Stock Keeping Units Meaning
Retailers and producers use SKUs, or stock-keeping units, which are unique codes that include product details like brand, size, color, and type. These codes are a combination of letters and numbers and help track how much of each product is available, where it is stored, and how well its sales are. SKUs can consist of 8 or more characters.
Sellers or Retailers use these codes to differentiate items in their inventory system. Stock keeping units are applicable for physical products, services, and other intangible goods. It’s worth noting that unlike UPC (Universal Product Code), these SKU codes are not universal. Retailers create their own unique codes for sales and inventory management.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- How Do SKUs Work?
- How to create an SKU?
- Example
- Do’s and Don’t
- Importance of SKU
- SKUs Vs. UPC
- Advantages and Disadvantages
Key Highlights
- Stock keeping units (SKUs) are scannable unique alphanumeric codes a retailer, manufacturer, or wholesaler assigns for each product.
- It helps in product differentiation, identification, inventory management, reordering, and measuring sales performance.
- Effective SKU management can boost sales, save costs, and improve customer satisfaction and shopping experience.
How Do SKUs Work?
Let’s understand how stock keeping units work in the inventory management system.
#1: Assigning SKU Code
The process of using SKUs in inventory management starts with assigning a unique code to each product in a store. It contains product information, such as size, color, style, and other characteristics.
#2: Input at POS
When a customer purchases a product, the SKU code is scanned or manually entered into the POS (Point of Sale) system at the checkout counter.
#3: Transaction Recording
The POS system then records the product’s SKU, along with the sale price, transaction details, and other information.
#4: Inventory Update
Once the sale is complete, the POS system updates the inventory by deducting the product sold associated with that SKU. This process ensures that the inventory reflects the current quantity available for each product in real time, maintaining accurate stock levels.
#5: Sales Analysis
SKUs also help track and monitor product levels to analyze sales and identify popular products.
When the product stock falls below a set threshold, the retailer uses these stock keeping units to identify products that need restocking. Moreover, it simplifies the product returns, exchanges, and repairs. For instance, when a customer returns a product, the retailer can use the SKU to obtain transaction details and streamline the return process.
How to Create an SKU?
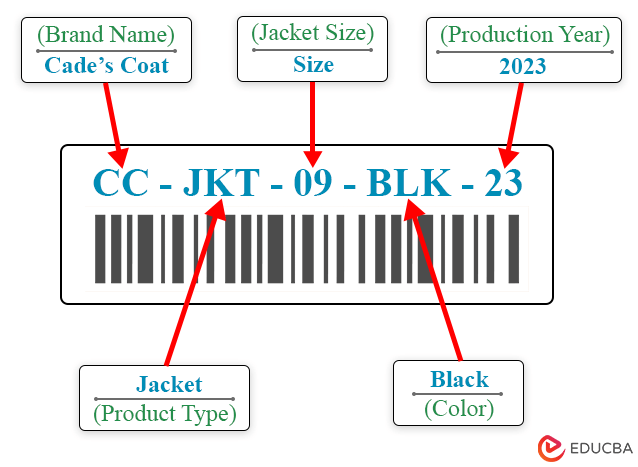
Every retailer or company creates their code using numbers and letters that reflect the details of the product. You can follow the following steps to make your stock keeping units.
Step #1: Use a Top-Level Identifier to Highlight Important Details
The first code should always highlight important details. It is the highest or top-level identifier, like your company name, brand, or product category. It usually starts with an alphabet of 2-3 letters.
Step #2: Specify a Product Variation Identifier to Represent Special Features
The next digits should be unique identifiers representing special features such as product code, type, material, etc. You can also use numerical codes to identify any product characteristic.
Step #3: Add Specific Details to Distinguish Products
This should represent the color, size, or any feature that distinguishes the product. It usually means the last details of the product.
Step #4 Finish the SKU Code with a Sequential Number
After adding all the product details, finish the code with a sequential number or the manufacturing year to distinguish old and new stock.
Step #5: Compile SKUs into Your Point-of-Sale System
After successfully creating product SKUs, add these details to your point-of-sale (POS) software system. This software helps track inventory and store transaction details.
Step #6: Generate a Scannable Barcode for Each Product SKU
After adding your SKU codes to your inventory software, create a scannable or barcode using a generator.
Step #7 Print Barcodes and attach to Products
Finally, print the SKU barcodes and attach them to your products. It will make scanning easier and update stock levels in the inventory whenever a product gets sold.
Example
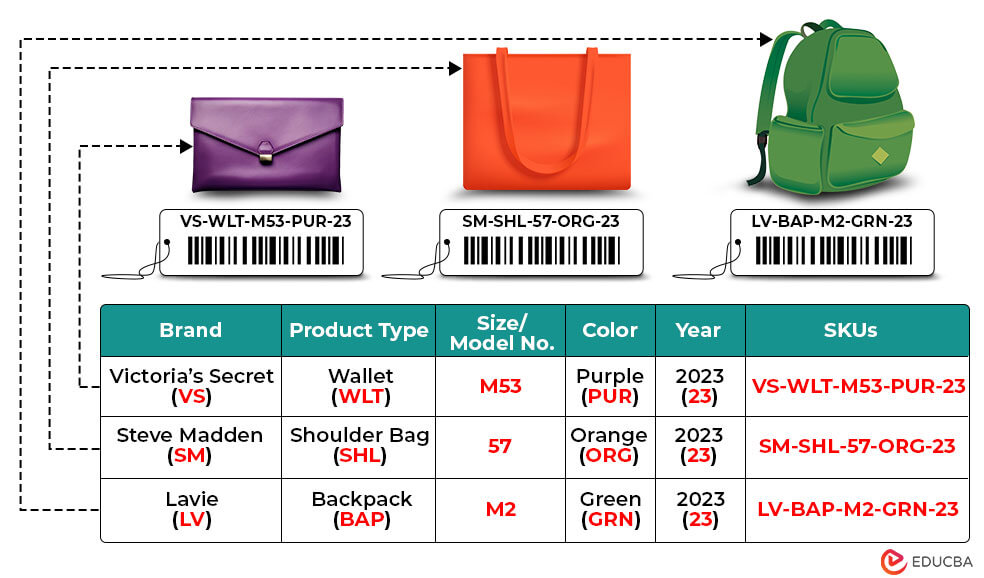
Christy runs a bag shop and wants to improve the shopping experience for her customers. She sells wallets, shoulder bags, and backpacks from brands such as Victoria’s Secret, Steve Madden, and Lavie. Let’s help Christy in creating stock keeping units for her shop.
Solution:
Let’s sort bags into the following category:
1. Brand: We will use the first two letters of each brand, like:
- “VS” for Victoria’s Secret
- “SM” for Steve Madden
- “LV” for Lavie.
This makes it easier for customers to find their favorite brands.
2. Product Type: Let’s sort bags into types like:
- “WLT” for Wallets
- “SHL” for Shoulder bags
- “BAP” for Backpacks.
It helps customers quickly find the style they want.
3. Size/Model No.: Now, we will assign a number or character for sizes or models, such as:
- “M” for Mini size
- “53” for 5×3 inch (Length x Height), or a code like “57” for model no.
4. Color: Let’s categorize bags by color using codes like:
- “PUP” for Purple
- “ORG” for Orange
- “GRN” for Green.
5. Year: Lastly, we will organize bags by manufacturing year, like “23” for 2023. This helps Christy keep track of what’s new.
This will help Christy arrange her bags neatly, making it easier for customers to find what they want.
The image below shows the stock keeping units for Victoria’s Secret, Steve Madden, and Lavie bags.
Do’s and Don’t
The following are the do’s and don’ts when creating stock keeping unit code.
| Do’s | Don’t |
| Use numbers and letters in uppercase. | Never use the same SKU for different products. |
| Keep it short (8-12 characters). | Avoid starting with “0” or “1” that are visually similar to “o” or “I” to avoid confusion. |
| First digits show the highest-level category. | Don’t use special characters like #, @, /, etc. |
| Begin with letters (2-3 digits). | Don’t use standard manufacturer’s codes. |
Importance
SKUs are important for the following reasons.
1. Product Differentiation
Having unique SKU codes makes it easy to differentiate one product from another. This, in turn, facilitates customers in identifying their preferred product in the store without any hassle during the purchase process.
2. Inventory Management
It is useful in inventory management by keeping track of product stock levels and turnover. It also facilitates reordering and prevents overstocking or stockouts. When the product stock falls below a set threshold, the retailer can use the SKU to identify products that need restocking.
3. Sales Analysis
SKUs provide valuable insight into product performance, helping retailers identify top-selling items, seasonal trends, and slow-moving stock, allowing for informed sales and marketing strategies to maximize profit. It also monitors and tracks services and warranties related to products.
4. Increase Profit
Retailers use SKUs to showcase popular products to their target audience both online and in-store. Additionally, SKUs enable them to suggest alternative products to customers when a particular item is out of stock, which helps to enhance sales through alternative options.
5. Improve Store Design
Retailers can design stores in an organized way by helping customers to find products easily. They can keep similar products in one compartment or according to brand, new arrivals, type, etc. This will improve customer shopping experience.
6. Financial Reporting
It is useful to accurately track and maintain individual product sales, determine profitability, and assess the business’s overall performance. This is important in making informed product pricing and marketing decisions.
Stock Keeping Units Vs. Universal Product Codes
Here’s the difference between stock keeping units vs. universal product codes.
| Particulars | Stock Keeping Units ( SKUs) | Universal Product Codes ( UPCs) |
| Definition | Identify specific products within a shop and contain product details. | Identify specific products universally and contain manufacturer details. |
| Nature | Unique to each retailer. | Standardized and universal across different retailers. |
| Characters | Alphanumeric | Numeric with barcode. |
| Length | Varying length of 8-12 characters. | 12 digits |
| Purpose | Useful for product differentiation and tracking inventory internally. | Useful in product identification and pricing at the point of sale. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of SKU
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of stock keeping units.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It assigns each product a unique code. | Assigning unique SKUs for numerous products can be time-consuming. |
| It enables efficiency in tracking inventory levels and organizing products. | Implementing SKU & POS systems and other equipment can be costly. |
| It facilitates easy product identification, making it easier to locate and manage them. | May cause confusion or complexity if different items are assigned similar codes. |
| It ensures that products are always available, improving customer experience and increasing sales profit. | It requires regular restocking, and mismanagement can result in lost sales and revenue. |
Final Thoughts
SKUs streamline product differentiation and inventory management, minimize error, and simplify the product tracking process. It also helps analyze inventory turnover, measure sales performance, and improve customer shopping experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1.What are the other types of product identifiers?
Answer: The following are the common product identifiers used by sellers.
- Global Trade Item Number (GTIN): It is a 13-number unique identifier developed by the international organization GS1 for all tradable products and services.
- Manufacturer Part Numbers (MPN): It is a unique alphanumeric code usually issued by manufacturers to identify each product. This code also applies to e-commerce websites such as Amazon.
- Amazon Standard Identification Numbers (ASIN): It is a unique 10-character (alphanumeric) code used to identify each product sold on Amazon. This code differs for each country, and companies may use different ASINs for the same item.
Q2. What are common SKU mistakes to avoid?
Answer: The following are some common mistakes to avoid while using SKUs.
- Avoid identical SKUs for different products to prevent confusion in inventory management.
- Keep consistent SKU formats and use barcodes to prevent tracking errors. Avoid using complex structures for labeling.
- Regularly audit SKUs and inventory to maintain accurate stock levels and prevent discrepancies.
- First, try SKUs in your inventory system to identify any technical issues that could disrupt scanning processes.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on stock-keeping units was informative and helpful to you. To learn more, check out the following related articles.