Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to SQL DDL Commands
Data Definition Language or DDL commands in standard query language(SQL) are used to describe/define the database schema. These commands deal with database schema creation and its further modifications. Some popularly known DDL commands are CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE, and COMMENT.
There is nothing to get overwhelmed by the names of DDL commands mentioned in the previous sentence. We will explore each of these commands in this post, but first, let us have a look at this summary table.
| Command | Description |
| CREATE | Used for creating database objects like a database and a database table. |
| ALTER | Used for modifying and renaming elements of an existing database table. |
| DROP | Used for removing an entire database or a database table. |
| TRUNCATE | Used to remove all the records from a database table. |
| COMMENT | Used to write comments within SQL queries. |
Commands of SQL DDL
Now we will try to understand each of the above mentioned DDL commands in great detail in the subsequent sections.
1. CREATE
CREATE is a data definition language(DDL) command that is used for creating database objects such as database and database table.
The syntax for creating a database is as follows :
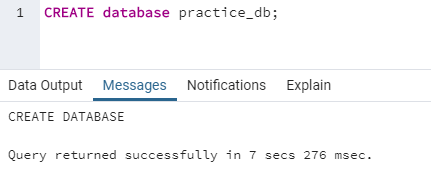
CREATE DATABASE database_name;Here is an example to illustrate database creation in SQL.
CREATE database practice_db;We Have created the database. Let us create a database table now. But for that, we first need to know the syntax.
The basic syntax for creating a table in SQL is as follows:
CREATE TABLE public.customers
(
column_name_1 datatype [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name_2 datatype [NULL | NOT NULL],
.
.
.
column_name_n datatype [NULL | NOT NULL]
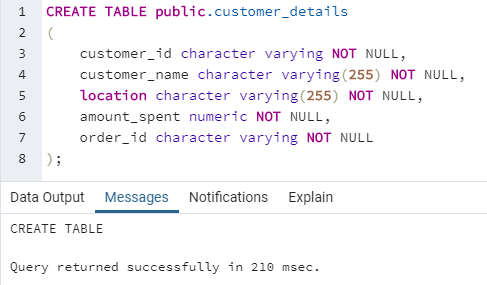
)Here is an example to illustrate database table creation using the CREATE command.
CREATE TABLE public.customer_details
(
customer_id character varying NOT NULL,
customer_name character varying(255) NOT NULL,
location character varying(255) NOT NULL,
amount_spent numeric NOT NULL,
order_id character varying NOT NULL
);2. ALTER
ALTER command in SQL is used to add, rename or modify, drop/delete columns in an existing database table. It can further be used to add and remove various constraints on an existing database table.
The syntax used for altering a table in SQL by adding a new column is as follows :
ALTER TABLE table_name
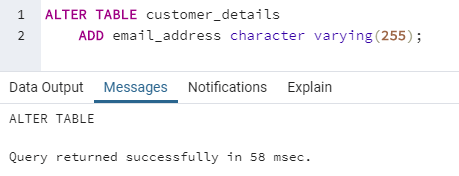
ADD (Columnname_1 datatype)Here is an example to add a new column to an existing table.
ALTER TABLE customer_details
ADD email_address character varying(255);The syntax used for renaming a table is as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name_1
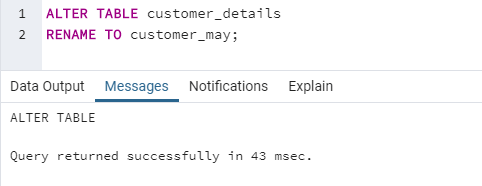
RENAME TO table_new_name;Here is an example to rename an existing database table.
ALTER TABLE customer_details
RENAME TO customer_may;The syntax used for altering a table in SQL by deleting existing columns is as follows :
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP columnname_1 , columnname_2, ...Here is an example to remove an existing column from a database table.
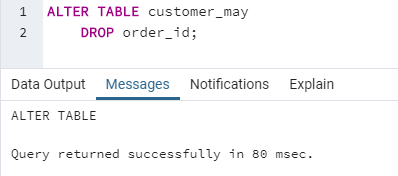
ALTER TABLE customer_may
DROP order_id;3. TRUNCATE
TRUNCATE TABLE command is used to remove all the data records from the database table. It deletes all the rows permanently. Ergo, we cannot perform a rollback operation to undo a TRUNCATE command.
The generic syntax used for writing TRUNCATE command is as follows :
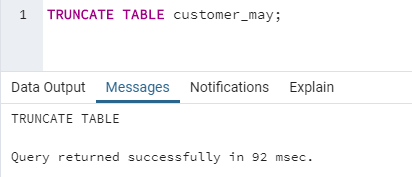
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;Now let us have a look at an example illustrating TRUNCATE command.
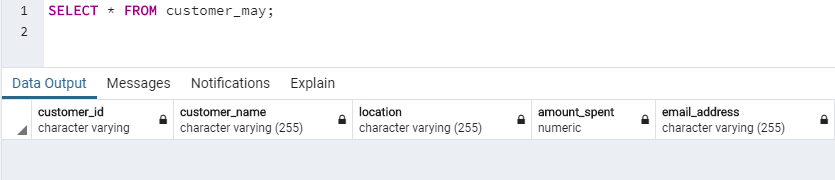
TRUNCATE TABLE customer_may;We have successfully removed all the records from the database. Let us check it using the following SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM customer_may;So what do we observe? We observe that the TRUNCATE command erases all the data from the table but maintains the table structure.
4. DROP
DROP TABLE SQL command is used to delete a database object from the database. We can even delete the database using the DROP command. We cannot perform a rollback operation to undo a DROP database/table command.
The basic syntax for writing DROP command to delete a database in SQL is as follows :
DROP DATABASE database_name;The syntax for writing DROP command to delete a database in SQL is as follows :
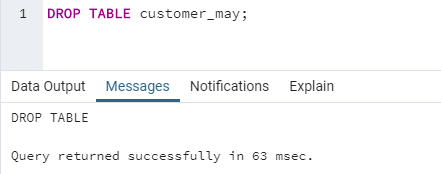
DROP TABLE table_name;Here are a few examples to illustrate the use of the DROP command in SQL.
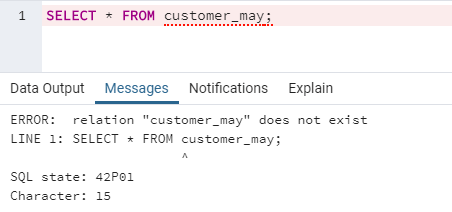
DROP TABLE customer_may;We have successfully deleted the table. In the previous section, we learned about the TRUNCATE command. Let us check how DROP is different from the TRUNCATE command.
SELECT * FROM customer_may;From the above image, it can be clearly observed that unlike the TRUNCATE command DROP statement deletes the entire table including the table structure.
5. COMMENT
Comments in SQL are similar to comments in other programming languages such as Java, C++, Python, etc. They are primarily used to define a code section for easier understanding. Comments can be a single line, multi-line, or even inline types.
Here are a few examples to illustrate commenting in SQL.
(i) Single line comment.
-- this is a single line comment
SELECT * FROM customers;(ii) Multi-line comment.
/* this is a multi line comment
SELECT * FROM customers; */
SELECT customer_id FROM customers;(iii) Inline comment.
SELECT customer_id FROM customers /* WHERE store_state = 'KA'*/;Conclusion
SQL DDL commands are used for creating new database objects (CREATE command), modifying existing database objects (ALTER command), and deleting or removing database objects (DROP and TRUNCATE commands).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DDL Commands” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.