Updated July 25, 2023
Definition of Temporary Account
Any account which begins with the zero in each fiscal year & is closed at the end of the year to start again with zero in the next year can be referred to as a temporary account.
Accounts are closed so there the balances of one year don’t get mixed up with the other. This process of resetting the temporary account & preparing them for the next period is done through passing closing entries. The resetting of temporary accounts to zero can be done on any period, yearly, monthly, or quarterly. These are not of continuous nature & are generally closed before the preparation of financial statements.
What is Temporary Account?
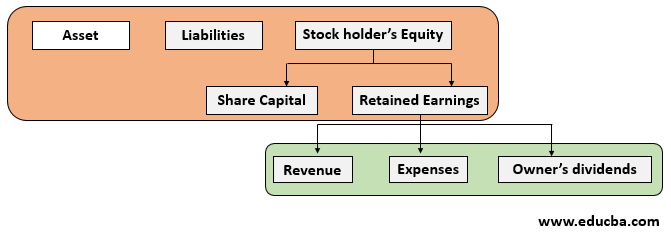
Every business is represented by its Balance Sheet. Once the fiscal year closes, all the accounts representing the transactions of the business for that year are summarized into the Balance sheet. These include various assets, liabilities, owner’s equity, retained earnings, etc. While assets, liabilities & capital directly represents the going concern of the business, they remain in the balance sheet along with the company’s existence. The net profit/loss made by the company is summarized and grouped into reserves & surplus in the balance sheet. The net profit/ loss is the summary of various income & expense accounts.
The temporary accounts can also be referred to as nominal accounts. While the asset, liabilities and retained earnings accounts being permanent accounts relate to the company’s position forever, the temporary account gives us a picture of the financial performance of the company over a certain period of time.
Temporary accounts include revenue accounts, expenses accounts, gain or loss on capital transactions accounts, memorandum accounts & any drawing account. Generally, these accounts are used to prepare the business’s Income statement. At the end of the period, closing entries are recorded to summarize the balance of the temporary accounts which gives us the net profit/loss made by the business for the period. This profit after distribution of dividend or any loss made is shown as part of reserves and surplus / retained earnings in the balance sheet & technically it is part of the owner’s equity. So, these are the accounts that accumulate the transaction information until they’re transferred to the capital account.
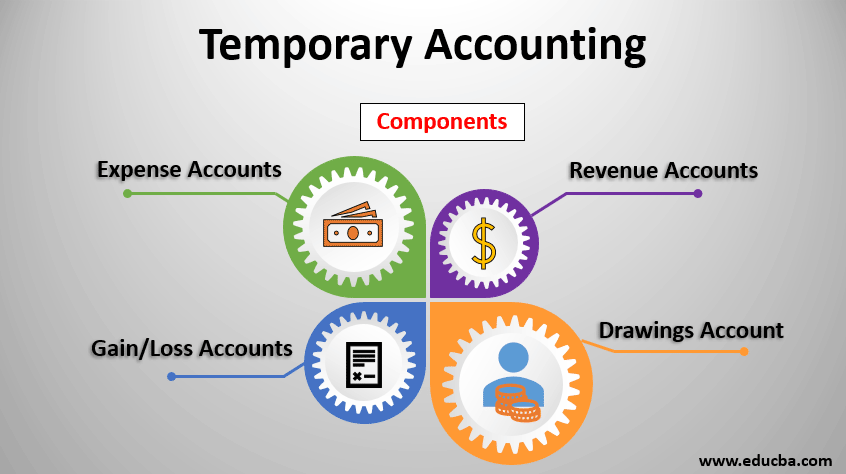
Components of Temporary Accounts
Below are the different Components of temporary accounts:
1. Revenue Accounts
- These are the accounts in which the transactions of income/revenue earned by the company’s business are recorded. Examples: Sales a/c, Discount received account, etc.
- By default, the revenue account will have credit entries & has a credit balance. Any credit notes given to the customers are recorded as debit entries in the revenue account either as a separate discount account or within the revenue/sales account itself. The balance in the revenue account will increase with every credit transaction & vice versa. For closing the revenue account, a debit entry should be passed.
- For example, if in a revenue account, if the credit balance at the end of the period is $105,000, then a debit entry shall be passed in revenue account making the balance in revenue account as zero & the credit shall be passed to any income summary account or profit and loss account.
2. Expense Accounts
These are the accounts in which the transaction of all expenses made by the company’s business are recorded. for example, Purchases a/c, salaries a/c, rent a/c, etc.
In general, any expense account will have debit entries & a debit balance. For closing the expense account, a credit entry should be passed. The balance in the expense account increase with every debit entry & vice versa. For example, if in an expense account, if the debit balance at the end of the period is $ 75,000, then a credit entry shall be passed in the expense account making the balance in the revenue account as zero & the debit shall be passed to any income summary account or profit and loss account.
3. Gain/Loss Accounts
These are the accounts in which the gain or profit made usually on capital transactions are recorded. For example, Gain/loss on the sale of Fixed Assets, etc.
Any gain or loss made through capital transactions is usually recorded through a nominal account. When it is again recognized, this account will have a credit balance & when a loss is recognized, this account gives a debit balance. Depending upon the balance, a respective entry will be passed to close this account & pass this balance to an income summary account or a profit and loss account.
4. Drawings Account
A special case where the balance in a temporary account not being transferred to the income summary account is the proprietor’s drawing account. This account usually will have the debit balance & a credit entry is required to be passed to close this account. The balance in the drawings account will increase with every debit entry. The balance in this account shall be transferred directly to the capital account instead of the income summary account or profit and loss account.
Once all the temporary accounts are closed to the income summary account or profit & loss account, the net balance determines the financial performance of the business. If the profit & loss account is having a debit balance, it means that the business has made a loss & a credit balance means that the business has made a profit. Any dividends that are to be distributed to the owners will be debited from the profit and loss account & the net balance will be transferred to retained earnings which becomes part of the owner’s capital.
In the above representation, accounts highlighted in green are temporary accounts and orange are permanent accounts.
When the trial balance is prepared at the end of the period, it contains all the accounts both temporary and permanent in it with their balances. Once the closing entries are passed in all the temporary accounts, a post-closing trial balance may be prepared which contains only the summary of the balances in real accounts or permanent accounts. Here the retained earnings account will be properly adjusted with the current year’s profit/loss.
Conclusion
Summarizing with the topic, just to ensure that the financial performance of the company from time to time & also to avoid the mix up between the periods, some accounts are to be closed before preparation of financial statements & balance should be set to zero. These accounts are temporary accounts & upon closing, the balance would be transferred to a profit & loss account or income summary account.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to a Temporary Account. Here we discuss the different components of temporary accounts which include revenue accounts, expense accounts, and gain/loss accounts, etc. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –