Updated July 7, 2023
Stagflation Meaning
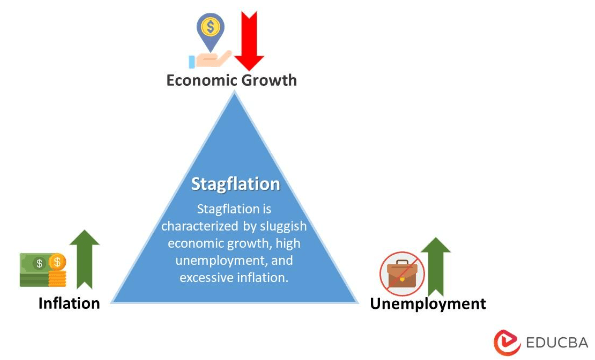
Stagflation refers to an economic phenomenon where the timing of an increase in the inflation rate coincides with that of stagnant economic growth. The term stagflation is a combination of the words “inflation” and “stagnation.”
The 1970’s Chancellor of the Exchequer, Iain Macleod, first used the term.
Key Highlights
- Stagflation occurs when an economy experiences slow growth, rising unemployment, and increasing costs at once.
- It has been a common occurrence in the developed world since the 1970s.
- It also has some advantages because it has profitable effects on some securities, asset prices, and stapled goods.
- The public, and the government, should research it to grasp how they can improve their chances for economic success.
Explanation
Stagflation was never thought to happen in a real-world economy until it occurred in the West during the 1970s crisis. Even the policymakers despise such a situation. Grave consequences happen if the State proves unable to handle the stagnant economy coupled with a sudden price hike.
What causes such a unique phenomenon to occur are various reasons, out of which two that stand out the most are the supply shock and poor fiscal policies. However, it also has some positive connotations since it makes a profitable impact on certain bonds, commodity prices, and some stapled commodities.
While the State has obligations to tackle the situation, citizens should study it. They will understand where they can boost their opportunities for monetary success. A misery index helped demonstrate its effects during the 1970s. This indicator, which was just the inflation rate plus the rate of unemployment added together, monitored how stagflation affected a country’s citizens.
Examples of Stagflation
The first ever example occurred in the United Kingdom in 1965 when Ian Macleod, a British Conservative Party member, used the term “stagflation” for the first time and warned the House Commons in the British Parliament about the gravity of the situation. In Macleod’s words: “We now have the worst of both worlds—not just inflation on the one side or stagnation on the other, but both of them together. We have a sort of ‘stagflation’ situation. And history, in modern terms, is indeed being made.”
A famous example is the first real-world premiere of the process, which caught the international eye. During the 1970s energy crisis, the Western world faced petroleum shortages, mainly in the United States. Around this time, the Middle East countries took a political decision to restrict trade-offs with the US, and the labor market conditions were flunking simultaneously despite an enormous amount of cash flow from the Federal Reserve.
Causes of Stagflation
- According to one theory, stagflation happens once a country’s economic capability for production decreases by a sharp spike in the price of oil.
- A classic example is the oil crisis of the 1970s, which led to a sharp increase in the price of oil worldwide, driving up the cost of commodities and fueling an increase in unemployment. Prices increased even as more people lost their jobs due to rising transportation expenses, which made it more costly to produce goods and deliver them to retail shelves.
- Poor monetary policies can also immediately play a role in economic downfall. For example, the government can create a policy that radically increases the minimum wage limit for industrial workers without foreseeing the impact it will have on the prices of a commodity that will lead to an immediate decrease in purchasing power for those not involved in the industrial sector.
- Another constant theory is that of a supply shock. A supply shock is a sudden change in supply rate leading to a profound change in prices that is either causing an excessive supply or excessive demand. Excessive supply leads to losses for the producers because it exceeds the pace of demand. Therefore threatening the employment rate in the future. Similarly, excess demand leads to scarcity due to the mediocre rate of supply, which also results in the sudden increase in prices of the aggrieved commodity, leading to a decrease in purchasing power.
- Another significant but not vastly popular reason is the end of the Bretton Woods System. The Bretton Woods system used a fixed amount of gold as a standard economic unit to establish financial and commercial relations between countries like the U.S., Canada, Japan, and more. When the international economy accepted the dollar as the direct currency for trade and measure of a nation’s economy, the prices of gold and oil became volatile after many years of steadiness.
Stagflation vs. Inflation
1. Meaning
- A prolonged rise in the overall cost of all products and services, not just a selective few, over time in an economy refers to inflation. Inflation results when the supply of money expands more quickly than the sector can create products and services.
- Stagflation occurs with significant unemployment, slow economic development, and inflation. These economic circumstances don’t typically coexist.
2. Impact
- The people most adversely affected by inflation include those who have retired and are on a government pension, traders who own long-term bonds, and people with credit line debts.
- As a result of reduced salaries and a higher chance of job loss during stagflation, consumer confidence may get affected. Higher manufacturing costs and reduced sales might hurt small businesses, resulting in lower company profits and stock values. It happens to affect the investors.
3. Causes
- The primary cause of inflation is an imbalance between supply and demand for services and goods. Inflation happens if the money supply expands more quickly than the GDP.
- The economy tends to slow down or “stagnate” when growing inflation is frequently followed by the Federal Reserve’s adoption of a more aggressive monetary policy, which eventually results in stagflation.
4. Duration
- In most of the world’s economies, inflation is, to some extent, a constant. The Great Inflation, which affected more severe settings in the US, lasted from 1965 until 1982.
- Instead of years, stagflation typically gets assessed in a few months or quarters. As an extreme scenario, stagflation persisted from 1973 to 1982 in several economies.
Advantages
Can a citizen foresee any advantages in such adversity? While many assets tend to perish in stagflation, there seem to be some resilient entities that work their way through the situation. The following are those:
- A bond is a loan in which the money lender- the bondholder- for the government or a company puts an interest rate that the borrower is obliged to pay frequently until the initial amount of lent gets returned. The amount returned, with the interest rate, is the ‘principal.’ Bonds whose interest rates get adjusted with the inflation rate tend to benefit a lot to the bondholder.
- With producers always looking for increasing profits within the capacity of their production units, inflation offers a mandatory price rise to the commodities for a while until there is a balance between supply and demand.
- During inflation, a consumer’s budget gets refocused solely on stapled commodities provided by the cheapest producer available in the market despite the price rise. Companies providing such commodities come from healthcare, energy, and food.
Disadvantages
- A country experiencing stagflation will see rising commodity prices, diminished spending power, low GDP, firm closures, a fall in consumer expenditure, and increased unemployment because of corporate layoffs.
- Dealing with stagflation is like choosing between the blue and the red pill with their setbacks. Let’s say the blue pill helps you solve inflation, but then comes the economic recession. On the other hand, if you choose a red pill to solve the employment rate, which is a key symptom of recession, it leads us back to inflation. So it’s misery not for the nation but for those running the State. The problem of stagnation is hard to resolve once it starts, both in social terms and budget deficits.
Tips to Consider When Getting Your Company Ready for Stagflation
- Increasing your business’ production is the best strategy for avoiding stagflation. Consider investing in equipment or software that can automate tasks to deliver the same quantity of goods or services.
- Look for strategies to reduce spending to counteract rising costs for labor and commodities. Finding methods to reduce expenses and counteract inflationary pressures is crucial.
- Ask your vendors for longer payment terms possible to increase cash flow by lowering past-due accounts receivables (AR).
- Take into account minimizing your debt. A debt with floating interest rates should get replaced with a debt with set interest charges if the interest rate increases.
- A company may get positioned to withstand even the worst financial crisis if one shifts investments into relatively low. But, recession-proof sectors like health, basic goods, utility, and discounted retail or if someone ensures personnel flexibility in the recruiting process.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What triggers stagflation?
Answer: Stagflation is a state of affairs with high levels of unemployment, poor economic activity, and increasing costs. The 1970s had stagflation as a consequence of monetary, fiscal, and oil crisis policies.
Q2. Is stagflation more detrimental than recession?
Answer: Stagflation is more harmful than a recession since it indicates that inflation and unemployment are at historically high levels.
Q3. How does stagflation differ from inflation?
Answer: Stagflation is a mix of high inflation and concurrently poor growth. Inflation is an overall upward trend in the prices of goods and services over time.
Q4. What is the Solution to Stagflation?
Answer: Stagflation cannot get cured completely. One can try to increase productivity to a level that will result in more growth without more inflation. As a result, it would be possible to strengthen monetary policy and control the inflationary element of stagflation.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about Stagflation. To learn more about related topics, visit the following links: