Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to SQL DATEPART()
DATEPART() function in SQL returns a specific part of the DATE or TIMESTAMP expression such as year, month, week, day, hour, etc in the form of an integer value. The function works with a set of two arguments, an input date and the name of the part that has to be extracted from it.
However, datepart() function works in SQL Server, Oracle, and Azure SQL databases only. For other database management servers such as PostgreSQL and MYSQL, we can use functions like EXTRACT().
You may refer to the following set of abbreviations and the part of that they represent in the DATEPART() function as a reference card.
| Datepart | Corresponding abbreviations |
| Year | yy, yyyy, year |
| Quarter | qq, q, quarter |
| Month | mm, month |
| Day | Day, DD |
| Week | Ww, wk, WEEK |
| Day of the Week | DW |
| The week according to ISO Week System | iso_week, soak, isoww |
| Hour | HH, HOUR |
| Minute | minute, n |
| Second | second, ss, s |
| Millisecond | millisecond, ms |
| Microsecond | microsecond, mcs |
| Nanosecond | nanosecond, ns |
| Timezone offset | tzoffset, tz |
Syntax
The basic syntax for writing DATEPART() function is as follows :
DATEPART ( datepart_abbreviation , date_expression )Parameters
The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows :
Datepart_abbreviation: It represents the specific part of the date that we want to extract in the form of an integer. We already saw the list of abbreviations above. Specify the abbreviation that you want to use.
Date_expression: It represents the date column or expression. DATEPART supports the following data types only.
Date, time, datetime, datetimeoffset, datetime2, smalldatetime So, make sure that the date expression mentioned by you is the incorrect format.
Return Value: Datepart function returns an integer value representing the extracted part. For example, DATEPART(month, ‘2020/06/19’) will return 6 to represent JUNE.
We can use the DATEPART() function as a part of SELECT, UPDATE, WHERE, HAVING, etc. or any other SQL statement which accepts expressions.
Examples to Implement SQL DATEPART()
Having discussed the syntax and arguments used in a DATEPART() function, let us try some examples to understand it further.
Example #1
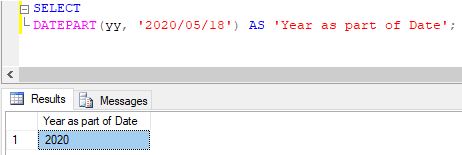
Extracting year from a given date
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(yy, '2020/05/18') AS 'Year as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: Other abbreviations like YEAR, YYYY can also be used to obtain the year part from the given date.
Example #2
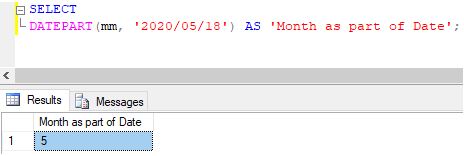
Extracting month from a given date
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(mm, '2020/05/18') AS 'Month as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we can observe that the DATEPART function returns 5, i.e. the integer value corresponding to May. We can also use other abbreviations like MONTH in Datapart_expression to obtain the same result.
Example #3
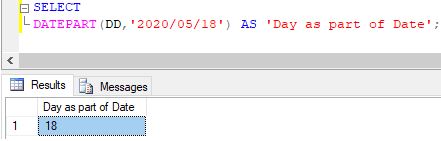
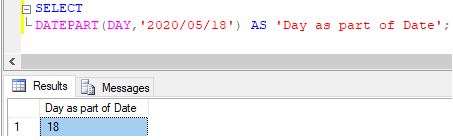
Extracting day of the month from a given date
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(DD,'2020/05/18') AS 'Day as part of Date';Output:
OR
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(DAY,'2020/05/18') AS 'Day as part of Date';Output:
Example #4
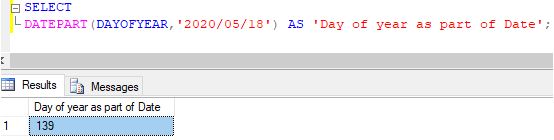
Extracting day of the year from a given date.
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(DAYOFYEAR,’2020/05/18′) AS ‘Day of the year as part of Date’;
Output:
We can also use other alternative abbreviations for DAY OF YEAR, such as :
SELECT DATEPART(DY,'2020/05/18') AS 'Day of week as part of Date';All of them will yield the same integer value.
Example #5
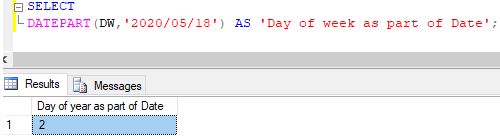
Extracting day of the week from a given date
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(DW,'2020/05/18') AS 'Day of week as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: DW or Day of the Week represents the integer value corresponding to the day’s count in the sequence of weekdays starting from Sunday. For this particular date, 18th May 2020 falls on Monday, which is the 2nd day of the week and hence the result.
Example #6
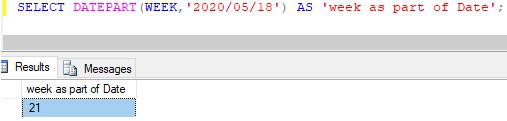
Extracting the week’s number from a given date (considering year as a whole)
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(WEEK,'2020/05/18') AS 'week as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: The WEEK, WK, ISOWK, etc. returns the week number as per ISO 8601-week numbering system. As per the convention, it counts the number of weeks starting from THURSDAY in a given year. Usually, there are 52 or 53 weeks in an entire year. Hence, the return value of the above function will lie somewhere in between 1 to 53.
Example #7
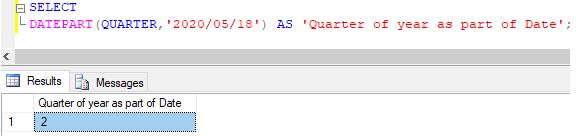
Extracting quarter of the year from a given date
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(QUARTER,'2020/05/18') AS 'Quarter of year as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: There are 4 quarters in a year. The expressions such as Q, QQ, a quarter when used in the datepart function return the quarter of the year corresponding to the given date.
Example #8
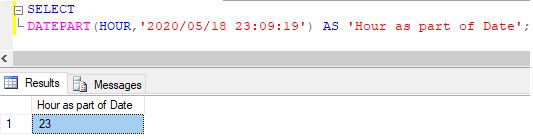
Extracting hour part from a given datetime expression
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(HOUR,'2020/05/18 23:09:19') AS 'Hour as part of Date';Output:
Explanation: We can even extract other parts such as hour, minutes, seconds, nanosecond, timestamp offset etc from a given timestamp. You may refer to the above and the next two examples for illustration.
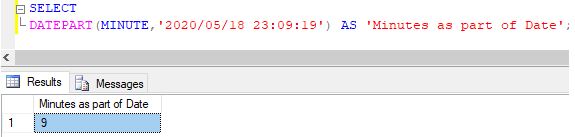
Example #9
Extracting minute part from a given datetime expression
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(MINUTE,'2020/05/18 23:09:19') AS 'Minutes as part of Date';Output:
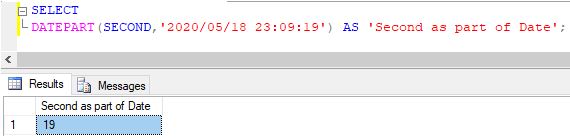
10. Extracting the second part from a given datetime expression
Code:
SELECT DATEPART(SECOND,'2020/05/18 23:09:19') AS 'Second as part of Date';Output:
Conclusion
DATEPART function() is used to extract a specific part such as year, month, day, etc. from a datetime expression. It is very useful in analyzing data and performing quick search operations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DATEPART()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.