Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to SQL BLOB
BLOB (Binary Large Object) is a data type in standard SQL used to store large amounts of data. It is basically a binary string of variable length, stored as a sequence of bytes or octets. BLOB data type is generally used to store large files such as images, media files such as video and audio clips in the database. We can write a BLOB value to the database as binary or character string depending on the file or requirement.
Syntax and parameters:
The basic syntax for creating a database table with columns of BLOB data type is as follows:
CREATE TABLE tablename (
Column_name1 BLOB CONSTRAINT,
column_name2 data type CONSTRAINT,
.
.
.
);The parameters used in the above mentioned syntax are similar to CREATE TABLE statement. The only difference being usage of BLOB data type instead of any other data type. We can simply use the keyword BLOB for using binary large object data type in MySQL and ORACLE databases. However, other databases such as PostgreSQL and SQL SERVER call binary large objects data types as BYTEA, binary instead.
Examples of SQL BLOB
Given below are the examples of SQL BLOB:
Example #1
SQL query to illustrate creation of a blob type field.
Code:
CREATE TABLE product_details_oracle
(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
description BLOB
);Output:
The product_details_oracle table has been successfully created with a description field of BLOB data type.
Example #2
SQL query to illustrate value insertion in BLOB data type field.
Next let us insert a few records in the product_details_oracle using the following INSERT statements.
Code:
INSERT INTO product_details_oracle VALUES(1,'product12', utl_raw.cast_to_raw('This is a blob description'));Output:
Code:
INSERT INTO product_details_oracle VALUES
(2,'product11', utl_raw.cast_to_raw ('This is a new blob description'));Output:
We have successfully inserted two records in the table. In the insert statements mentioned above, you might have observed the utl_raw.cast_to_raw function. This function is basically used to convert values to raw data type.
Example #3
SQL query to illustrate value updation in BLOB data type field.
We can simply update a BLOB column using the generic update statement as shown below.
Code:
UPDATE table_name SET BLOBColumn = 'New Value' WHERE condition_expression;But if you want to empty the blob storage and return the BLOB locator to initialize it further, you can use empty_blob() function. In this case, we have updated BLOB column for record with id = 2.
Code:
UPDATE product_details_oracle SET description = EMPTY_BLOB()
WHERE id = 2;Output:
BLOB data type in other SQL databases:
What if you do not have access to ORACLE or MySQL databases but you still want to create a Binary Large Object data type. Here, we have used postgreSQL for illustration. In postgreSQL , we use BYTEA keyword instead of BLOB as shown in the following CREATE TABLE statement.
Code:
CREATE TABLE product_details(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
description BYTEA
);Output:
The command has successfully created the product_details table. Similar to the table in the oracle database, the description field has been kept as BYTEA type.
Next, let us insert a few records in the table. In MySQL and PostgreSQL, unlike ORACLE we do not require any hex_to_raw() or cast_to_raw() functions.
Code:
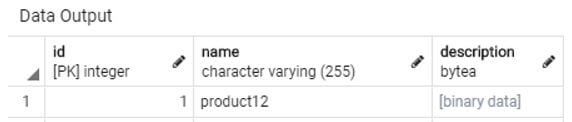
INSERT INTO product_details VALUES(1,'product12', ('This is a blob description'));Output:
The record has been successfully inserted in the table. We observe from the data output of the SELECT statement that the description field has not been shown as text but has been converted into binary data.
Code:
SELECT * FROM product_details;Output:
Let’s insert a few more records to work with BLOB data types.
Code:
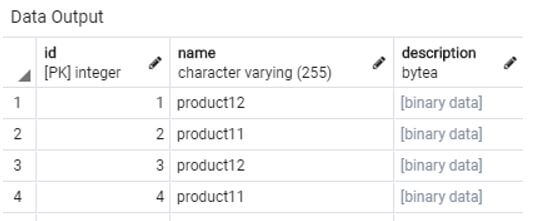
INSERT INTO product_details VALUES(2,'product11','This is a new blob description'),
(3,'product12','This is a blob description'),
(4,'product11','This is a newer blob description');Output:
The inserted rows in the product_details table looks something as follows.
Code:
SELECT * FROM product_details;Output:
Binary data in WHERE clause comparisons:
What if you want to compare BLOB or BYTEA data types in your SQL queries. We can use BLOB similar to other data types for comparison.
Example #4
Find the id, name and description for products that have exactly the same descriptions.
Code:
SELECT p1.id, p1.name, p1.description
FROM product_details as p1, product_details as p2
WHERE p1.description = p2.description AND p1.id != p2.id;Output:
In this query, we have tried to filter records by comparing description fields in the WHERE clause.
Advantages of using BLOB Data Type
- BLOB are very convenient data types when it comes to storage of big data files such as movies, songs, TV shows etc. They can easily be encrypted and referenced.
- However, not all SQL databases support BLOB data type. They require a large amount of storage space and hence have slower return time.
Conclusion
In this article we saw about BLOB data type. BLOB is a binary object data type in standard query language (SQL) that is used to store large files such as images, movies, audio clips etc in the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL BLOB” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.