Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Solvency Ratio
The term “solvency ratio” refers to the liquidity ratio that measures the ability of a company to pay off its entire liabilities by using the internal cash accrual generated from the business.
In other words, it indicates whether the cash flow of the company will be sufficient to cover its short-term and long-term liabilities or whether it will default.
The higher the value of the SR, the better the company’s liquidity position, while a lower value indicates a greater probability of default on its debt obligations. As such, the SR is extensively used by both existing and prospective lenders or investors to assess the ability of a company to pay off its debts or other obligations.
Formula
The formula for the solvency ratio can be derived by dividing the summation of net income and non-cash charges (like depreciation & amortization) by the summation of total short-term and total long-term liabilities. The numerator of the expression is akin to net cash accrual. Mathematically, the SR is represented as,
Although the value of the SR is expected to differ for industries, however, there is a thumb rule that a value of more than 20% is indicative of the company’s financial soundness.
Examples of Solvency Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the SR in a better manner.
Example – #1
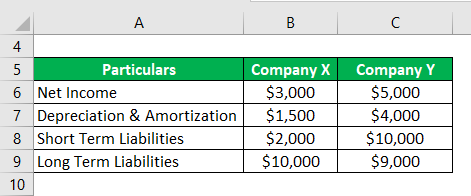
Let us take the example of two companies (Company X and Company Y) operating in the same industry, wholesale grocery. Now the current year’s financial information is available for both companies: Based on the given, calculate which company has a better solvency ratio in the current year.
Solution:
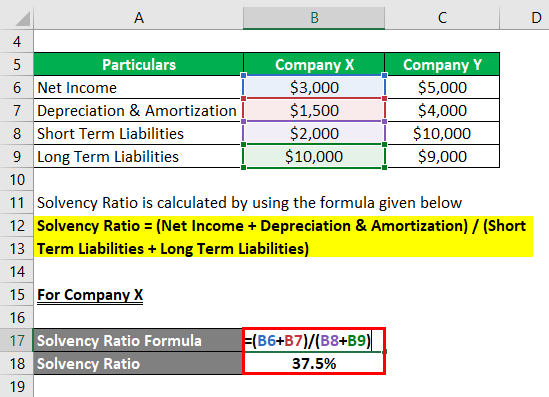
Solvency Ratio is calculated by using the formula given below
Solvency Ratio = (Net Income + Depreciation & Amortization) / (Short Term Liabilities + Long Term Liabilities)
For Company X
- SR = ($3,000 + $1,500) / ($2,000 + $10,000)
- SR = 37.5%
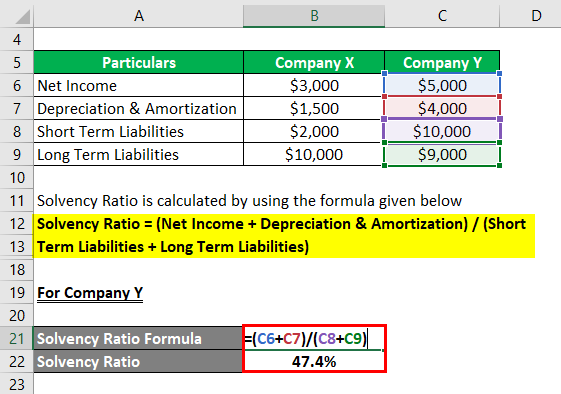
For Company Y,
- SR = ($5,000 + $4,000) / ($10,000 + $9,000)
- SR = 47.4%
Therefore, Company Y has a better SR than Company X in the current year.
Example – #2
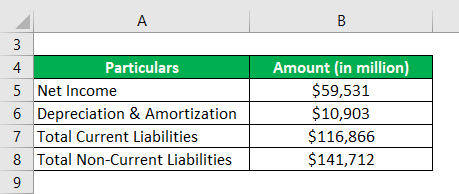
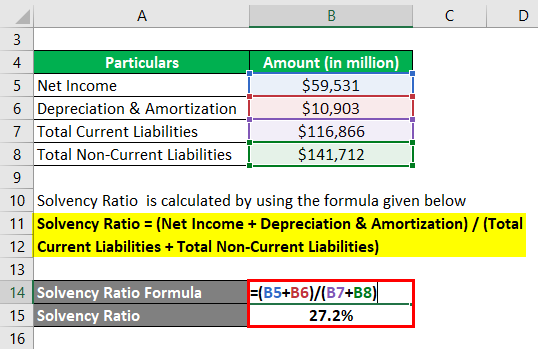
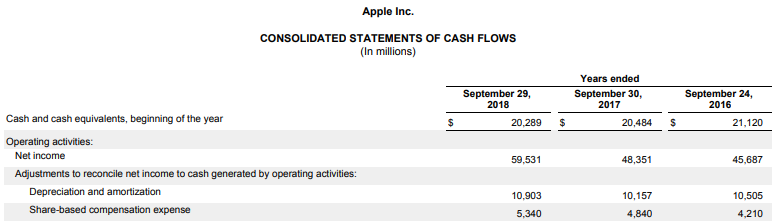
Let us take the example of Apple Inc. to calculate its solvency ratio for 2018. The following financial information is available for the year:
Solution:
Solvency Ratio = (Net Income + Depreciation & Amortization) / (Total Current Liabilities + Total Non-Current Liabilities)
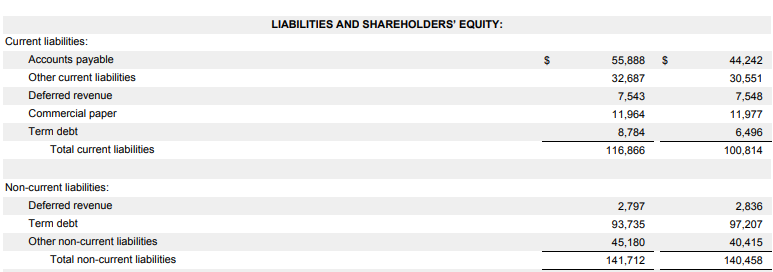
- SR = ($59,531 Mn + $10,903 Mn) / ($116,866 Mn + $141,712 Mn)
- SR = 27.2%
Therefore, Apple Inc.’s SR stood at 27.2% for 2018.
Source: Apple Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Example – #3
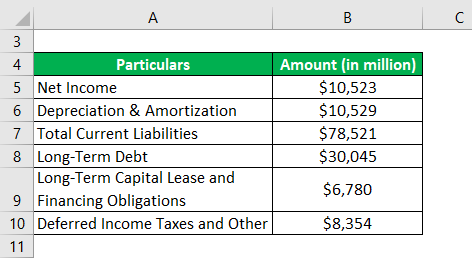
Let us take the example of Walmart to calculate its solvency ratio for the year 2018. The following financial information is available for the year:
Solution:
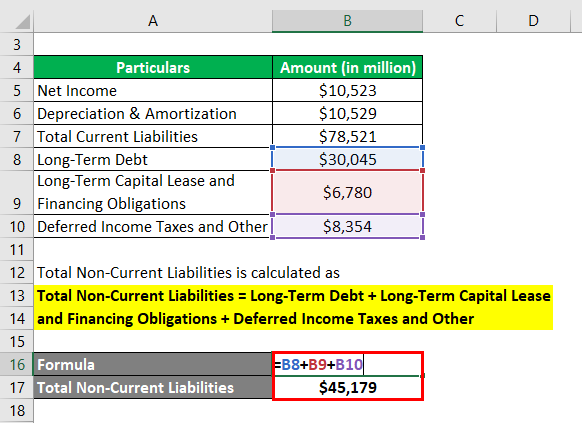
Total Non-Current Liabilities is calculated as
Total Non-Current Liabilities = Long-Term Debt + Long-Term Capital Lease and Financing Obligations + Deferred Income Taxes and Other
- Total Non-Current Liabilities = $30,045 Mn + $6,780 Mn + $8,354 Mn
- Total Non-Current Liabilities = $45,179 Mn
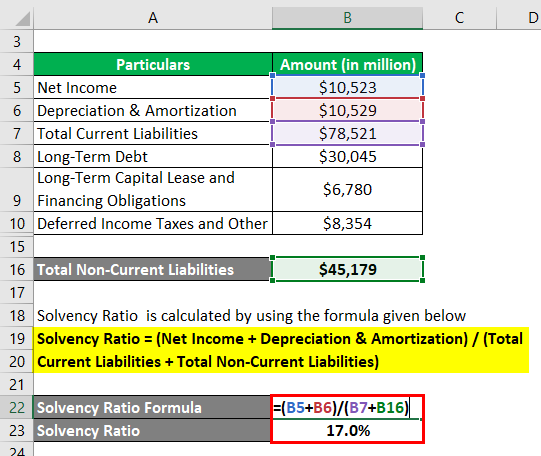
Solvency Ratio = (Net Income + Depreciation & Amortization) / (Total Current Liabilities + Total Non-Current Liabilities)
- SR = ($10,523 Mn + $10,529 Mn) / ($78,521 Mn + $45,179 Mn)
- SR = 17.0%
Therefore, Walmart’s SR stood at 17.0% for the year 2018.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- The ratio captures how well the net cash accrual from the business can cover its liabilities.
- The ratio helps compare companies’ liquidity positions in the same industry.
Disadvantages
- The ratio may be influenced by an unusually high proportion of earnings from a business that is not the core operation
- The ratio ignores the other major sources of liquidity like cash, marketable securities, etc., which should primarily cover long-term liabilities. As such, an entity with poor cash management and high receivables may have a better solvency ratio due to high net income from rising credit sales.
Conclusion
The solvency ratio is a useful liquidity measure that assists existing and prospective creditors or investors in assessing a company’s financial health. However, it is important to exercise caution when using this metric due to the potential impact of certain accounting methods, such as revenue recognition on an accrual basis. It is essential to consider the specific accounting practices employed by the company to ensure a comprehensive and accurate evaluation of its solvency position.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Solvency Ratio. Here we discuss how SR can be calculated with its formula with examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –