the company shares held by its investors.
- Outstanding share constitutes voting right and ownership in a company, whereas float share won’t provide voting right and ownership.
- The outstanding share is used in various financial calculations, market capitalization, and earnings per share, whereas float share is only a determinant of the financial calculations.
- If the floating share is well below the share outstanding, the stock price has the potential to be volatile as there are only a few shares for trading at any given time; a larger public float can mean less volatility.
- Outstanding stocks belong to private or public companies, whereas float stock belongs to public companies listed on the stock exchange.
Shares Outstanding vs Float Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Shares Outstanding vs Float
| Basis of comparison |
Shares Outstanding |
Float stock |
| Meaning | Outstanding shares refer to the shares held by stockholders, company officials, and investors in the public domain, including retail investors, institutional investors, and insiders | Float stock refers to a company’s shares that have been issued to the public and are available for investors to trade in the stock market. |
| Elements | It constitutes both the elements of a stock float and restricted shares. | It constitutes only one element of a stock (float stock only). |
| Availability | It constitutes all the shares of the company held by its investors. | Available for the general public. |
| Financial calculations | The share outstanding is used in various financial calculations, market capitalization, and earnings per share. | Float share only acts as a determinant of the financial calculations. |
| Economic ownership | It gives voting and ownership rights. | It won’t provide any voting and ownership rights. |
| Issuer | Private or public limited company. | Public companies which are listed on the stock exchange. |
| Stock size | It constitutes a major portion of the issued shares (All the company stocks except treasury stocks). | It constitutes a minor portion of the issued stock available for trading. |
| Risk availability | Low risk | High risk |
Conclusion
The company’s stock structure plays an important role in the growth of the company. There should be a balance between float stock and the stock held by its investors because If the floating share is well below the share outstanding, the stock price has the potential to be volatile as there are only a few shares for trading at any given time, a larger public float can mean less volatility.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Shares Outstanding vs Float. Here, we discuss the Shares Outstanding vs Float key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.