Tax Evasion Meaning
Tax Evasion is when a citizen tries to evade federal, state, and income taxes using illegal techniques. One method to avoid taxes is not paying at all or paying less than the obligatory amount.
For instance, a company with an income of $20,000 falls under the 12% tax bracket. However, it might report only $9,500 to save 2% tax.
People provide misinformation in the reports, transfer money to foreign accounts, attest to allowances they are unqualified for, etc. Various countries’ tax divisions, like IRS, HM Revenue & Customs, ITD, etc., consider it a crime and impose penalties. The citizens or businesses implementing tax evasion are also called tax dodgers.
Key Highlights
- Tax evasion is an approach to saving taxes by employing illegal schemes. These tax offenders are generally called tax dodgers.
- It is a punishable offense where the offender may receive a fine as well as face imprisonment.
- People use money laundering, report false financials, intentionally skip paying taxes, and practice various other methods to evade taxes.
- It comes under numerous tax frauds, but the terms are not interchangeable. However, it is different from tax avoidance. Where tax avoidance is legal, tax evasion is not.
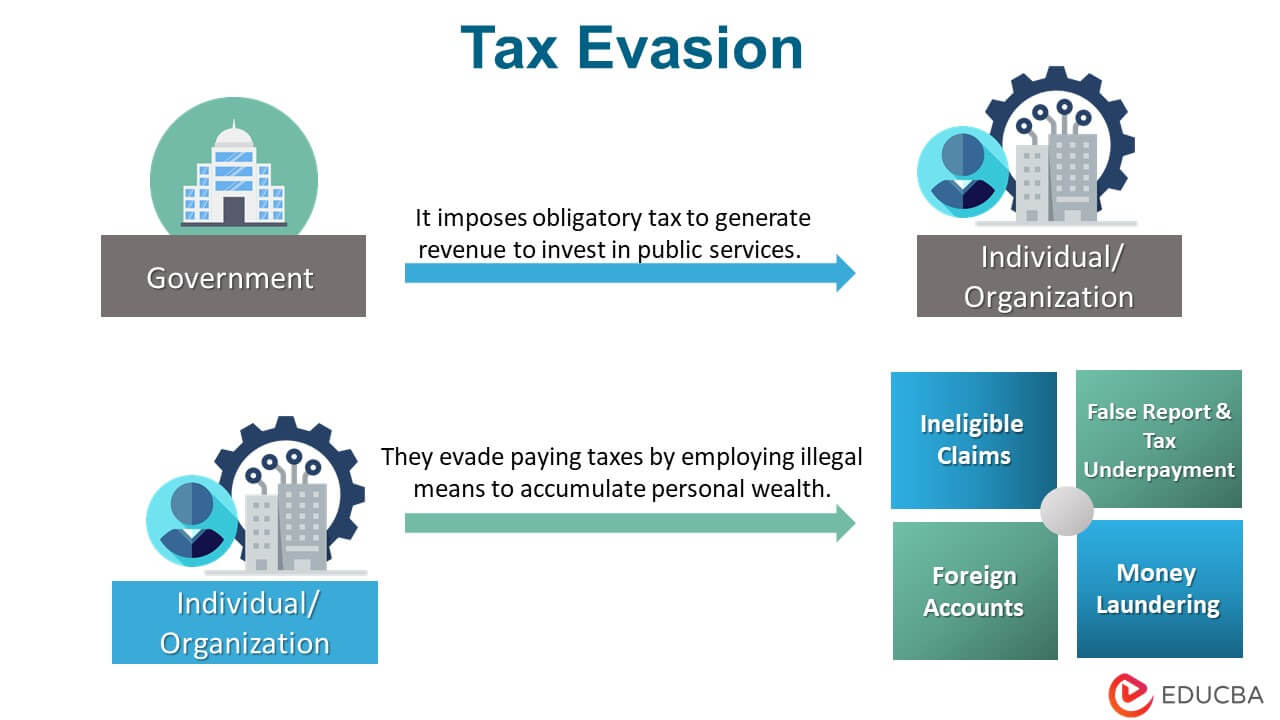
How Does Tax Evasion Work?
- Generally, the government imposes a tax on income to generate revenue for the country. The funds are then viable to run development projects for the citizens.
- When people avoid paying the necessary taxes while still enjoying the public benefits, it adversely affects the government’s revenue stream. Which, in turn, leads to poor public services.
- On that account, the government must oversee tax reports and press charges against tax dodgers.
- As reporting taxes can be complex, the regulations may excuse any minute unintentional mistakes. However, if any inaccuracy is purposeful, the revenue department might set up an inquiry.
- In case of a genuine mistake, one only has to pay an official charge. On the contrary, serious offenses can even lead to jail time.
Tax Evasion – Methods & Examples
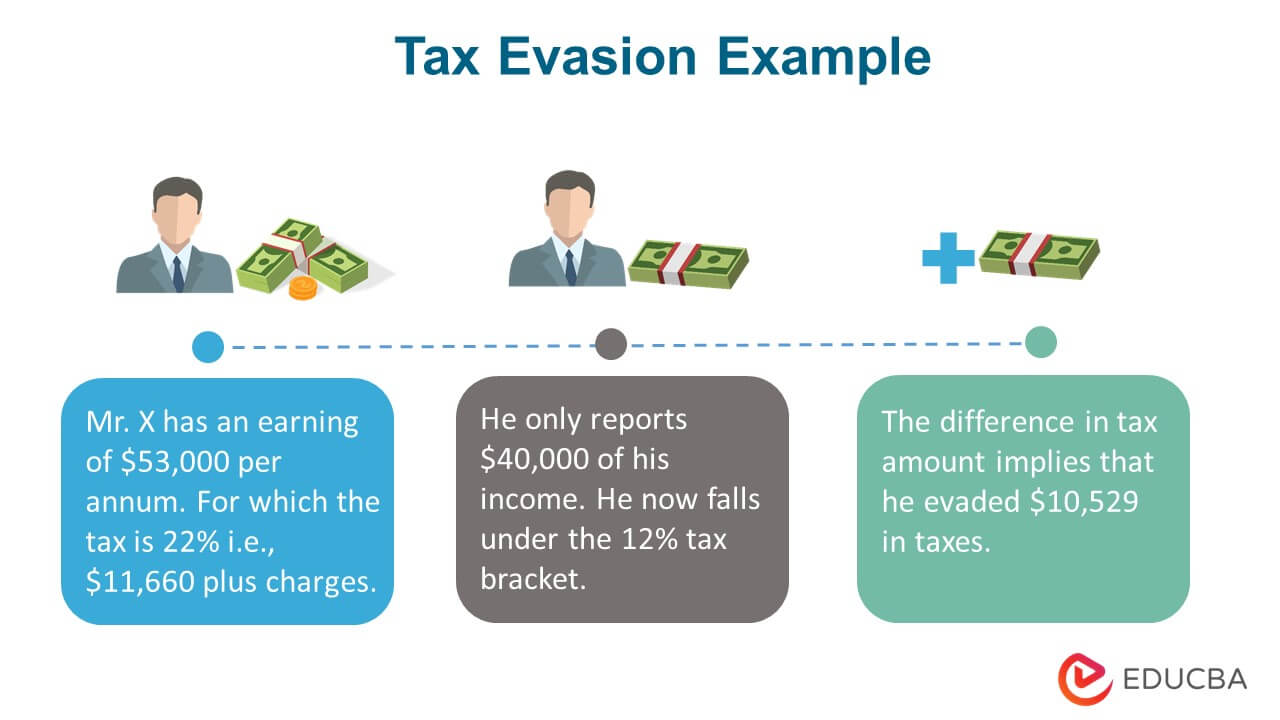
False Reporting & Tax Underpayment:
- It is when someone reports less income than their actual earnings
- It comes under an attempt of assessment according to IRS sections
- For example, Mr. X earns $53,000 every year. However, the income tax reports show that the earnings are $40,000 per annum. As per the tax rate and calculations, Mr. X possibly evades $10,529 of tax.
Money Laundering:
- It is when an individual or organization hides the source of illegally earned money to save tax as well as the consequence of the illegal activity.
- In some cases, they might use methods to turn the money into legal money but still less in quantity.
- For example, Company ABC accumulates $1,000,000 from illegal business activity. They use charity of $250,000 and a donation of $400,000 to convert it into white money. However, it only shows $650,000 while saving $350,000.
Foreign Accounts:
- If a citizen holds bank accounts, brokerage accounts, etc., in another country, they are liable to report them.
- It is only a requirement if, during the financial year, the aggregate amount exceeds $10,000
- For example, Company XYZ operates in the US but has various bank accounts in different foreign countries. They report all the bank accounts except for one in the UK. It saves them a tax on that amount but counts as a crime.
Ineligible Claims:
- It is when businesses or primarily individuals lie about a few specifications to be eligible for tax saving schemes.
- They do so to avail any tax benefits the specifications can provide.
- For example, Ms. Z is fifty-seven years old. However, to avail of senior citizen benefits, she falsifies her age as sixty-four.
Real Cases of Tax Evasion
John Everson:
- In a recent case, an electrical engineering business owner was responsible for tax evasion.
- On 7th October 2022, a report from the Department of Justice stated that John Everson owed the IRS more than $500,000.
- He had evaded tax returns by distributing his funds in several bank accounts in the name of non-profit organizations.
- He will be sentenced in 2023 when the judge decides after three conviction rounds.
Ufotable:
- Hikaru Kondo, the founder of Ufotable Studio, was convicted of tax law violation in 2021
- He falsified the tax reports and caused a loss of $1.25 million for the tax department
- Along with a twenty-month prison time, the studio is also penalized $265,000
- Additionally, the studio claims to have paid all due taxes to the government.
Walter Anderson:
- In 2006, Walter Anderson, a Telecommunications Entrepreneur, accepted tax evasion for two continuous years, 1998 and 1999
- According to his scheme, he opened companies in foreign countries and used the income to invest in his US business
- This way, he had almost avoided paying $365 million in taxes
- After he pleaded guilty, the judge sentenced him to upto ten-year prison time in 2007.
Tax Evasion – Causes
- Countries with higher illiteracy rates imply a population’s low educational level. As taxes are complex and lack simplicity, many people can find difficulty in reporting taxes
- With inflation, the government raises tax and interest rates, which in turn, can lead to tax fraud
- In today’s time, a significant group of individuals lacks the integrity to be honest, which makes it easier for them to commit such crimes
- One of the significant reasons is also the tax administration’s inadequacy in being efficient
- Tax havens are considerably the prominent causes of evasion of taxes. It is a sovereignty that imposes low to null taxes on foreign investments. It motivates people to save their money and cut back on obligatory taxes.
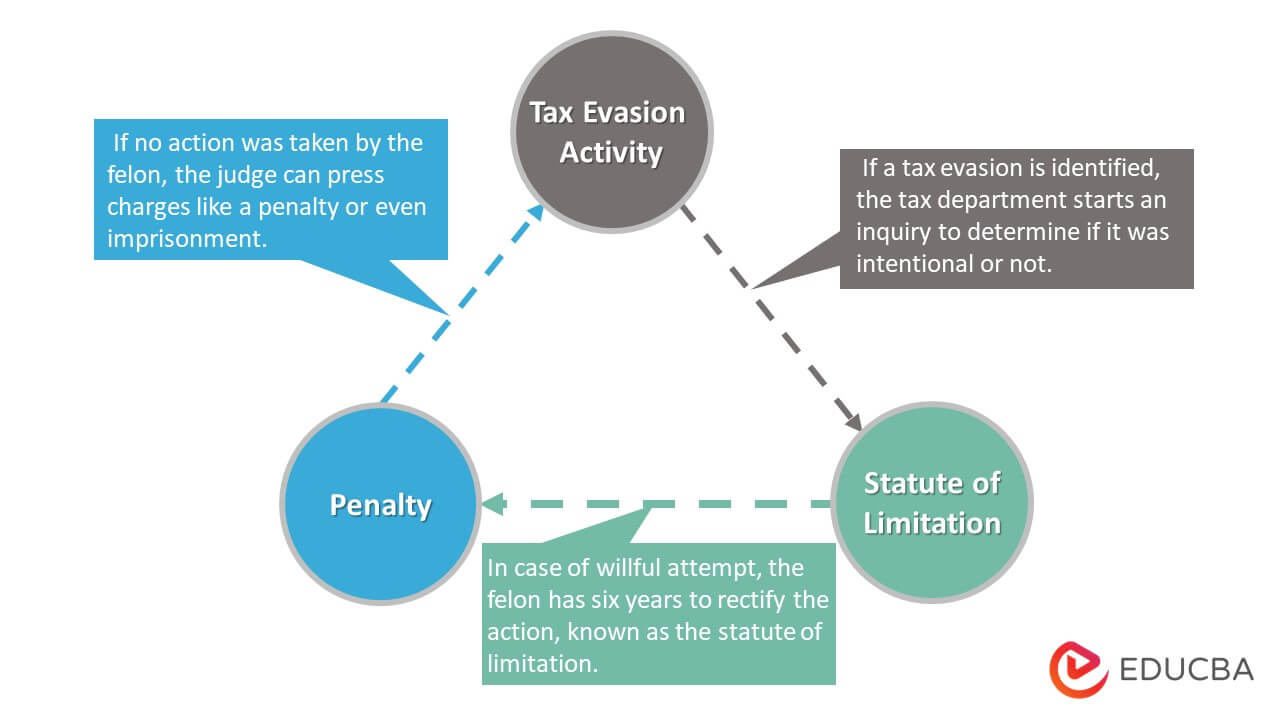
Tax Evasion – Statute of Limitations
- The juridical body of the US set the time for the statute of limitation as six years.
- It generally means that the government body has to wait for a specific period before taking any legal action against the evasion.
- The statute of limitation begins from the tax filing date or the statutory due date when the evasion was performed. Whichever comes later.
- For instance, if an individual missed reporting taxes for the last year and had to report the due in April 2022. However, in the previous year, they also committed an evasion in December 2021. Considering both offenses, the statute of limitation will begin in April 2022, and the government can only take action after April 2028.
Tax Evasion – Consequences
Under the 7201 section of the IRS, the income tax act by ITD, and various other sections implied by different countries, tax dodgers are liable to the following consequences. However, the punishment depends on the level of crime. According to this, the offender may face either one or both of the consequences.
Penalty:
- It is when a felon is charged with a willful attempt to either report inaccurate assessment or make inadequate tax payments.
- The maximum penalty for an individual is $100,000, and $500,000 for a corporation.
- They also have to pay any additional legal charges.
Imprisonment:
- If the violation is substantial, like not filing taxes for years, money laundering, etc.
- In such a case, the prison time can last upto five years.
- They are also required to pay any costs incurred during the legal proceedings.
Difference between Tax Avoidance and Tax Evasion
Tax Avoidance:
- It is when one uses legal approaches to reduce tax amounts.
- It is not a felony but rather a frequent method taxpayers use to claim tax benefits.
- People can lower their tax payments through charitable contributions, investments, availing various schemes, etc.
Tax Evasion:
- It is the use of illegal methods to dodge taxation.
- It is a criminal offense, and the taxpayer can even serve imprisonment along with fines.
- Here, the person deliberately hides financial information to accumulate personal wealth.
FAQs
Q1. What is tax evasion? Is it a felony?
Answer: Tax evasion is a criminal offense where an individual or an organization uses illegal methods to avoid paying taxes. It is a type of tax fraud that can result in a loss in revenue for the central government. Common methods are tax underpayment, inaccurate reports, availing inapplicable benefits, etc. Yes, it is a crime according to section 7201 of the IRS.
Q2. How to avoid tax evasion?
Answer: Government bodies can avoid tax evasion by employing simple tax structures, strict laws and policies, and even lowering tax rates. Other techniques include conducting knowledgeable seminars for the public to understand the tax system.
Q3. How to report tax evasion?
Answer: Anyone wanting to report evasion of taxes can fill out the 3949-A Form with the IRS. Your data will be confidential, and you may also receive a reward for which one has to fill out the 211 Form. Similarly, in other countries, one can report tax evasion by visiting their country’s respective income tax website or office. For instance, you can report tax evasion in India through the Income Tax Department’s website.
Q4. What are the consequences of tax evasion? Does one get jail time?
Answer: Anyone guilty of tax evasion might have to face one or both consequences. One is a penalty that can go upto $100,000 or $500,000 for an individual and an organization, respectively. Another is imprisonment for up to five years.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to tax evasion. We discuss what it means, its causes, examples, penalties, and the difference between tax evasion and tax avoidance. Visit the following articles to learn more.