Updated June 15, 2023
Introduction to Splunk Interview Questions And Answers
You have finally found your dream job in Splunk but are wondering how to crack the Splunk Interview and what could be the probable Splunk Interview Questions for 2023. Every interview is different, and the job scope is different too. Keeping this in mind, we have designed the most common Splunk Interview Questions and Answers for 2023 to help you get success in your interview.
Below are the topmost helpful Splunk Interview Questions and Answers.
Part 1 – Splunk Interview Questions (Basic)
This first part covers basic Interview Questions and Answers.
1. What is Splunk? Why is Splunk used for analyzing machine data?
Answer:
One of the most used analytics tools out there is Microsoft Excel, and the drawback with it is that Excel can load only up to 1048576 rows, and the machine data are generally massive. Splunk comes in handy in dealing with machine-generated data (big data); the data from servers, devices, or networks can be quickly loaded into Splunk and analyzed to check for any threat visibility, compliance, security, etc. It can also be used for application monitoring.
2. Explain how Splunk works.
Answer:
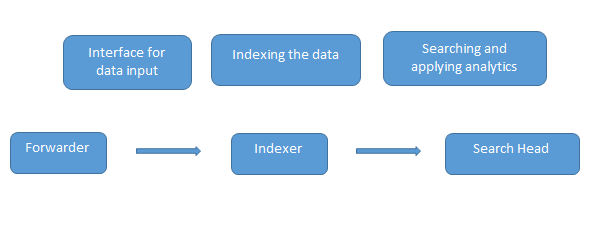
The indexer indexes the machine data and keeps it on the server. Search Head is the GUI that Splunk provides for searching and analyzing (searches, visualizes, surveys, and performs various other functions) the data. The deployment server manages all the components of Splunk, like the indexer, forwarder, and search head, in the Splunk environment.
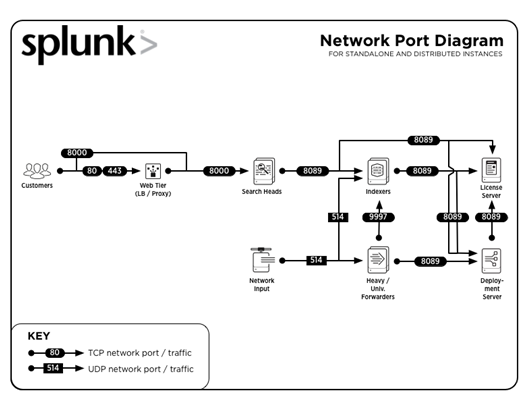
3. What are the common port numbers used by Splunk?
Answer:
Common ports numbers on which services are run (by default) are:
| Service | Port Number |
| Management / REST API | 8089 |
| Search head / Indexer | 8000 |
| Search head | 8065, 8191 |
| Indexer cluster peer node / Search head cluster member | 9887 |
| Indexer | 9997 |
| Indexer/Forwarder | 514 |
Let us move to the next Splunk interview questions.
4. Why use only Splunk?
Answer:
There are many alternatives for Splunk, which give a lot of competition to it. Some of them are as below:
- ELK/Logstash (open source)
Elasticsearch is used for searching it’s like the search head in Splunk; Log stash is for data collection, which is similar to the forwarder used in Splunk; and Kibana is used for data visualization (the search head does the same in Splunk)
- Graylog (open source with commercial version)
Like the ELK stack, Graylog has different components; it uses Elasticsearch as its core component, but the data is stored in Mongo DB and uses Apache Kafka. It has two versions one core version, which is available for free, and the enterprise version, which comes with functions like archiving.
- Sumo Logic (cloud service)
So what makes Splunk the best among all is that Splunk comes as a single package of the data collector, storage, and analytics tool inbuilt. Splunk is scalable and provides support/professional help for its enterprise edition.
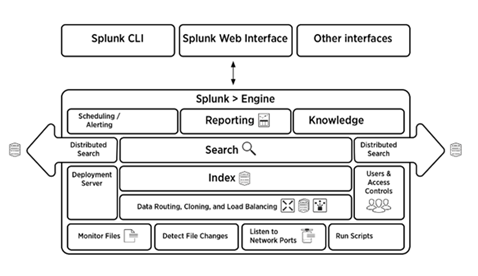
5. Briefly explain the Splunk Architecture.
Answer:
The below picture gives a brief overview of the Splunk architecture and its components.
Part 2 – Splunk interview questions (Advanced)
Let us now have a look at the advanced interview questions.
6. What are the components of Splunk architecture?
Answer:
There are four components in the Splunk architecture. They are:
- Indexer: Indexes machine data
- Forwarder: Forwards logs to index
- Search head: Provides GUI for searching
- Deployment server: Manages the Splunk components(indexer, forwarder, and search head) in a distributed environment
7. Give a few use cases of Knowledge Objects.
Answer:
A few examples are:
- Application Monitoring: This can monitor applications in real-time with configured alerts that notify admins/users when an application crashes.
- Physical Security: In the event of a flood /volcanic etc., the data can be used to draw insights if your organization is dealing with any such data.
- Network Security: You can create a secure environment by blacklisting the IP of unknown devices, thereby reducing data leaks in any organization.
8. Explain the Search Factor (SF) & Replication Factor (RF).
Answer:
The indexer cluster has both a Search Factor and a Replication Factor, whereas the Search head cluster has only a Search Factor.
9. What are Splunk buckets? Explain the bucket lifecycle.
Answer:
The lifecycle of the Splunk bucket includes four stages hot, warm, cold, frozen, and thawed.
- Hot: This bucket contains the recently indexed data and is open for writing.
- Warm: Depending on your data policies, it moves to warm buckets after the data falls into the hot bucket.
- Cold” The next stage after warm is tricky, wherein the data can’t be edited.
- Frozen: By default, the indexer deletes the data from frozen buckets, but these can also be archived.
- Thawed: The retrieval of information from archived files (frozen buckets) is known as thawing.
10. Why should we use Splunk Alert? What are the different options while setting up Alerts?
Answer:
In Splunk, environment alerts can arise due to connection failures, security violations, or breaking of any user-created rules.
For example, you send notifications or a report of the users who have failed to log in after utilizing their three attempts in a portal to the application administrator.
Different options that are available while setting up alerts are:
- A webhook can be created to write the warnings to hipchat or GitHub.
- Add results, .csv or pdf, or in line with the body of the message so that the root cause of the signal can be identified.
- Tickets can be created, and alerts can be throttled from a machine or an IP.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Splunk Interview Questions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.