Introduction to ERP Systems in Supporting Inventory Audits
Efficiency and accuracy are crucial for remaining competitive in the fast-paced business environment. Many companies are turning to ERP systems (Enterprise Resource Planning) to streamline their operations, integrating everything from finance to supply chain management. One key area where ERP systems offer significant benefits is inventory audits, which require meticulous tracking and data accuracy. In this article, we will see how ERP systems for inventory audits can enhance the process and support businesses in maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
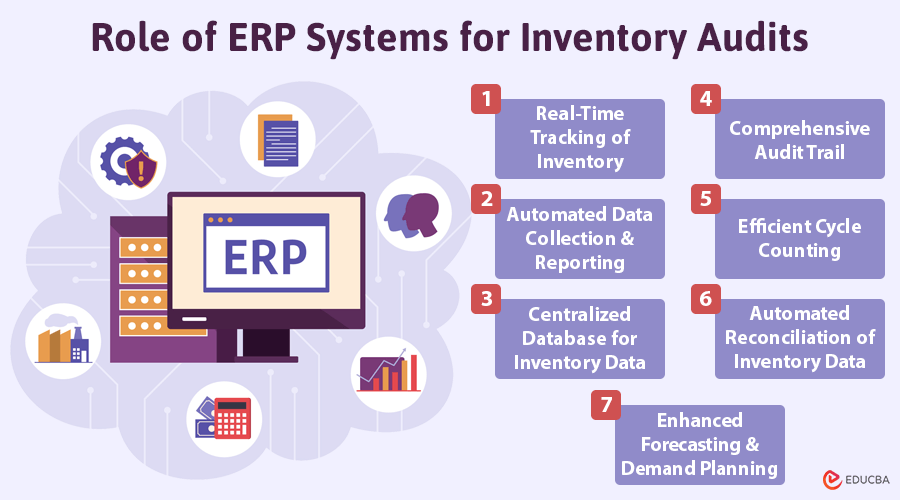
Role of ERP Systems for Inventory Audits
The role of ERP systems for inventory audits are:
#1. Real-Time Tracking of Inventory
ERP systems for inventory audits offer real-time tracking capabilities that give businesses a live view of their stock. Every stock movement—from incoming shipments to outgoing orders—is updated instantly within the ERP system. This live tracking minimizes the chance of discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory levels.
With real-time updates, auditors can verify inventory data quickly, reducing delays and errors common in manual systems. Ultimately, this provides a clearer and more accurate picture of inventory status.
#2. Automated Data Collection and Reporting
Manual data entry is a common cause of mistakes in inventory management. ERP systems streamline this process with automated data collection tools like barcode scanners and RFID readers. These devices instantly capture inventory details and feed them directly into the ERP platform, reducing the need for human input.
The system then generates standardized reports automatically, making it easier for auditors to review consistent, accurate records. By automating data collection and reporting, businesses save time and minimize the risk of inaccuracies during audits.
#3. Centralized Database for Inventory Data
A common challenge in inventory audits is inconsistent data across different departments or systems. It solves this problem by consolidating all inventory data into a single, centralized database. This unified platform allows every department to access the same up-to-date information, eliminating discrepancies.
A centralized database makes it easier for auditors to trace inventory movements, verify transactions, and understand the context of changes. It provides a single source of truth, simplifying the audit process and improving overall data integrity.
#4. Comprehensive Audit Trail
Transparency is crucial for successful inventory audits. ERP systems automatically generate a detailed audit trail for every inventory transaction, adjustment, or transfer, including timestamps and user identification. This clear activity record helps auditors trace each item’s history, identify patterns, and resolve discrepancies.
The audit trail ensures accountability, providing a transparent chain of custody that meets internal audit requirements and regulatory standards. This level of detail is invaluable for efficient and reliable audits.
#5. Efficient Cycle Counting
Instead of relying solely on annual physical inventory counts, businesses can use ERP systems’ cycle-counting capabilities for inventory audits. Cycle counting involves regular, partial inventory checks, dividing stock into smaller, manageable segments.
With ERP support, cycle counting becomes less disruptive and more precise, allowing businesses to maintain accurate inventory records throughout the year. This reduces the burden of annual audits and ensures ongoing inventory accuracy.
#6. Automated Reconciliation of Inventory Data
Discrepancies between recorded data and actual inventory are common issues during audits. ERP systems automatically reconcile inventory counts with system records, flagging inconsistencies in real time. This proactive reconciliation helps businesses identify and correct issues early rather than during a formal audit.
By resolving discrepancies as they arise, companies improve the reliability of their inventory data, making the audit process smoother and more efficient.
#7. Enhanced Forecasting and Demand Planning
Beyond inventory audits, ERP systems provide tools for better forecasting and demand planning. By analyzing historical sales data and seasonality trends, it helps businesses predict future inventory needs accurately. This helps companies keep stock levels balanced, minimizing the chances of overstocking or running out of inventory, making audits more difficult.
Accurate demand planning ensures a stable inventory, contributing to a more consistent and predictable audit process.
Final Thoughts
Embracing ERP systems for inventory audits is not just about improving operational convenience; it is a strategic move toward greater accuracy, transparency, and accountability. ERP systems optimize the audit process by integrating automation, real-time tracking, and centralized data, helping businesses maintain accurate records and meet compliance standards. For companies looking to enhance their inventory management and streamline audits, ERP systems offer a robust foundation for long-term success.
Incorporating it enables businesses to stay competitive, reduce errors, and save time—all while achieving higher accuracy and reliability in their inventory records.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on the role of ERP systems for inventory audits has been insightful. Check out these recommended articles for more information on optimizing your business operations and enhancing inventory management.
