Updated November 15, 2023
Difference Between Stock vs Options
Stock is the most common tool to invest in the markets for individuals, mutual funds, pension funds, investors, etc. Buying a stock makes you an owner of the given company for a fraction of the total number of shares outstanding. Options make you deal with a price; they don’t have any ownership, dividends, or other benefits for the stock owners. Options are usually one of the most preferred instruments fund managers use to hedge their exposure or the traders to trade the share price. Prospects have many key things associated, like expiry, lot size, option type, volatility, etc. Advisors often recommend that individuals who cannot actively operate refrain from using options due to their complexity.
Types of Stock
1. Preferred Stock: Preferred stock owners have superior claims on a company’s assets than common stock owners. Dividend payment to them is prioritized more than common stock owners and is usually fixed or aligned with a benchmark like LIBOR. They usually come with no voting rights.
2. Common Stock: They own the company, and most investors have them in their portfolio, most commonly traded on exchanges. When listed, they come with ownership benefits like stock bonuses, dividends, and company shares of its subsidiaries.
Types of Option
1. Call Option: Call Option is the option type that gives you the right, not the obligation, to buy the company’s stock at a certain price by paying off the premium. This enables you to participate in the upside growth of the company or the stock price, while your downside risk is just the premium paid. This is the option that many senior-level employees get in the form of remuneration to help them be motivated for a company’s upside growth potential by issuing them call options.
2. Put Option: The Put Option is the option that gives the option buyer the right but not the obligation to sell the stock at a certain price. This caps the downside risk for your investment, or you can use them to gain will the stores go down by trading.
Fund managers commonly use them to cap off the risk in the market investments by buying the put options.
Head To Head Comparison Between Stock vs Options (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 difference between Stock vs Options
Key Differences Between Stock vs Options
Both Stocks vs Options are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Differences:
- Investors primarily view stocks as long-term investments in businesses with the potential for wealth creation, similar to real estate, gold, and other assets. On the other hand, options are primarily utilized as trading instruments to capitalize on stock price movements.
- Stocks come with ownership benefits like dividends, stock bonuses, and Voting rights. Options come with no benefits for the option holder.
- Stocks, when used as invested instruments used for a long-term view with more than 6 to 10 years, Options are more of short terms ranging from a few weeks to months for hedging portfolios.
- Stocks are used by individuals, mutual fund managers, pension fund managers, traders, and portfolio managers. Options are limited used by traders and portfolio managers (as hedging tools)
- By paying the premium, investors purchase options that grant them the right to buy or sell the stock at a predetermined price. Importantly, the option buyer is not obligated to exercise these rights, limiting their downside. Conversely, stock buyers are obligated to bear the full downside of the stock.
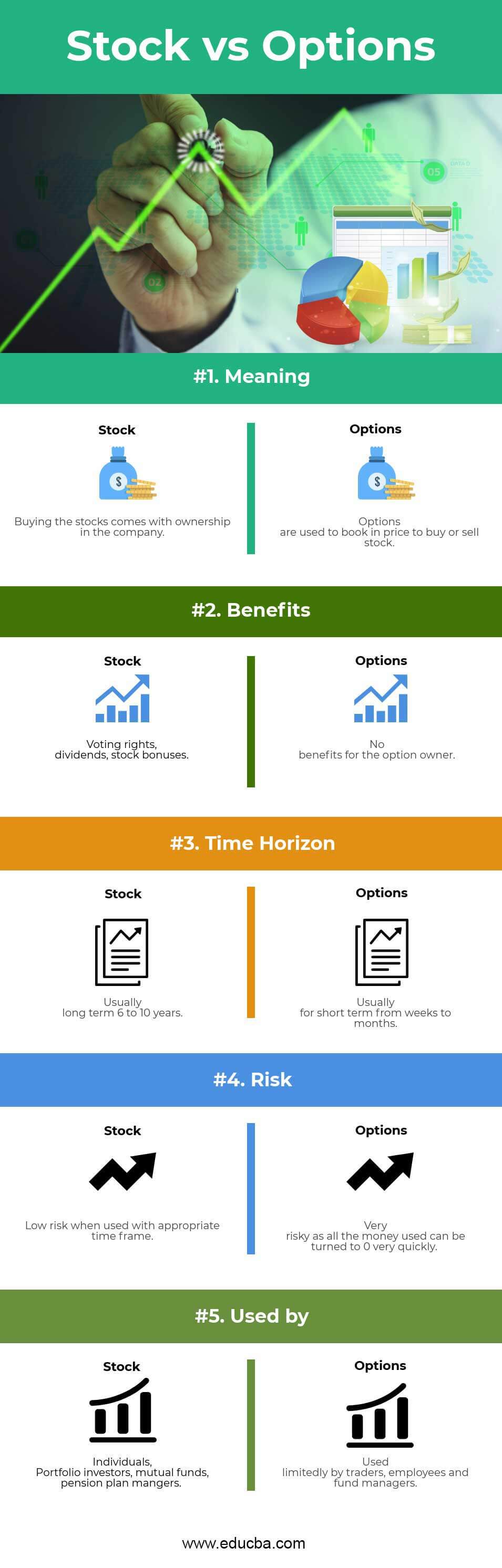
Stock vs Options Comparison Table
As you can see, there are many Comparisons between Stock vs Options. Let’s look at the top Comparison between Stock vs Options as follows –
|
The Basis of Comparison |
Stock |
Options |
| Meaning | Buying the stocks comes with ownership of the company | Options are used to book at a price to buy or sell stock |
| Benefits | Voting rights, dividends, stock bonuses | No benefits for the option owner |
| Time Horizon | Usually long term 6 to 10 years | Usually for short term, from weeks to months |
| Risk | The low risk when used within an appropriate time frame | Using all the money carries a high risk, as it can quickly turn to zero. |
| Used by | Individuals, Portfolio investors, mutual funds, pension plan managers | Used limitedly by traders, employees, and fund managers. |
Conclusion
Investing in stocks involves voting rights, dividend eligibility, stock bonuses, etc. Investors predominantly utilize stocks for investment purposes, and stocks come with a multitude of upsides as well as downsides. Still, generally, as we have seen stocks in the USA, India has significantly outperformed any other asset class over the long duration for wealth creation.
But quite oppositely, Options are a tool to have financial benefit or security from the price movement of the stock price. They are usually time-bound, are generally very high risk, and might end at zero without benefits to most options owners. Purchasing an option for a premium grants you the right to buy or sell the stock at a certain price without any obligation. As a result, the downside is significantly low.
Therefore, seeing Stocks as predominantly an investment option is a lot more practical and simple and has more benefits. Options pricing is complex, and traders use them as trading tools for hedging portfolios or gaining significant exposure to stock price movements.
Buying stocks or options can be done simultaneously; they are not mutually exclusive. Trading stocks is usually easier with low capital requirements as they are less risky, whereas trading in options is very risky. Hence, the brokers usually need the full capital in advance as there are chances that the capital might go down to zero.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Stock vs Options. Here, we also discuss the Stock vs Options differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.