Updated July 29, 2023
Difference Between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance
The following article provides an outline for Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance. Taxes are the result of your earnings or generating wealth by running a business. Paying taxes by an individual or an entity is mandatory by law; however, it is still voluntary compliance. Payment of taxes can be done by planning or avoiding to the extent permissible using various tax-saving instruments. There is a third way, which is Tax Evasion, where the income and the expenses are misrepresented to not pay the liable taxes in part or full.
Tax Evasion
It is a situation when a taxpayer deliberately avoids disclosing/what is the true tax liability. Instead, they either choose non-payment or underpayment of taxes, which is not just ignorance of any law but is illegal and a punishable offense. It is willfully practiced by not reporting income at all or showing incorrect income and reporting expenses that are not legal or simply by not paying the liable taxes.
Tax Avoidance
It is a method of reducing the taxes that an individual or an entity is obliged to pay but in a legitimate way. It is a planned step taken by way of tax-saving instruments to lower these obligations.
Head To Head Comparison Between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 differences between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance:
Key Differences Between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance
Let us discuss some of the major differences between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance.
- Tax Evasion is a known fraud of not paying the liable taxes, while Tax Avoidance is a well-structured plan to identify methods to reduce the outflow towards tax payments.
- The Government of any country offers areas and multiple options to the public and entities in reducing and encouraging investments that serve as tax-saving instruments.
For example, Individual Retirement Account (IRA) in the United States allows you to save money for your retirement in a tax-advantaged way. The earnings grow as tax-deferred until withdrawn.
The Equity Linked Tax Saving Scheme, under Section 80C, in India is another example of tax saving on the total tax deduction, which not only makes one avoid the huge amount of taxes but also encourages investments and returns. It has a lock-in period of 3 years, which also means the taxpayer will have a good opportunity to earn returns from the market.
However, if the road taken is towards understating income earned or overstating tax mentions in lieu of not paying the exact taxes, it calls for uneventful consequences like prosecution.
For example, Carlos Ghosn, the ex-CEO of Nissan, has been arrested on allegations of false accounting details, under-reporting his earnings, and misusing the company assets. Greg Kelly, who was a Nissan director and head of Human Resources, was also arrested as he helped Ghosn structure complex deferred payment plans, which were never reported. This amount approximately totaled $80 million.
- The accountants or any party involved in producing false returns for the taxpayer is also subject to prosecution but not to pay their clients’ taxes.
For example, in the corporate scandal of India-based Satyam Computer Services, the chairman confessed that he had manipulated the accounts in many forms – inflate the company’s revenue, falsifying income tax returns, and fabricating invoices. PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) was serving as the independent auditors for the entity that was fined $6 million by the US Securities and Exchange Commission for not following the auditing standards and duties related to the auditing of the books of accounts for Satyam Computer. The Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI), in March 2018, barred PwC firm from auditing any listed company in India for 2 years as the firm has been found complicit with the fraud.
In the case of tax avoidance, the accountants are known to plan well for those informed taxpayers who look for legal methods to reduce the amount of taxes towards their business or income earned. They provide you with help by imparting knowledge on the probable legal methods to reduce your income outflow to the possible limit.
- Tax Evasion leads to the encouragement of black money and other black market transactions owing to practices like manipulation of books, and overstating expenses to reduce the taxable income, among others. On the other hand, Tax Avoidance encourages informed taxpayers, who would invest money into instruments like Retirement funds. This would mean not only reducing their tax liability but the usage of taxes by another Government body for the betterment of services.
- There are 3 things to confirm a Tax Evasion – attempt, intent, and willingness. When the taxpayer attempts the hoax, it depicts the intent by doing things like understating the income, etc. This consequently establishes the willfulness it has of doing something wrong or illegal in this case.
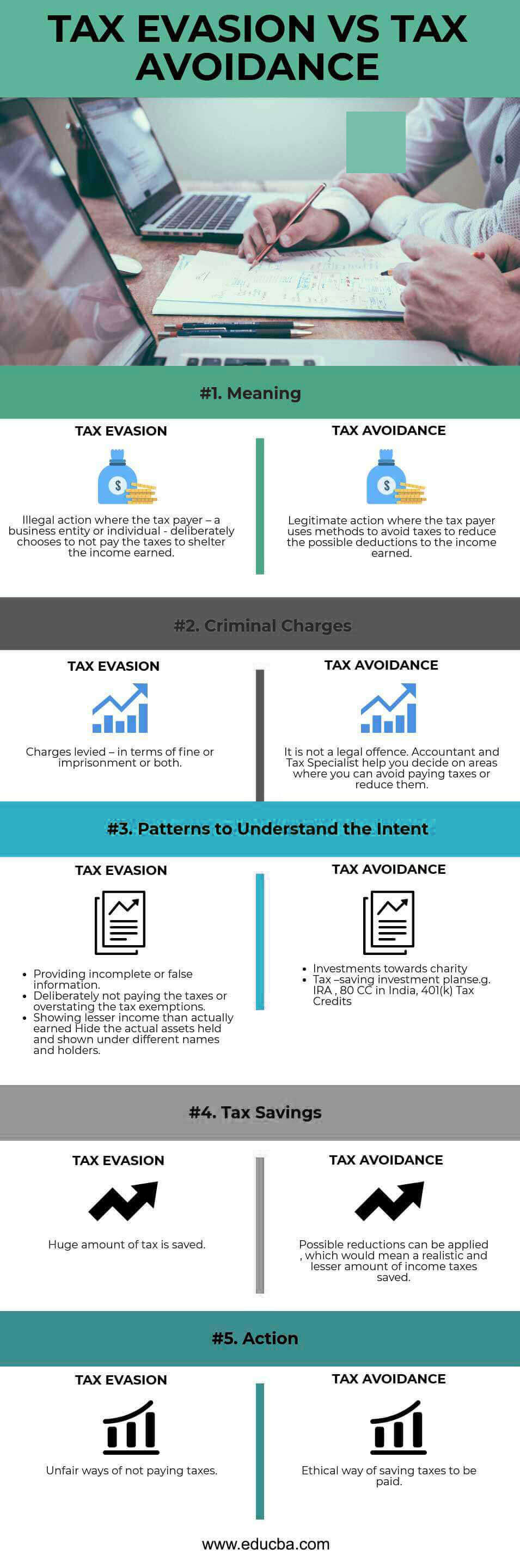
Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance Comparison Table
Let’s look at the top 5 Comparison between Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance
| Basis of Comparison | Tax Evasion | Tax Avoidance |
| Meaning | Illegal action where the taxpayer, a business entity, or an individual deliberately chooses to not pay the taxes to shelter the income earned. | Legitimate action where the taxpayer uses methods to avoid taxes to reduce the possible deductions to the income earned. |
| Criminal Charges | Charges levied – in terms of fine or imprisonment or both. | It is not a legal offense. Accountants and Tax Specialists help you decide on areas where you can avoid paying taxes or reduce them. |
| Patterns to Understand the Intent | Providing incomplete or false information. Deliberately not paying the taxes or overstating the tax exemptions. Showing lesser income than actually earned Hide the actual assets held and shown under different names and holders. | Investments towards charity. Tax–saving investment plans, e.g. IRA, 80 CC in India, 401(k) Tax Credits. |
| Tax Savings | A huge amount of tax is saved. | Possible reductions can be applied, which would mean a realistic and lesser amount of income taxes saved. |
| Action | Unfair ways of not paying taxes. | Ethical way of saving taxes to be paid. |
Conclusion
An issue in tax saving can also arise due to a lack of understanding and ignorance of the Tax Laws of the country. What really differentiates ignorance from fraud would be the intent and extent of the taxpayer to alter the current situation and income and how engaged is he in the act. There is a provision governing taxation laws that allows the taxpayers to reduce their taxes which are unintentional non-payment or obscurity in the law. This is termed a ‘Tax Loophole’, which offers some scope to the person or business to avoid any law by not directly violating the same. Some examples are transferring assets to your children to avoid taxes, investing in stocks and bonds for long-term capital gains, and so on.
The Auditors of company books, Government officials, and other monitoring bodies are developing the mechanism and keeping a very close eye on each taxpayer and what each one is liable to pay. One such example is how the Government keeps an updated record of the income of all the Households and then tracks back the same, depicting that the total expenditure should equate to the income within the economy. There will always be a fine line of difference between legal and illegal methods of tax payment – moving your tax residence to a tax haven or by just becoming a perpetual traveler! There can be merged borders in every entity if proven a misdeed or forbidden by the existing laws; it undoubtedly invites punishments.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance. Here, we discuss the Tax Evasion vs Tax Avoidance key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –