Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to Splunk
Splunk is a software platform that helps organizations search, monitor, visualize, and analyze big data generated in gigs from websites, servers, mobile applications, sensors, networks, etc. It can visualize your real-time environment, identify data patterns, and help you with business intelligence. On top of that, it is a highly scalable solution.
Visualizing data in Splunk starts with ingesting the data. Splunk’s free version invokes relevant programs to handle various log data formats like Apache log, Tomcat log, db2 log, etc.
Once data is brought into Splunk, it transforms the dataset into a series of events. Splunk is known for handling time series data very well.
Splunk Free Version has the Following Components
1. Search head: Helps in searching through GUI.
2. Indexer: Indexes machine data.
3. Forwarder: Forwards logs to the indexer.
Splunk Forward is of two types:
- Universal Forwarder(UF): This Splunk agent is usually installed on non-Splunk systems to collect data locally. However, it can’t index/parse the data.
- Heavyweight Forwarder(HWF): This is a sample instance of Splunk with far more functionality.
It can collect data locally, forward it and index it. In short, parsing also gets done.
4. Deployment Server: This helps Splunk to be used in the distributed environment.
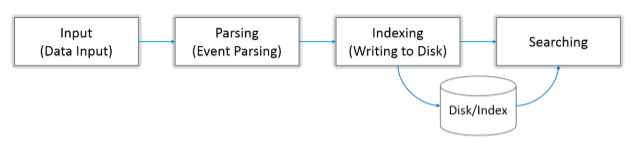
Splunk all over can be broadly divided into three stages:
- Data Input
- Data Storage
- Data Searching
a. Data Input: When data comes to Splunk from a data source, it breaks it into chunks of 64K and annotates each block to metadata keys. Metadata keys combine hostname, source & source type of data.
b. Data Storage: Data storage comprises data parsing & indexing.
This process is known as data parsing, when data gets examined, analyzed, and transformed into relevant information. In the same way, Splunk takes data and breaks it into data streams and individual events.
Indexing comes only after parsing, which means Splunk free version writes the parsed events to the disk index. Indexing gives the facility of easy data accessing and searching.
Splunk free version is capable of indexing varieties of data, such as:
- Config file
- Log files
- Messages
- Scripts
- Alerts
- Tickets
c. Data Search: Search is the core functionality of any tool/app from a massive chunk of data. Splunk has an extensive set of commands, functionalities, and arguments, enabling you to filter, modify, group, and reorder your search.
Splunk’s free version can search in a single line or multiline events.
Types of Splunk Licenses
- Enterprise license
- Forwarder license
- Beta license
- Free license
- Licenses for search heads (for distributed search)
- Licenses for cluster members (for index replication)
Splunk free version lacks: Authentication, Scheduled searches, Distributed searches, Forwarding to Non- Splunk, Deployment management
Splunk generates graphs, reports, dashboards, and alerts through excellent visualization from real-time data correlation in the searchable repository.
Detailed Usage of Splunk
- Proactive Activity Monitoring: Splunk free version helps to monitor and track user activities & privileged accounts. This can help an organization identify suspicious activity/threats in real-time manners.
- Security & Fraud: Detection and investigation of malware or other suspicious activities are more accessible by Splunk. Along with detection, it also shoots the remedial activities specific to the dashboard and relevant to the reports. This is done by capturing granular performance and event data from the virtualization layer and correlating them with other entities like datastore.
For example:
1. The high volume of emails to the non-corporate domain can be the case.
2. Excessive use of the port.
3. Web uploads from non-corporate sites by users.
- Monitoring systems: Splunk free version helps you identify when your critical systems may go down. This is done by analyzing the logs sent between the systems.
- Detect Exfiltration: It helps isolate the events and logs that require more attention.
- Capacity Monitoring and Planning: With the help of Splunk, you can fully visualize the environment and recognize the resources which are under/over-utilized. You can visualize the trend of your resource usage and can predict resource usage. Planners could also plan for real-time reallocation of resources for huge traffic management.
- Inventory Monitoring: The Splunk free version helps you keep track of all configuration items in your environment, like hosts, virtual machines, data stores, and networks.
- Change Tracking: Splunk helps track changes in topology, networks, resources, etc. You can compare various metrics to understand the problem and make a fact-based decision.
Comparison of Splunk Free Version with Spark
- Splunk is proprietary, whereas Spark is an open-source tool.
- Splunk is for collecting machine-generated data and visualizing it. Spark is the in-memory processing of big data.
- Users utilize Splunk in streaming mode, while Spark operates in streaming mode (e.g., real-time streaming for any app) and batch mode.
People often compare Splunk with Tableau when they view it as a visualization tool. Knowing the difference can help you decide which one goes best for various scenarios of an organization.
Comparison of Splunk Free Version with Tableau
- Splunk is an end-to-end solution. From the collection of data to indexing and visualization of data (structured, unstructured, or semi-structured data), it performs all. However, Tableau is just a visualization tool.
- Splunk is basically for machine-generated datasets like ATMs, data centers, IT performance, mobile devices, etc.
Splunk competitors are IBM Log Analysis, Micro Focus ArcSight, and LogRhythm.
Conclusion
Splunk is a brilliant, dynamic, and versatile tool. Gathering the statistics of your business can help you reshape the business in a very efficient way.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Is Splunk Free. Here we have discussed the basic concepts, Splunk free version, and types of Splunk licenses. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –