Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to Project Management Life Cycle
The following article provides an outline for Project Management Life Cycle. Projects are part and parcel of our professional life. In the world of ever-changing technology and business trends, project management is in great demand. According to PMI, a project is defined as temporary, with a definite beginning and end in time. Also, the project is unique without routine operation and is meant to meet the singular goal with a specific set of operations. PMI further defines project management as the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. Whether the project is software development, or new product launch, or even a movie, its management will progress through five life cycle phases.
Phases of Project Management Life Cycle
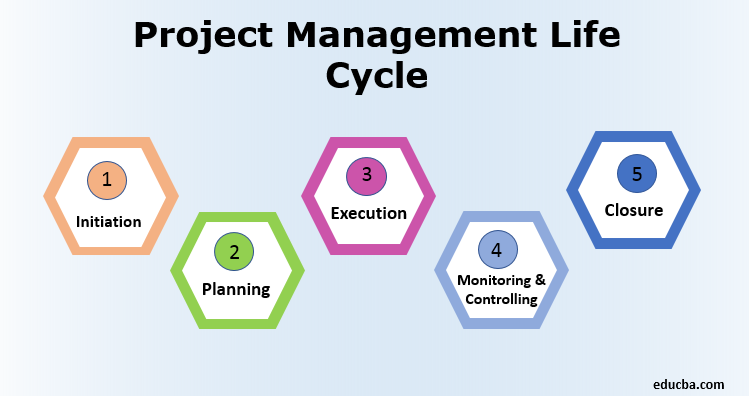
Here are the five life cycle phases of project management:
1. Initiation Phase
This is the starting point of the project. The project gets conceptualized in this phase.
In this stage, the following steps are implemented:
- The project idea is either created, or the client approaches the idea. The idea can be the solution to an existing problem or a new opportunity in business (e.g., a new smartphone model launch).
- A business case document is created, providing the solution to implement the idea after the brainstorming sessions consisting of the team, client, and project managers.
- Project managers and concerned teams check the feasibility of implementing the project in terms of profits, cost, timeline, resources, etc.
- Once the project has passed this feasibility test, it is proposed for approval from the leadership team of the company/business unit.
- During approval, SOW for the project is signed, and the budget is allocated.
After the successful completion of the above steps, the project is moved to the planning phase.
2. Planning Phase
This is the second phase of project management. During this phase, a detailed project plan is created. This plan includes tasks, resources required, timelines, costs, etc. In addition, further planning for prioritizing requirements is done. The Gantt chart, which indicates timelines for various tasks, is one of the important documents created for planning.
Different plans that are created depending on the type of project are:
- Communication Plan: A good communication plan ensures the success of the project. It determines how the information will be shared amongst the various groups involved (setting up the mail, Skype, creating a distribution list, etc.) The escalation matrix is part of this plan that is used to escalate teams for issues.
- Resource Plan: It identifies resources required for project and consumption and schedules to procure the resources. The mapping of human resources is outlined in this plan.
- Quality Plan: The plan consists of a detailed description of quality standards adopted, quality testing, and assurance used to maintain the standards.
- Deployment Plan: It includes the outline of deploying the project deliverables. The approach towards deployment, the responsibility of team members during and after the deployment, issue tracking, and support on the project post-completion of the project.
Post the completion of various plans, risk management is carried out depending on the criticality of the project. Identifying the potential threats and analyzing the impact of such threats occur from the part of this sub-phase. A risk management report is prepared with a plan to mitigate future threats.
3. Execution Phase
Done with the project idea finalization and planning. Now it’s time to set to work. In this phase, previous planning is put into action. This phase depends highly on planning. The better the plan better will be the execution.
Project managers follow the below steps in this process:
- Resource allocation and ensuring its timely delivery.
- Assigning tasks to team members on a daily basis.
- Taking daily meetings.
- Creating a status report based on daily meetings and the progress of the project.
Here the entire team comes into the picture as it starts with actual work (e.g. development of software, manufacturing). Daily targets are set; the team has to ensure to meet them; in case of delay, they have to report to project managers.
4. Monitoring and Controlling Phase
This phase is merged with the execution phase because both occur at the same time. The main objective here is to ensure that execution is carried out per the plan. Timelines and costs adhere.
The below points are implemented during monitoring:
- Set the key performance indicators (KPI’s).
- Compare the progress plan or status report with the project plan to measure KPI’s.
- For any deviation from the project, reduce the deviation and redefine KPI’s.
- Update the plan for any changes to meet the deadline.
- Monitor budget utilization.
- Monitor the quality of the project.
5. Closure Phase
Now that project is completed, and it is time to deploy the project to the client or launch it in the market. This is where the collaborated efforts come to a fruitful end!! A deployment plan created in the planning phase comes into action.
The closure phase has:
- Releasing the deliverables(product/service) to the stakeholders.
- Communicating the closure to stakeholders and business partners.
- Signing off business documents.
- Releasing the team members and closing the contracts.
- Payment and documentation filing.
- Documenting lessons learned and best practices adopted during the project so that it can be used for future reference for other projects.
- Setting up support and maintenance structure as per the requirement.
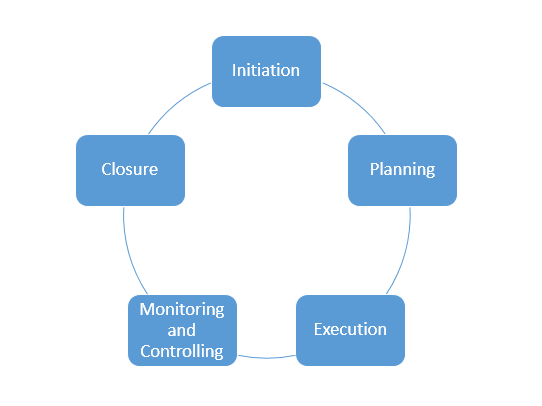
So above are the project life cycle phases. Although initiating a new project may seem like a gigantic task but breaking it into phases ensures the achievable target. But these phases aren’t mutually exclusive; they may overlap in practice. The execution and control phases that we have seen above occur at the same time. Likewise, the same thing can happen in other phases too.
Planning-Execution Merger
- The possibilities of issues and changes in requirements from the client in the execution phase can lead to changes in the project plan. The planning is again carried out in the execution phase. The agile methodology that is widely used for software projects provides the flexibility to incorporate such last-minute changes.
- Large projects are divided into small modules like manufacturing and quality can be different modules for a product. Completion of one module can correspond with initiation for other projects.
- It can be concluded that these stages are dynamic in nature, but with the help of different tools for project management, we can ensure the successful completion of the project.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Project Management Life Cycle. Here we have discussed the basic concept with five phases of the project management life cycle. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –