Updated March 16, 2023

Introduction to String Array in Python
String Array can be defined as the capacity of a variable to contain more than one string value at the same time, which can be called and accessed at any time in the program during the execution process. There is no pre-defined feature for character data types in Python, as every single character in python is treated as a string by itself. The various types of a string array in python are the Lists, the negative indexing, accession by index, looping, appending, the length using len() method, removing using pop() method, clear(), copy(), etc.
Accessing of Elements
Python does not have built-in support for Arrays. Python lists are used to serve the purpose, so we will look into Lists. It is to be noted that Python does not have a character data type. A single character in itself is a string with length 1. Square brackets are used to access the elements of the String.
Lists of String Array in Python
Below are the lists of a String array in Python:
1. List
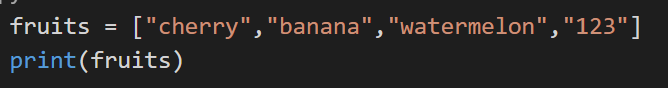
When there is a need for order and a requirement of frequent change, we prefer selecting the list. Another feature of the list is it allows duplicates. Here is a simple example of a list.
Code:
Output:
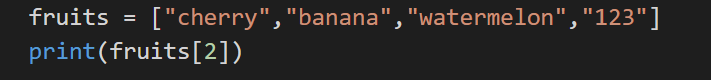
2. Accessing by Index
We can even access a particular element by referring to an index.
Code:
Output:
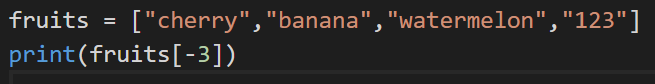
3. Negative Indexing
We can even access indexing negatively. In this case, that last most element will have an index of -1; the second last will be -2, the third last will be -3, so on and so forth.
Code:
Output:
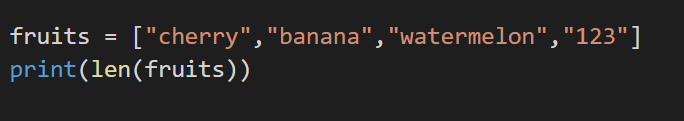
4. Length
We can even return the length of an array by using the len() method.
Code:
Output:
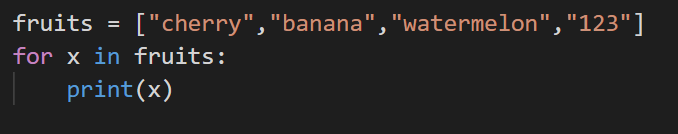
5. Looping
Looping through the array element is also an easy task. We use ‘for in’ while looping through the array.
Code:
Output:
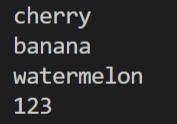
6. Appending
If one has to append to the list, then it is possible using ‘append()’
Code:
Output:
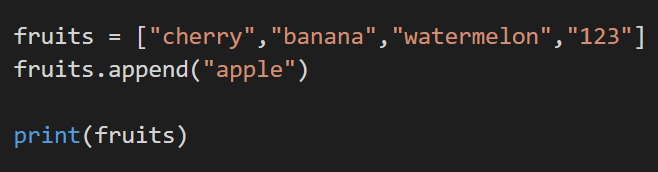
7. Removing
Removal of any element can be done via the pop() method. Here we can be specific about the deletion of any particular element by referring to the index.
Code:
Output: As pop(1) represents the second element from the list. It is removed.
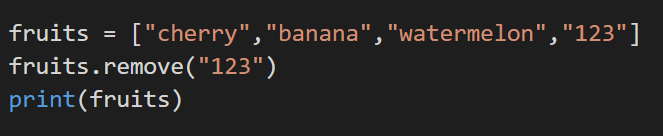
We can also use the remove() method and mention the particular element that can be removed.
Code:
Output:
Methods of String Array in Python
We have a list of underlying methods that can be used over the list and arrays. We have come across append(), pop() and remove() previously. We shall discuss here other methods that can be used.
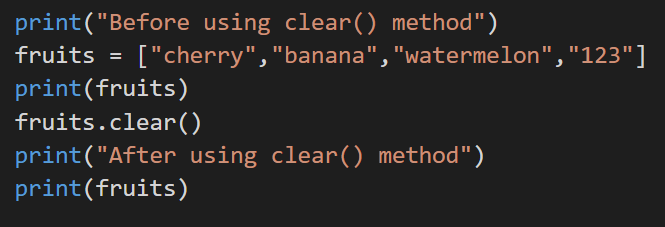
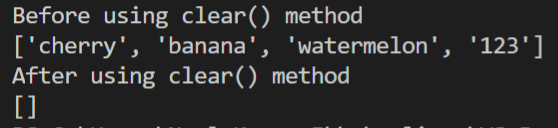
1. clear()
This removes all the elements from the list, and it will present you with a list clear of all elements.
Code:
Output:
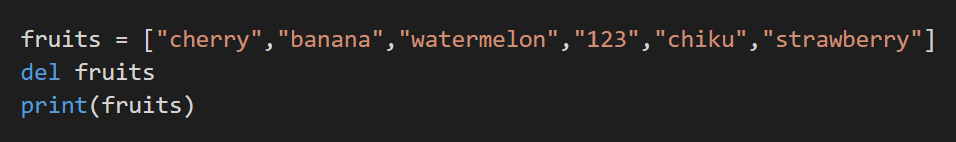
To remove the element from the list, we have removed the () method, a pop() method, which we have discussed. There is also a ‘del’ keyword that clears the list.
Code:
Output: The del list deletes the list, and we get the following output.
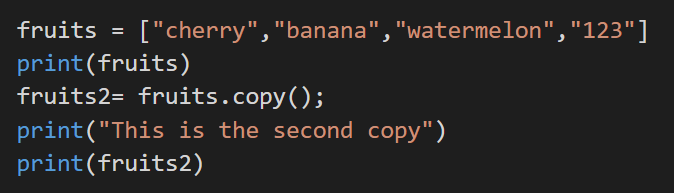
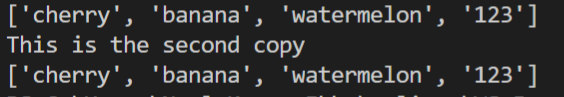
2. copy()
This method returns a copy of the list. As you can see from the example below.
Code:
Output:
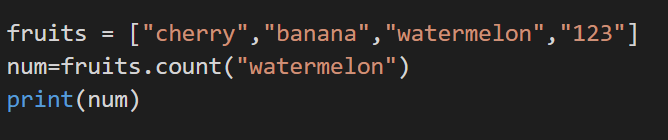
3. count()
Returns to us the number of elements in the list with a specified value.
Code:
Output:
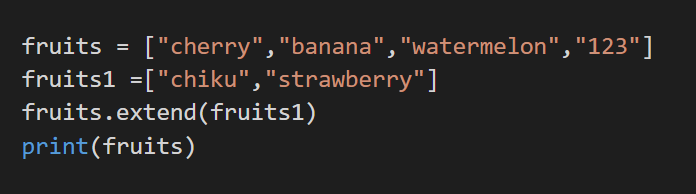
4. extend()
We add the elements to the end of the list here with the help of another list. Then the second list forms the extends the first list. Here it is how it is done.
Code:
Output:
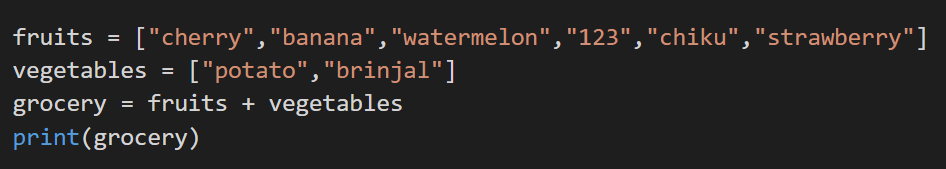
The list has append() and extends the () method to concatenate or join two lists, but the ‘+’ operator can also perform this action. We shall see this simple join in the step below:
Code:
Output: Grocery list is the concatenated list of the above ‘fruits’ and ‘vegetables’ list.
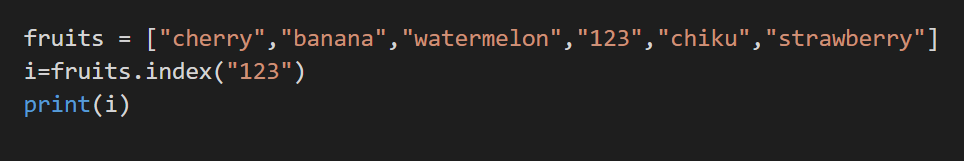
5. index()
This method returns the position of the occurrence of the particular element.
Code:
Output:
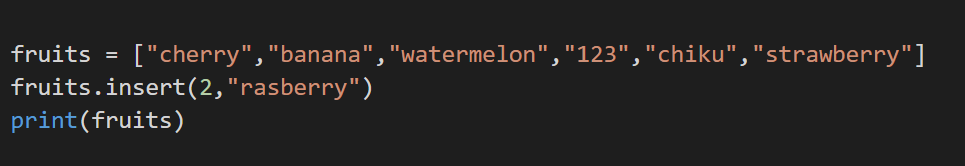
6. insert()
This method returns the element which has to be inserted at a specified position. This method takes 2 arguments, first the index and the second, the element that has to be positioned at that index.
Code:
Output:
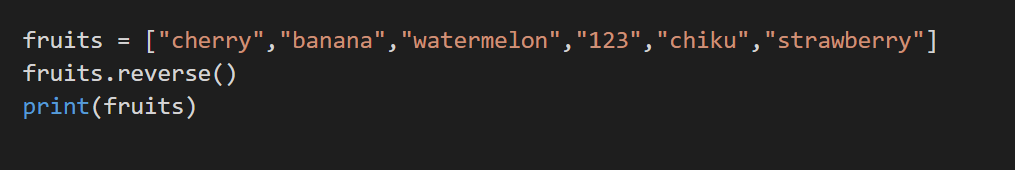
7. reverse()
This method reverses the sorting order of the list. This method returns a reversed iterator object.
Code:
Output: We see how the entire list is reversed here.
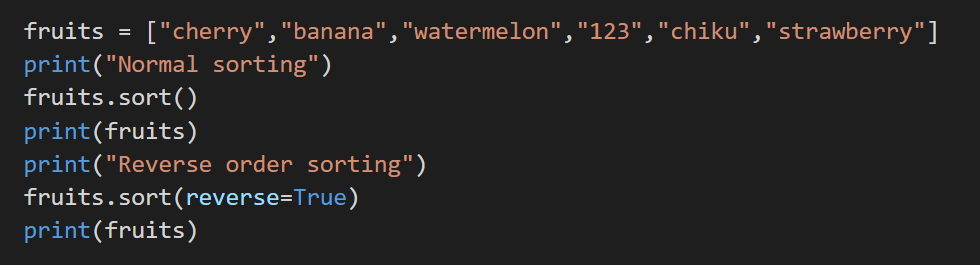
8. sort()
This method will arrange the list in alphabetical order, or it can also be said that it sets the list according to ascending order.
The method takes 2 parameters; one of the parameters is reversed, and the other one is key which may specify the sorting criteria. If reverse=true, then the list will be sorted in descending order, whereas if the reverse=false then ascending. The 2 parameters are optional.
Below is an example where we have used the reverse parameter.
Code:
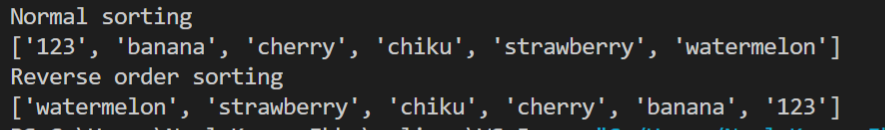
Output: Here, we see the default sorting and, in the other, the reverse of the previous one.
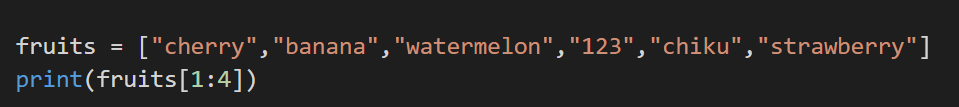
9. Range of Indexes
If we need a selective list of elements from where to start and where to end, we go for this option.
Example: Suppose if we want only the 1st, 2nd and 3rd element of the list, then we would do the below. It is to be noted that the list begins with 0, and it does not include the last range.
Code:
Output:
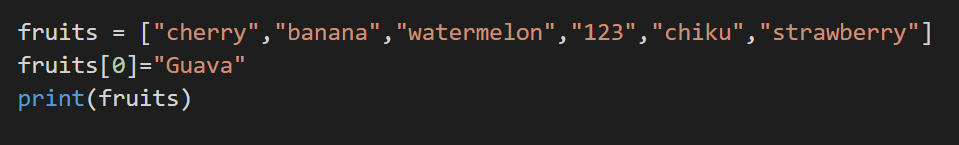
10. Change of the item value
The value of a specific item can be changed.
Code
Output:
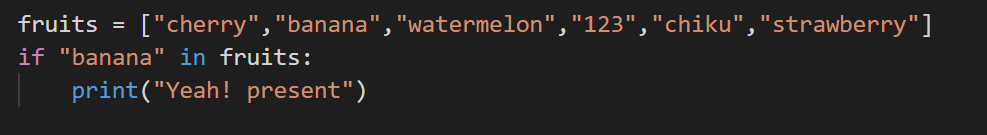
11. Checking whether an element presents or not.
Suppose we have to check if a particular element is present or not, then use the ‘in’ keyword. Here we make use of the ‘if’ keyword to confirm the presence of an element.
Code:
Output:
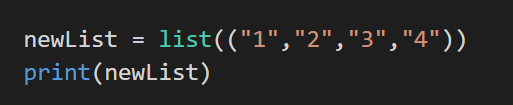
12: list() constructor
There is also a list of the constructor that is used to make a new list. A good note must be taken that here square brackets are dropped [] and instead double rounded brackets are used (( )).
Code:
Output:
Conclusion
It is also to be understood that Python has no support for Array; it is still a list that we have used. However, Numpy is a library that can be used to create the 2D, 3D array and is used at computing scientific and mathematical data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to String Array in Python. Here we have discussed overview, accessing of elements, python list and methods with codes and outputs. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –