Updated May 8, 2023
Introduction to StringTokenizer in Java
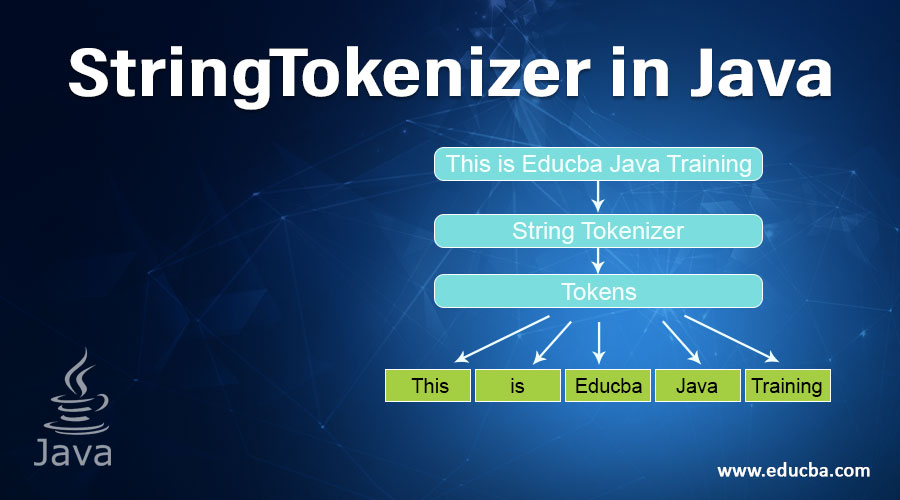
The following article provides an outline for StringTokenizer in Java. String Tokenizer in java allows an application to break a given string into tokens based on some delimiter. Each Split part of a string is called a token. A string tokenizer internally uses a substring method of the String class to create tokens. String tokenizer internally maintains the index of the last token and computes the next token based on this index.
In this article, we will see a detailed description of different constructors available in the string tokenizer class. In addition, there will be java code examples showing the creation of string tokenizer instances and usage of different methods available in them.
Here is the declaration of string tokenizer in java:
public class StringTokenizer extends Object
implements Enumeration<Object>String Tokenizer Constructors
String Tokenizer is a part of the Legacy framework.
The following are the main constructors of the string tokenizer Class.
- StringTokenizer (String str): This creates a string tokenizer for the specified string. This set default delimiter which can be space, tab, newline, carriage return character, and form-feed character.
- StringTokenizer (String str, String delim): This creates a string tokenizer for a specified string, and tokens will be generated based on a specified delimiter.
- StringTokenizer (String str, String delim, boolean returndelims): This creates a string tokenizer for a specified string, and tokens will be generated based on a specified delimiter. The third parameter is a boolean value that specifies whether delimiters are required as tokens.
The above-specified constructors can be used depending on the requirement.
Important methods of string tokenizer in Java
| Method Name | Description |
| boolean hasMoreTokens() | This method checks whether there are more tokens available. |
| String nextToken() | This method returns the value of the next available token. |
| String nextToken(String delim) | This method returns the value of the next available token based on provided delimiter. |
| boolean hasMoreElements() | This works similarly to hasMoreTokens. |
| Object nextElement() | This method is the same as nextToken but returns an object. |
| int countTokens() | This method returns a number of tokens. |
Examples
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
Let us see an example of a string tokenizer class showing the use of the first constructor.
Code:
package com.edubca.stringtokenizerdemo;
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
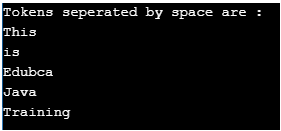
//create string tokenizer instance
StringTokenizer st1 =
new StringTokenizer("This is Edubca Java Training");
System.out.println("Tokens separated by space are : ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
}
} Output:Example #2
In this example, we will see the use of the second constructor of a string tokenizer class that accepts a string and delimiter.
Code:
package com.edubca.stringtokenizerdemo;
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
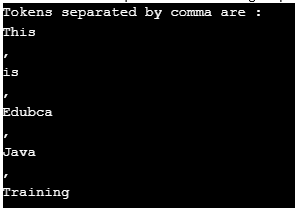
//create string tokenizer instance
StringTokenizer st1 =
new StringTokenizer("This,is,Edubca,Java,Training", ",");
System.out.println("Tokens separated by comma are : ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
}
}Output:
In the above example, we have seen how to create tokens based on a given delimiter in the string tokenizer.
Example #3
In this example, we will see the use of the third constructor of a string tokenizer class that accepts a string, delimiter and boolean value.
Code:
package com.edubca.stringtokenizerdemo;
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
//create string tokenizer instance
StringTokenizer st1 =
new StringTokenizer("This,is,Edubca,Java,Training", ",",true);
System.out.println("Tokens separated by comma are : ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
}
}Output:
As we can see in the above output delimiter is also considered as a token.
Example #4
In this example, we will how to handle multiple delimiters in java string tokenizer.
Code:
package com.edubca.stringtokenizerdemo;
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerDemo{
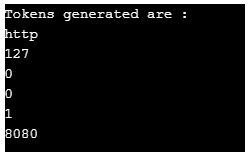
public static void main(String args[]){
String stringvalue = "http://127.0.0.1:8080/";
//create string tokenizer instance with multiple delimiters
StringTokenizer st1=new StringTokenizer (stringvalue,"://.");
System.out.println("Tokens generated are : ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
}
}Here is the output produced after running the above code:
The above tokens are generated by tokenizing strings based on multiple tokens (://.).
Example #5
In this example, we will see the use of the count tokens method in the string tokenizer.
Code:
package com.edubca.stringtokenizerdemo;
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
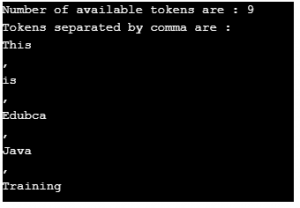
//create string tokenizer instance
StringTokenizer st1 = new StringTokenizer("This,is,Edubca,Java,Training", ",",true);
System.out.println("Number of available tokens are : " + st1.countTokens());
System.out.println("Tokens separated by comma are : ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
}
}Output:
Conclusion – StringTokenizer in Java
From the above discussion, we have a clear understanding of what is string tokenizer in java, how it’s created, and what are the different methods available in the string tokenizer class.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to StringTokenizer in Java. Here we discuss their introduction, declaration, String Tokenizer Constructors, and examples. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –