Updated March 23, 2023
Difference Between TDM and FDM
TDM vs FDM are different types of multiplexing methodology. And both of them have different specifications for the input signals as well as different areas of applications. In a communication system, we can neither have a separate channel for transmitting the information coming from various sources nor it is possible to transmit the signals sequentially one by one. So, we must have an effective technique for managing the same. “Multiplexing” is one such technique.
Multiplexing ≈Mixing
Multiplexing is the process in which data coming from different sources are combined and transmitted over a single data channel.
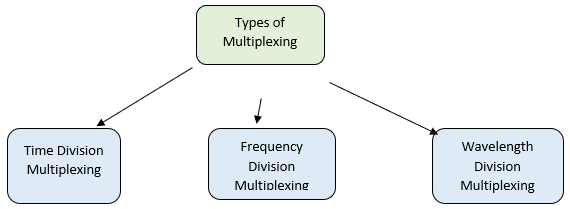
There are various multiplexing techniques available as stated under:
Multiplexing is a mode of transportation of the signal in a network. It helps in effective communication of the information present in either Analog or digital form over a given channel. It also helps us optimize the transmission cost for transmitting the information.
Head to Head Comparison Between TDM and FDM (Infographics)
Below are the top 10 differences between TDM vs FDM:
Key Differences Between TDM and FDM
Let us look at the key differences:
- Definition: TDM is a process of transmitting multiple data streams over a single channel. Where each signal is divided into a fixed-length time slot. Whereas FDM is a process in which the total available bandwidth is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands where each band carries a separate signal.
- Basic Criteria: The time is divided into various different fixed length slots and each of the signals is allocated with a time slot on a round-robin basis whereas FDM generates a different channel for different signals and each of them occupies a different frequency band.
- Frequency Utilization: TDM total available bandwidth is used on a time-sharing basis whereas in FDM the entire frequency band that is available is divided into multiple channels where each channel is separated by a guard band which also leads to ineffective utilization of the frequency band.
- Requirement: Framing Bits (sync pulses)are used at the start of each signal so as to enable synchronization and also for the retrieval of information back during demultiplexing. In FDM guard band is used to separate two different signals and also to avoid overlapping.
- Complexity: TDM system requires identical systems for various data streams which make the circuitry simple compared to FDM systems where different circuitry, bandpass filter, etc are required for data coming from different streams which makes the design of FDM system quite complex
- Type of Signal: TDM can be used for transmission of both Analog as well as Digital signals. While FDM is mostly employed for analog signal
- Advantages: TDM is protected against crosstalk when compared to FDM systems.
TDM vs FDM Comparison Table
Some of the comparisons of TDM vs FDM are highlighted below:
|
Basis of Comparison |
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) |
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) |
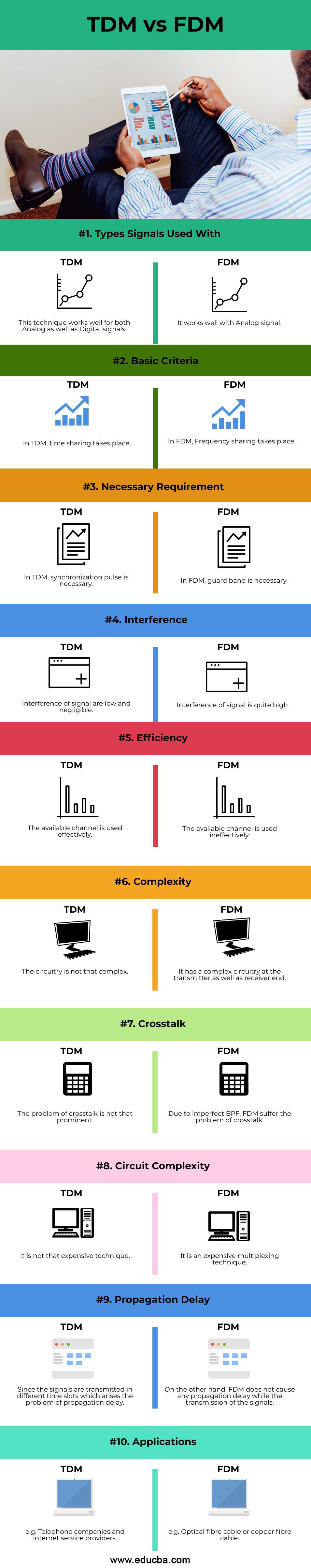
| Types signals used with | This technique works well for both Analog as well as Digital signals. | It works well with the Analog signal. |
| Basic criteria | In TDM, time-sharing takes place. | In FDM, Frequency sharing takes place. |
| Necessary requirement | In TDM, the synchronization pulse is necessary. | In FDM, the guard band is necessary. |
| Interference | The interference of the signal is low and negligible. | The interference of signal is quite high. |
| Efficiency | The available channel is used effectively. | The available channel is used ineffectively. |
| Complexity | The circuitry is not that complex. | It has a complex circuitry at the transmitter as well as receiver end. |
| Crosstalk | The problem of crosstalk is not that prominent. | Due to imperfect BPF, FDM suffers the problem of crosstalk. |
| Circuit complexity | It is not that expensive technique. | It is an expensive multiplexing technique. |
| Propagation delay | Since the signals are transmitted in different time slots which arises the problem of propagation delay. | On the other hand, FDM does not cause any propagation delay while the transmission of the signals. |
| Applications | e.g. Telephone companies and internet service providers. | e.g. Optical fibre cable or copper fibre cable. |
Example of TDM and FDM
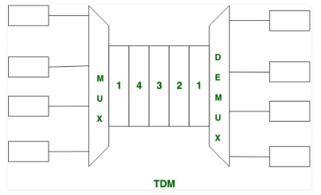
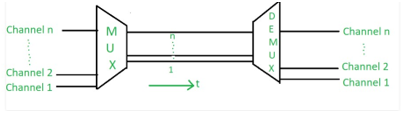
TDM: To understand the TDM system better let us consider each of these boxes to be the input stream. The data coming from various stream is divided into a unit which is allocated a given time slot for transmission on a round-robin basis. As shown in the diagram below 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th each of the input streams is provided with a slot First, second, third & fourth respectively. Once the allocation of each stream is completed then again, the fifth slot is allotted to data coming from the 1st input stream. This process goes on until the entire data streams are transmitted.
In the above figure,
- Mux: It is a device that performs multiplexing -> Where the signals are prepared for transmission.
- Demux: It is a device that performs demultiplexing -> It is the reverse of multiplexing where the signals are brought back to its original state. And all the unwanted information which was added during the transmission Is removed.
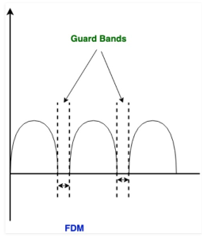
FDM: Let us consider an example for FDM here all the signals are transmitted at the same time but are allocated a separate frequency band. Each frequency band is separated by a suitable gap so as to avoid overlapping. This gap frequency is referred to as guard bands.
The above figure showing the FDM
The above figure showing the frequency distribution with a separating guard band.
**Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): In WDM different data streams having different wavelengths are transmitted in the light spectrum. Prism’s output is used at MUX because of its property to convert different wavelengths into a single line and is also used as an input to DEMUX. WDM is mostly used in optical fibre communication.
Conclusion
In the communications systems multiplexing and demultiplexing employs a great application for effective transmission of signals over a shared channel and transmitter end as well as retrieval of information at the receiver’s end. Based on the type of signal (Analog or digital signal) and the area of application we adopt a specific type of multiplexing.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to TDM vs FDM. Here we discuss the key differences with infographics and comparisons table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –