Updated July 31, 2023
Difference Between Tangible vs Intangible
The following article provides an outline for Tangible vs Intangible. Tangible means anything which we can touch, feel, and see. Any tangible assets are assets with physical existence and physical property; they can be touched—tangible assets are mostly associated with fixed assets. Examples of tangible assets include Land, Buildings, Machinery, Equipment, Cash, Stock, Plant, any property that has long-term physical existence or was purchased for business operations and not for sale, vehicles, etc. An Intangible Asset is an asset that does not have a physical existence. It is not possible to see, touch or feel these assets. An intangible Asset’s useful life is usually greater than one year. Example of Intangible Assets includes Goodwill, Patent, Brand, Copyright, Trademarks, and Permits, Patent, Brand, Copyright, Trademarks, and Permits, etc.
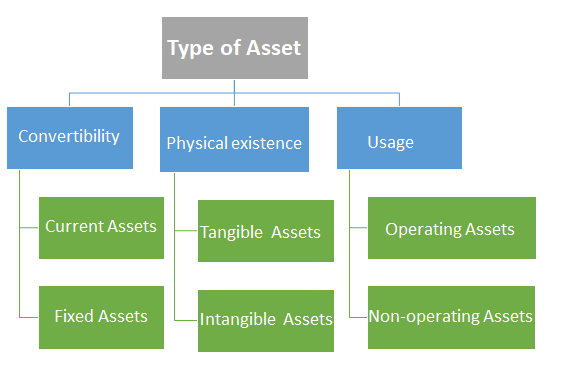
Types of Assets
Assets are divided into 3 main categories as per below.
Let’s discuss the asset category of Physical existence in detail:
Physical Existence
In this category, assets are divided based on their existence. Assets in this category are further divided into two subcategories.
- Tangible Assets
- Intangible Assets
1. Tangible Assets
Tangible assets are used as collateral for loans since such assets have a long-term valuation that is valuable to a lender. Tangible assets are purchased at a measurable price; it is much easier to value Tangible assets than Intangible Assets. Tangible assets require maintenance to support their values and production capabilities. Tangible assets are easily sold to raise cash in emergencies. High-risk industries such as banking and finance use their tangible assets to reassure investors, as this asset can always be liquidated and converted into cash.
2. Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets are further divided into two categories (a) Indefinite and (b) Definite. Any Intangible asset that stays longer with the company is called an Indefinite Intangible asset, for example, the company’s brand name, which stays as long as it continues operation. Any Intangible asset with a limited life is called a Definite Intangible asset. For example, a legal agreement to operate under another Company’s patent with no plan of extending the agreement.
Intangible assets cannot be used as collateral to raise the loan. The automobile industry has several Intangible assets, including patents, research, development, brand name, etc.
Let’s look at the example of tangible and intangible assets:
It’s just an example created by Taking XYZ as a person here; he has a business in car manufacturing, so for him, tangible assets are machinery, Buildings, all types of equipment used to produce cars, inventory, etc.
Now let’s say XYZ person needs a small part of the car for a production car, so he contacts the person with a small part production business and agrees to supply the small part to the XYZ person manufacturing unit. Still, the value of that contract is not clear at this moment, so this contract is an intangible asset for XYZ person at this moment because its value not yet fix, and its just and legal agreement between the two parties, which is not physical in nature.
Head To Head Comparison Between Tangible vs Intangible (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 differences between Tangible vs Intangible
Key Differences Between Tangible vs Intangible
Let us discuss some of the major differences between Tangible vs Intangible.
- An asset purchased by a company with monetary value and physically present is called a tangible asset. An Asset that doesn’t have material existence and has a useful life and economic value is called an Intangible asset.
- The decrease in value of tangible assets is referred to as depreciation, whereas in the case of intangible assets, it is termed amortization.
- Due to the physical presence of tangible assets, converting them into cash is easy. In emergencies, it is a little bit difficult to sell Intangible assets.
- The lender accepts tangible assets as collateral when granting a loan to the company, while intangible assets cannot be utilized as collateral for the loan.
- The existence of tangible assets is essential for a company’s functioning, whereas the non-existence of Intangible assets will not have that much impact on the company.
- Tangible assets actively contribute to the current market value, while intangible assets enhance potential revenue and worth.
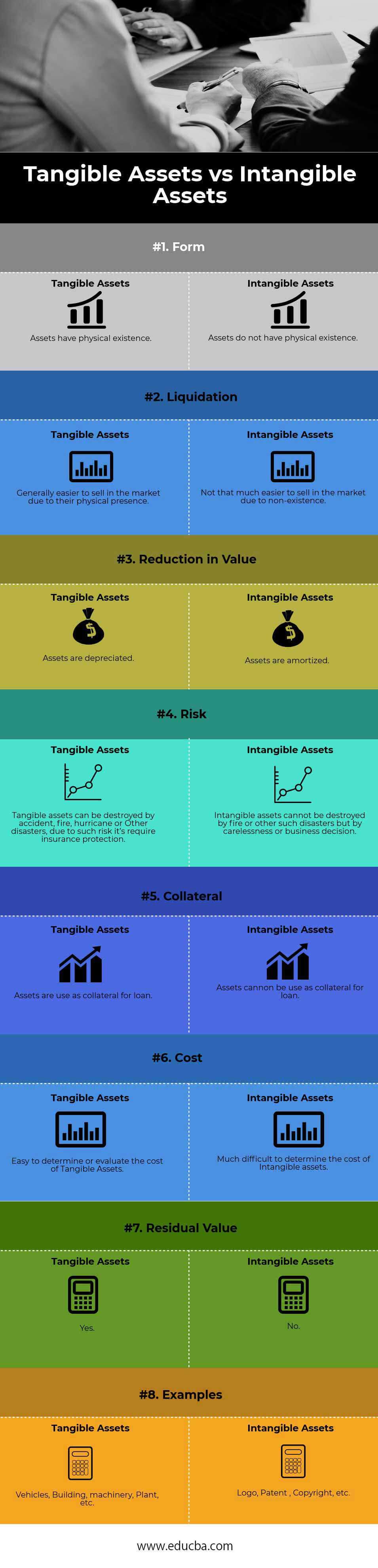
Tangible vs Intangible Comparison Table
Let’s look at the top 8 comparisons between Tangible vs Intangible:
| Basis of Comparison | Tangible Assets | Intangible Assets |
| Form | Assets have a physical existence. | Assets do not have a physical existence. |
| Liquidation | Generally easier to sell in the market due to their physical presence. | Not that much easier to sell in the market due to its non-existence. |
| Reduction in Value | Assets are depreciated. | Assets are amortized. |
| Risk | Accidents, fires, hurricanes, or other disasters can destroy tangible assets, necessitating insurance protection to mitigate such risks. | Carelessness or business decisions can destroy intangible assets like fire or other disasters. |
| Collateral | Assets are used as collateral for a loan. | Assets cannot be used as collateral for a loan. |
| Cost | Easy to determine or evaluate the cost of Tangible Assets. | Much difficult to determine the cost of Intangible Assets. |
| Residual Value | Yes | No |
| Examples | Vehicles, buildings, machinery, plant, etc. | Logo, Patent, Copyright, etc. |
Conclusion
Both tangible vs intangible assets are recorded by the company in their books of accounts. Tangible assets are very important for any company for the smooth running of its operations; Intangible assets help create a company’s future worth. To be successful company needs to have a good combination of tangible vs intangible assets. When comparing the two, both tangible vs intangible assets have their pros and cons, but they impact the functioning of the organization. Intangible assets provide a company with its identity through its strong brand name.
Nowadays, some survey suggests that intangible assets mostly generate companies’ value because of the effective usage of knowledge and knowledge management. Managing intangible assets is a crucial competitive advantage and sustainable performance in this knowledge or information economy era.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Tangible vs Intangible. Here we discuss the Tangible vs Intangible key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.