Updated July 10, 2023

Introduction to Stock Market
The stock market, also known as the equity market, is where the purchase and sale of securities occur through exchanges or over-the-counter.
The Indian Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act of 1956 defines the Stock Exchange as “An association, organization or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, established to assist, regulate and control business in buying, selling and dealing securities.”
Understand the Stock Market
Before we understand the stock market, let’s see what a stock means. A stock is a share of ownership in a company. The stock market forms an essential constituent of the capital market. It provides a common platform for the investors and corporations – the investors get a part of ownership in the company and make money through the dividends, and can sell the stocks at a premium called a capital gain; on the other hand, the companies get access to the capital required to run the business. Stocks are mainly a traded through exchanges. Today, most stock market trades are executed electronically, and the stocks are not available in physical form but electronically. This market is monitored by a market regulator, who designs a framework and lays down specific rules and policies within which this market operates.
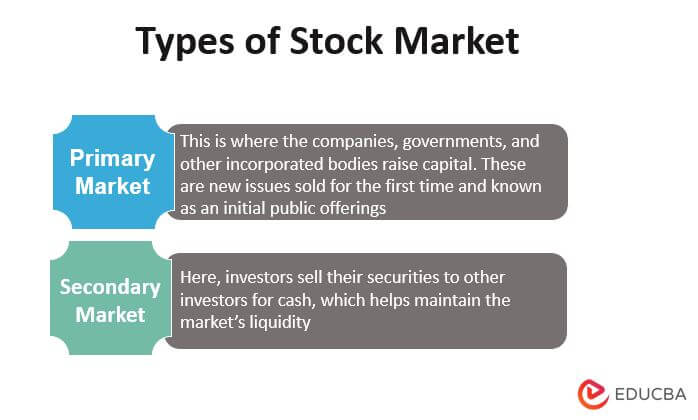
The Stock Market has Been Divided Broadly Into Two
- Primary market: This is where the companies, governments, and other incorporated bodies raise capital. These are new issues for the first time, known as initial public offerings.
- Secondary market: Here, investors sell their securities to other investors for cash, which helps maintain the market’s liquidity.
Market Participants Include
- Individual retail investors
- Institutional investors such as mutual funds, banks, insurance companies, and hedge funds
- Publicly-traded corporations
Importance
- It provides liquidity for the investors to buy and sell the shares quickly.
- It is an indicator of an economy’s strength and development.
- Source for corporations to raise money from the public.
- It promotes capital formation in the country.
- It is a medium for the general public to inculcate the habit of saving money. This money is an investment in corporations that utilize this money for productive purposes.
- It provides employment opportunities which leads to economic growth.
How Does the Stock Market Work?
Working in the stock market can be confusing, so people lose money in stock investing. Now let’s understand the mechanism of the stock market in simple words. As previously discussed, a stock market is where stocks are bought and sold. A company makes available its shares to the public, purchases by the investors, and, in turn, gets a stake of ownership in the company.
All of us know that this buying and selling is because of the economic law of supply and demand, which moves the prices of these securities and hence the market. For example, if there are a limited number of shares and the number of people who want to buy them is higher, the prices will increase for those shares and vice versa. This share demand depends on how well the company has been and is doing financially, though it also considers its plans.
The buying and selling work around the simple concept that investors want to make the highest returns: buying the stock before the prices go up and selling them before it decreases. So the investors make money either through the price differential or dividends the company announces on a per-share basis, based on their profits. Also, companies do not declare dividends even if they have made profits as they want to retain them for future growth and operations.
How to Invest in the Stock Market?
Anyone with money can invest in stocks, but only those who know and understand this market well can succeed in this industry. Majorly, stock trading takes place with the help of a broker who acts as the middleman between the investor and the stock exchange. Brokers who execute orders for investors are full-service brokers and charge a high commission against those who do not provide investment advice, called discount brokers.
When you trade, you are placing an order; let’s now look at the different types of orders:
When a stock is bought or sold at the current market price, it is the “market order.” If there are differences between the actual price and the quoted price, it is because of the rapid price fluctuations.
Another order is the “stop order” or the “limit order.” Here when it is a stop order, the broker is instructed to trade at a particular stock price, while a limit order requires the broker to sell at a specified stock price or something better.
When orders remain active until canceled is a “good ’til canceled” (GTC) order and when an order remains active only till the end of a current trading day is the “day order.” Stocks are usually traded in multiples of 100 and known as the “round lot“; conversely, trading in any other amount is known as an “odd lot.”
There are two conditions of the stock market- it can be a bull market or a bear market. A bull market indicates the constant upward movement of the stock market, whereas a bear market indicates a continuous downward trend.
Career
Numerous job options are available for those who want to build their careers in the stock market. It may involve investing in, analyzing, interpreting the stocks, and commenting on them. The following part discusses the various job options:
-
Stockbrokers
A stockbroker, also known as the financial adviser, typically buys and sells stocks, determines the best investment, and makes portfolio recommendations for clients. Brokers usually get their compensation through a commission on each trade they make or an annual fee. Even though individuals could be stockbrokers, the broker from the stock brokerage firm typically provides such services.
-
Securities Sales Agent
Stock brokerage companies employ securities sales agents, often called investment brokers, stockbrokers, and registered representatives. They get licenses to sell various financial services such as stocks, mutual funds, bonds, etc.
-
Financial Analysts
A financial analyst/stock analyst analyzes stock market trends and patterns along with company developments and gives investors suggestions to buy/sell/hold stocks. This analysis or research could be explicitly based on individual stocks or companies in a specific sector. The stock analyst works for brokerage firms, banks, Mutual Funds companies, and other companies providing financial services.
-
Trader
Stock traders engage in trading (buying/selling) securities. They trade for themselves, investing their money and keeping the profit/loss they make on stocks or on behalf of the financial institution they work for. When he works for an institution, he gets a salary plus a bonus based on his performance.
-
Investment Banker
Investment bankers usually have an MBA or a CFA degree. These bankers provide advisory services to publicly traded and private companies to help them issue stocks to the public.
-
Financial Reporter
Financial reporters’ main tasks involve reporting on the day-to-day activities of the stock market. They provide reports on the public companies’ earnings and interview industry people and traders. These reporters have in-depth knowledge of the stock market and journalism background. These journalists observe and comment on market movements via the Internet, broadcast, or print media which the investors and public can use.
-
Bank Investment Officer
A bank investment officer works for the bank clients for which he gets a salary rather than commissions. They make investment plans and trade on behalf of the clients.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Stock Market. Here we discuss the stock market, how it works, how to invest in it, a career, and its importance. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –