Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to String in C
String in C is defined as an array of characters that are terminated with a special character (Null character) ‘\0’. So a non-finished string includes the characters consisting of the list preceded by a null. Defining a string is similar to defining a one-dimensional array of characters.
Syntax
The basic syntax to declare as shown below:
// syntax to define a string in C
char string_name[size_str]; // Defining string_name with size of size_strExplanation: The “string_name” is the name which is given to string. “size_str” is the size of the string named as string_name. Here please note that the null character “\0” is stored additionally at the end of the string. This indicates the end character of every string.
How to Initialize String in C?
There are different ways to initialize strings in C. Please have a look at below different examples that show different ways to initialize a string in C.
Code:
// Different ways to initialize a string in C
char string_name[] = "mystring"; // string assignment to string_name
char string_name[9] = "mystring";
char string_name[] = {'m','y','s','t','r','i','n','g','\0'};
char string_name[9] = {'m','y','s','t','r','i','n','g','\0'};Explanation: All the above-mentioned methods assign string “mystring” to a string variable named string_name.
The below example shows how “MYSTRING” is stored in C with the null character “\0” at the end of the string. “\0” character stored at the end of the string is very helpful to identify the end of the string.
| M | Y | S | T | R | I | N | G | \0 |
Rules and Regulations
It is defined using double quotes and it will give an error if we define string using the single quote. For example, have a look at example code 1 to understand this concept.
Code:
char string_name[] = "mystring" // this is allowed because string is defined with double quotesCode:
char string_name[] = 'mystring' // this is not allowed because string is defined with single quotesTo read a string from the user, scanf() or gets() function is used and to display the string, puts() or printf() can be used. Example code 2 shows how a string can be read and display using these two methods.
Below are commonly used string functions:
- strlen(): This function is used to calculate the length of the given string.
- strcpy(): This function is used to copy a string.
- strcmp: This function is used to compare two strings.
- strcat(): This function is used to concatenate two strings.
Please refer to example code 3 to understand the string functions.
Examples to Implement String in C
Below is the example to implement:
Example #1
Code:
// Example code to explain valid string declaration using double quotes
// include all required header file
#include <stdio.h>
// main function
int main()
{
// Body of main function
char name1[] = "my example string1"; // string name1 is defined using double quotes which is valid
char name2[] = 'my example string2'; // string name2 is defined using single quotes which is not valid This will throw an error
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
Code:
// Example code to explain valid string declaration using double quotes
// include all required header file
#include <stdio.h>
// main function
int main()
{
// Body of main function
// Example of reading a string using fgets and displaying string using puts
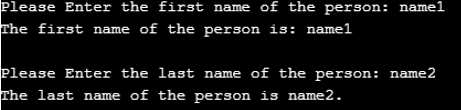
char first_name[30]; // declaration of first_name string
printf("Please Enter the first name of the person: "); // Asking for first name from the user
fgets(first_name, sizeof(first_name), stdin); // reading input string from the user using fgets function
printf("The first name of the person is: ");
puts(first_name); // displaying string using puts function
// Example of reading a string using fgets and displaying string using puts
char last_name[30]; // declaration of last_name string
printf("Please Enter the last name of the person: "); // Asking for first name from the user
scanf("%s", last_name); // reading input string from the user using scanf function
printf("The last name of the person is %s.", last_name); // displaying string using printf function
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3
Code:
// Example code to understand string functions in C
// include all required header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // this header file contains string functions
// main function
int main()
{
// Body of main function
// Example to calculate length of the string
char string1[20]="my string1";
char string2[20]="hello";
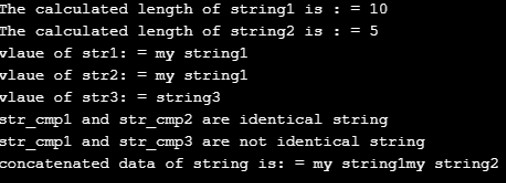
printf("The calculated length of string1 is : = %ld \n",strlen(string1));
printf("The calculated length of string2 is : = %ld \n",strlen(string2));
// Example to copy a string
char str1[20]= "my string1"; // declaration of string str1
char str2[20]; // declaration of string str2
char str3[20]; // declaration of string str3
strcpy(str2, str1); // copying str data to str2
strcpy(str3, "string3"); // copying "string3" to str3
printf("vlaue of str1: = %s \n",str1); // displaying the value of str1
printf("vlaue of str2: = %s \n",str2); // displaying the value of str2
printf("vlaue of str3: = %s \n",str3); // displaying the value of str3
// Example to compare strings
char str_cmp1[20]= "my string1"; // declaration of string str_cmp1
char str_cmp2[20]= "my string1"; // declaration of string str_cmp2
char str_cmp3[20]= "my string 3"; // declaration of string str_cmp3
int result_compare = strcmp(str_cmp1, str_cmp2); // if two strings are identical it will return 0
if(result_compare == 0)
{
printf("str_cmp1 and str_cmp2 are identical string \n");
}
else
{
printf("str_cmp1 and str_cmp2 are not identical string \n");
}
int result_compare2 = strcmp(str_cmp1, str_cmp3);
if(result_compare2 == 0)
{
printf("str_cmp1 and str_cmp3 are identical string \n");
}
else
{
printf("str_cmp1 and str_cmp3 are not identical string \n");
}
// Example to concatenate two strings
char str_cat1[20]= "my string1"; // declaration of string str_cat1
char str_cat2[20]= "my string2"; // declaration of string str_cat2
//concatenates str_cat1 and str_cat2 and resultant string is stored in str_cat1.
strcat(str_cat1,str_cat2);
// display the concatenated string
printf("concatenated data of string is: = %s \n",str_cat1); // displaying the value of str_cat1
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
This tutorial provided concepts related to string declaration, string initialization, and other string related concepts in C. These concepts are useful while working with them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to String in C. Here we discuss an introduction, syntax, how to initialize strings in C, along with rules and regulations and respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –