Introduction to Star Patterns in Java
In this document, first, we will see how to use Java programming to work with Star patterns programs. Star patterns are a common Java pattern program widely used to improve logical thinking and flow control knowledge. You need to use two loops or three loops (depending on the programs) to show Star patterns in Java Programming. The first loop is the outer loop, and the second loop is the inner loop that shows rows and columns, respectively.
This document is helpful for those Java programmers who want to know about design patterns to improve their object-oriented design and development abilities.
Examples of Star Patterns
Let us discuss some examples to easily understand the concept of patterns in Java.
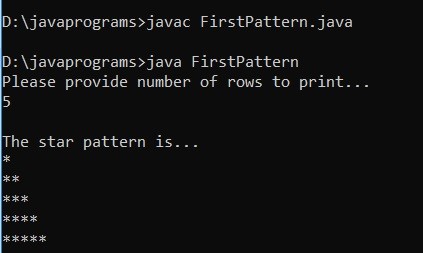
Example #1
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FirstPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = 1; n <= m; n++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
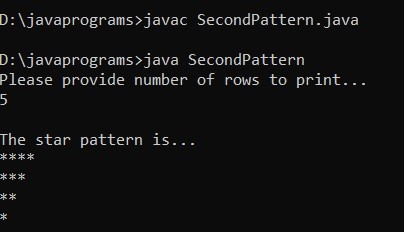
Example #2
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SecondPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = myrows; n > m; n--)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
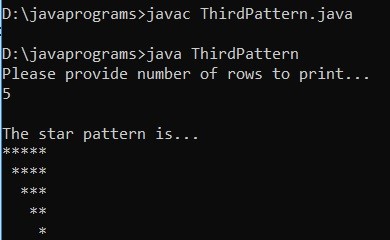
Example #3
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ThirdPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = 1; n < m; n++)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p=myrows; p>=m; p--)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
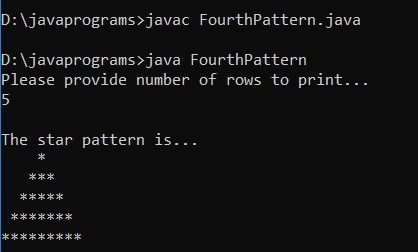
Example #4
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FourthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n=myrows; n>m; n--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p=1; p<=(m * 2) -1; p++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
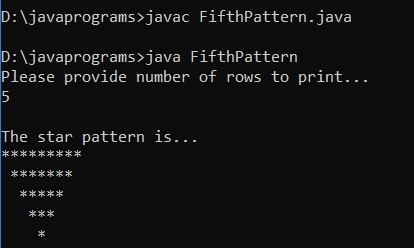
Example #5
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FifthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m=myrows; m>=1; m--)
{
for (int n=1; n<=(m * 2) -1; n++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
for (int p=myrows; p>=m; p--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}Output:
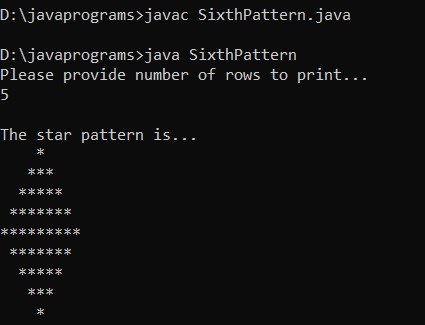
Example #6
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SixthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m=1; m<=myrows; m++)
{
for (int n=myrows; n>m; n--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p=1; p<=(m * 2) -1; p++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int m=myrows-1; m>=1; m--)
{
for (int n=myrows-1; n>=m; n--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p=1; p<=(m * 2) -1; p++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
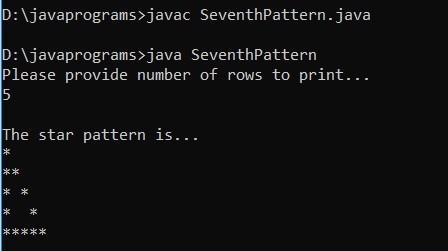
Example #7
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SeventhPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n=1; n<=m; n++)
{
if( n == 1 || n == m || m == myrows)
System.out.print("*");
else
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
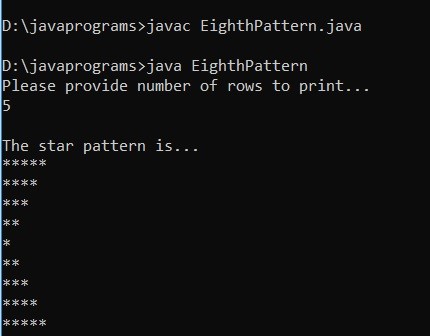
Example #8
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class EighthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = myrows; m >= 1; m--)
{
for (int n = m; n >= 1; n--)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int m = 2; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = m; n >= 1; n--)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
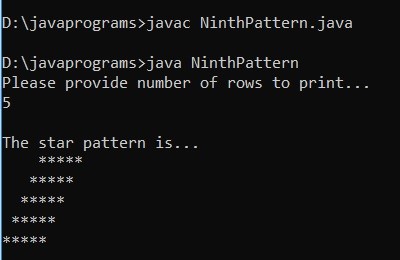
Example #9
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NinthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = myrows-1; n>=m; n--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p = 1; p <= myrows; p++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
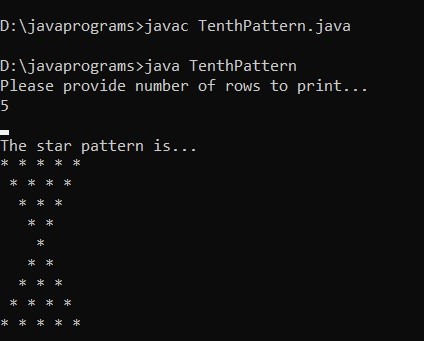
Example #10
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TenthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = 1; n < m; n++)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p = m; p <= myrows; p++)
{
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int m = myrows-1; m >= 1; m--)
{
for (int n = 1; n < m; n++)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int p = m; p <= myrows; p++)
{
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
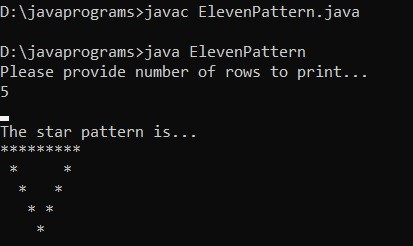
Example #11
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ElevenPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m=myrows; m>=1; m--)
{
for (int n=1; n <=(m * 2) -1; n++)
{
if( n == 1 || n == (m * 2) -1 || m == myrows)
System.out.print("*");
else
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int p = myrows; p >= m; p--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}Output:
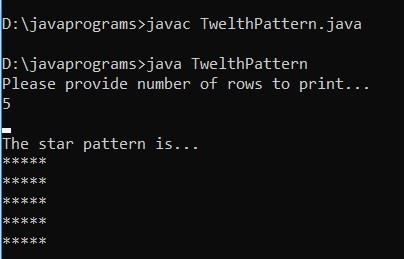
Example #12
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TwelthPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please provide number of rows to print... ");
int myrows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nThe star pattern is... ");
for (int m = 1; m <= myrows; m++)
{
for (int n = 1; n <= myrows; n++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Conclusion
So far, we have discussed different types of patterns in the Java programming language. These patterns are the best practices used by experienced object-oriented software designers. Users can be able to use these design patterns for the discussion of object-oriented software design. With the help of these patterns, inexperienced developers could learn software design quickly and faster.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Star Patterns in Java. Here we discuss the introduction and different examples along with the sample code. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –