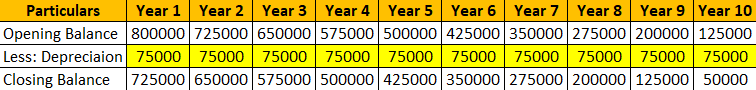Updated August 1, 2023
Straight Line Depreciation Formula (Table of Contents)
- Straight Line Depreciation Formula
- Examples of Straight Line Depreciation Formula (With Excel Template)
- Straight Line Depreciation Formula Calculator
Straight Line Depreciation Formula
The straight Line Method (SLM) is one of the easiest and most commonly used methods for providing depreciation.
The formula for calculating Straight Line Depreciation is:
- Cost of Asset: Actual cost of Acquisition of an Asset, after considering all the direct expenses related to acquiring of asset, borrowing cost, and any directly attributable cost to bringing the asset to its present condition and location, like Freight, Insurance, and Taxes.
- Salvage Value: An asset’s salvage Value means its expected realizable value at the end of its useful life.
- Useful Life of Asset: The Time period during which the asset can be used. After the end of useful life, the asset’s value becomes zero.
Examples of Straight Line Depreciation Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the Straight Line Depreciation formula calculation.
Example #1
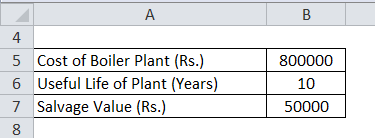
ABC Inc. purchased a boiler plant for Rs.800000. The plant’s useful life is 10 years. The plant can be sold at Rs.50000 at the end of 10 years. Calculate the depreciation to be charged each year using the Straight Line Method.
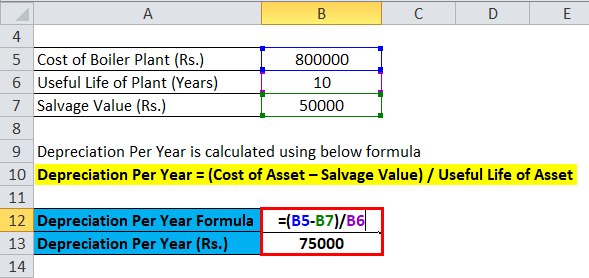
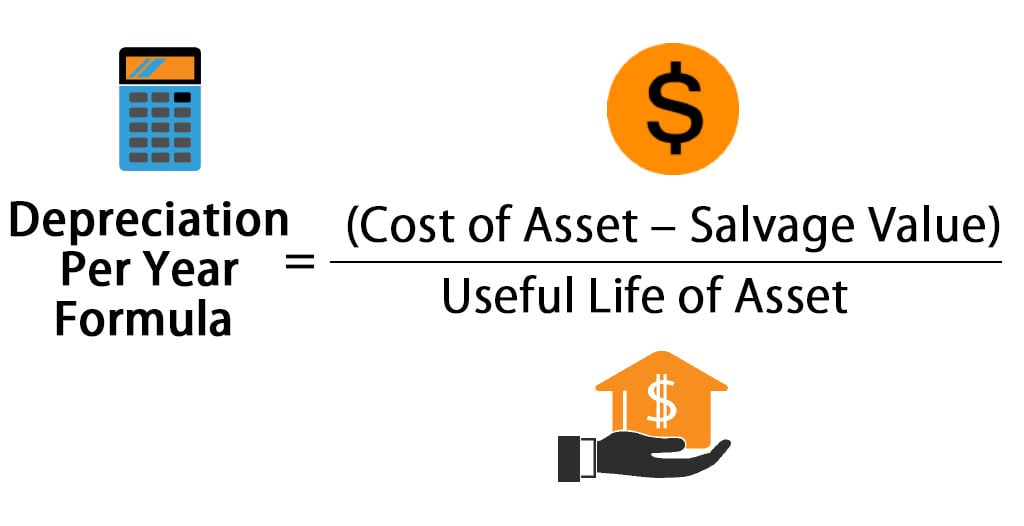
Formula to calculate Depreciation Per Year is:
Depreciation Per Year = (Cost of Asset – Salvage Value) / Useful Life of Asset
- Depreciation to be charged each year= (800000-50000)/10
- = Rs.75000
Fixed Asset Chart:
Straight Line Depreciation Formula – Example #2
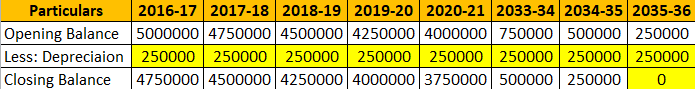
We take the example of Reliance Industries Ltd. Reliance uses the Straight Line Method of charging Depreciation for certain assets from the Refining Segment, Petrochemical Segment, and SEZ Unit/ Developer. The Audit Report of Reliance shows an extract, which can be seen in the image below.
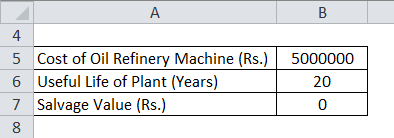
RIL purchased an Oil Refinery machine for Rs.50 lacs on 01/04/2016. RIL is expected to use this machinery for 20 years; after that Machine will be scrapped and will not have any residual value.
Formula to calculate Depreciation Per Year is as follows:
Depreciation Per Year = (Cost of Asset – Salvage Value) / Useful Life of Asset
- = (5000000-0)/20
- = Rs.250000
In such a case, RIL will charge a Depreciation of Rs.250000 each year, starting from 2016-17 till 2035-36. By the end of March 31, 2036, the Machine will fully depreciate and have a NIL value.
Straight Line Depreciation Formula – Example #3
Another example of using the straight-line depreciation method can be seen in the Financial Statements of Larsen & Toubro (L&T). L&T also provides depreciation on its assets using SLM. The extract of the annual report of L&T is inserted below:
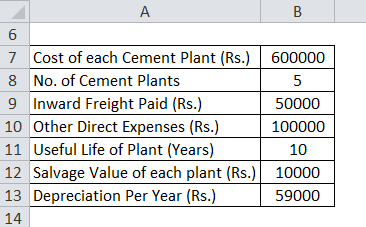
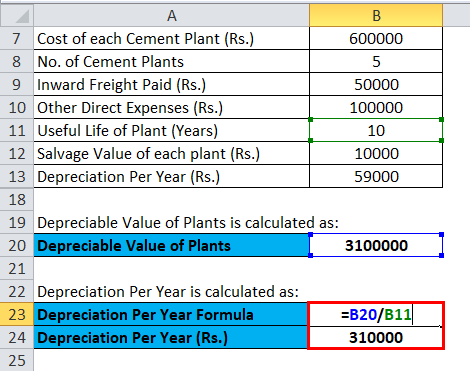
L&T purchased 5 Cement Plants for undertaking a capital expenditure on the construction of Roads at Rs.600000 each. It paid Rs.50000 for the freight to bring the plants to the construction site. It further incurred Rs.100000 to bring these plants to their working conditions. Plants will have a useful life of 10 years, after which they can be sold for Rs.10000 each.
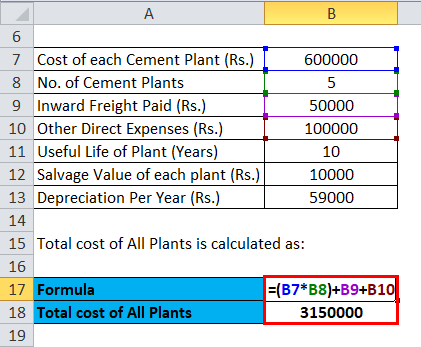
Calculation of total cost of All Plants:
- Actual cost of 5 Plants= Rs. (600000*5) + 50000+ 100000
- Actual cost of 5 Plants = 3150000
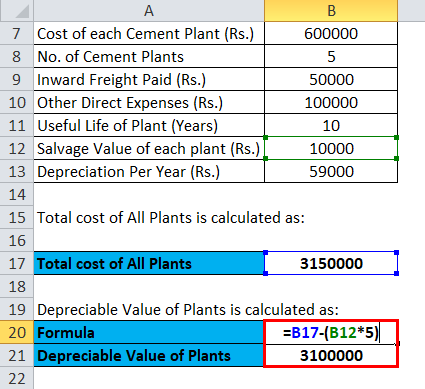
Calculation of Depreciable Value of Plants:
- Depreciable Value of Plants = 3150000 – (10000 * 5)
- Depreciable Value of Plants = Rs.3100000
Calculation of Depreciation Per Year:
- Depreciation Per Year = (3100000/10)
- Depreciation Per Year = Rs.310000
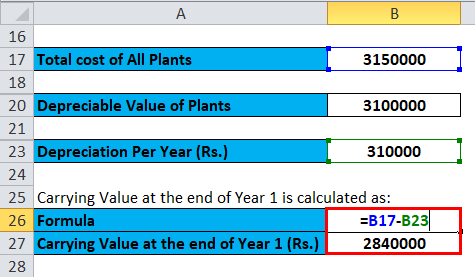
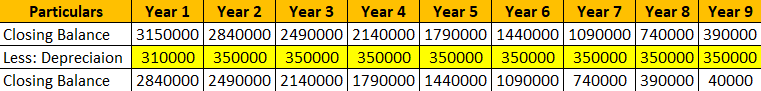
Calculation for Carrying Value at the end of Year 1 is:
- Book Value at the end of Year 1 = (3150000 – 310000)
- Book Value at the end of Year 1 = Rs.2840000
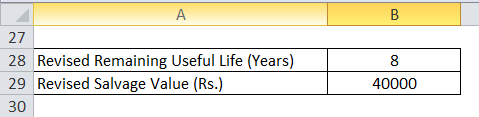
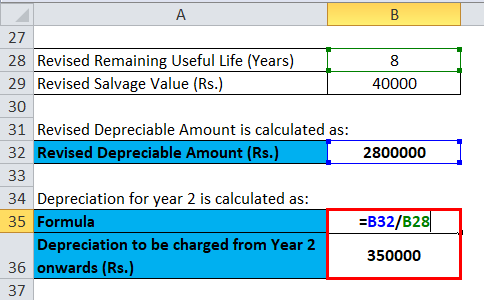
Suppose now, in Year 2, Management estimates the remaining useful life of plants to be 8 years and Residual Value to be Rs. 40000.
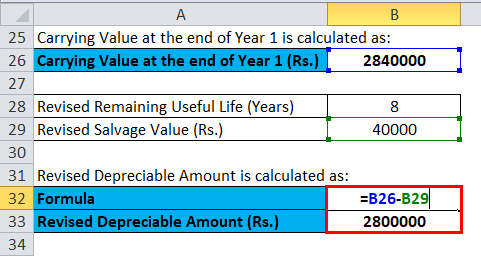
In this case, revised depreciation will be:
- Revised Depreciable Amount = Rs. (2840000-40000)
- Revised Depreciable Amount = Rs.2800000
Revised Depreciable Amount of Plants at the end of Year 2 is Rs.2800000
Calculation for Depreciation for year 2 is:
- = (2800000/8)
- = Rs.350000
Depreciation to be charged from Year 2 onwards is Rs.350000
Revising the estimates of the useful life of assets and the residual value also revises the depreciation amount while maintaining a constant depreciation charge yearly.
Explanation of Straight Line Depreciation Formula
Straight Line Depreciation Formula allocates the Depreciable amount of an asset over its useful life in equal proportion. The straight-line depreciation formula assumes that the asset will derive benefits evenly over its useful life. At the end of an asset’s useful life, the asset’s value becomes zero or equal to the realizable value. This method depreciates the asset in a straight, downward, sloping line.
The asset deducts the salvage or residual value from its purchase price to assess its depreciable value. The company estimates a salvage value it will earn when it sells the asset at the end of its useful life. The estimation of salvage value is made every year. If there is a change in the value estimation, it reflects the corresponding effect in the depreciable amount and, consequently, in depreciation.
Relevance and Uses
Straight-line depreciation is an accounting method most useful for getting a more realistic view of profit margins in businesses primarily using long-term assets. These assets include office buildings, manufacturing equipment, computers, furniture, and vehicles. These are considered long-term assets because they will last more than one year and are necessary to run the business daily. Using the straight-line depreciation method, this method evens out the profits and expenses at an equal rate.
The Straight Line Depreciation Method is the easiest method for calculating Depreciation. It is less prone to the risk of calculation errors since it does not involve complex calculations and data. Furthermore, it does not cause variation in each year’s Profit and Loss Statement as it provides Depreciation uniformly over its useful life.
Straight Line Depreciation Formula Calculator
You can use the following Straight Line Depreciation Calculator.
| Cost of Asset | |
| Salvage Value | |
| Useful Life of Asset | |
| Depreciation Per Year = | |
| Depreciation Per Year = |
|
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Straight Line Depreciation formula. Here we discuss How to straight Line Depreciation along with practical examples. We also provide a Straight Line Depreciation Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –