Updated July 7, 2023
Third-Party Insurance Meaning
Third-party insurance covers injury to an individual other than the insured, including damage to their property. For example, Harry was riding his bike when he accidentally hit a parked car, which caused damage to the car. According to his insurance, his agency is liable to pay the damages to the third party. So, he requests an insurance claim. His agency then pays the car owner(third party) for the damages.
It protects people who are not at fault in an accident. The most common application is in the field of motor racing. All motor vehicles operating on land and bearing a registration certificate must carry this insurance. As a result, if a driver causes an accident that damages other cars or the health of those in them, they will be fairly compensated. In addition, it provides protection only to the third party in the event of an incident. It is a legal requirement for all vehicle owners to have this insurance.
Key Highlights
- Third-party insurance is a policy that covers material, personal, and economic damages the policyholder may cause to a third party.
- It classifies as either liability insurance or property insurance, where the property can be a vehicle, real estate, etc.
- This policy covers injury treatment, damage repairs, or even death of the third party.
- The significant difference between third-party and comprehensive insurance is that comprehensive policy offers additional coverage, such as damages due to disasters, compensation for insured individuals, etc.
How Does Third-Party Insurance Work?
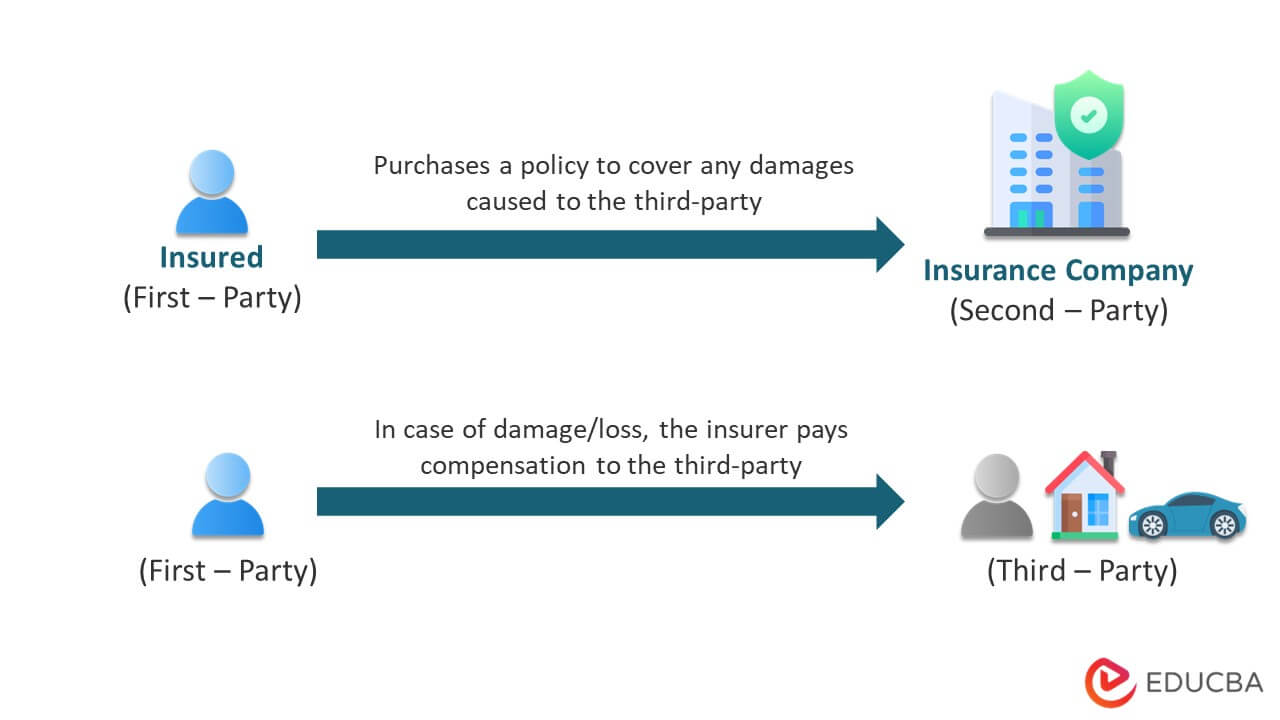
- In this policy, the first party is the insured, the second party is the insurer, and the third party is any other person.
- As per the policy, if the insured causes damage to the third party, they can raise an insurance claim with the insurer.
- The insurer then inquires about the incident, and if the claim is valid, they will cover any third-party costs such as medical care, damage repair, and more.
- Although, if the request is invalid due to drunk driving, intentional cause, or absence of the necessary document, then the company can reject to pay the compensation
- In general, after an accident by the insured, the insurance company must pay for the damages. However, if the insured was in an accident due to the other person, the other person’s insurance will be required to cover the costs.
Third-Party Insurance Types
Liability Insurance
- It covers the legal responsibility of a person or organization for injury caused to another person
- It pays for a third party’s bodily damage and protects the insured from the financial consequences of injuring someone
- It is essential for businesses as it protects them from lawsuits when someone gets injured in their establishment or events.
Property Insurance
- It provides coverage for the damage the insured individual/business causes to another person’s property
- The most common insurance is for vehicles like cars, motors, etc
- It also has personal liability coverage if someone gets hurt on the property.
What Does Third-Party Insurance Cover?
- The coverage includes civil liability, i.e., reimbursement for any injuries the person may sustain due to the insured. It can even have compensation in case of their death.
- If an accident occurs and the insured is at fault, the insurance company will pay for all material damages to the property or vehicle.
- However, the company will not cover damage to the insured or their property for most policies.
- For example, the insured gets into an accident that damages Person A’s bike and Person B’s fence and injures Person A and the insured. The company will then pay for the fence and bike repair. They will also pay for Person A’s medical care but not the insured’s medical expenses.
- It also covers any legal fees for lawsuits against the insured.
Third-Party Insurance on Vehicles
- It is coverage that a driver can buy to protect themselves in the event of a collision with an uninsured driver. Moreover, families often purchase it for their cars, vans, trucks, etc.
- It covers the other driver, any passengers in the insured car, and pedestrians who may have been injured during the incident.
- In some cases, it also covers damage to property, such as fences or buildings. Nonetheless, it does not cover damage to the insured vehicle.
- The price depends on various factors, such as mileage, regular driving distance, driver’s age, location, and more.
- Generally, third-party auto insurance is about $1,000 to $1,600 annually for coverage up to $300,000.
How to Claim Third-Party Insurance?
- The very first step is to lodge an FIR with the police. As it is an accident case, the insurance company will require you to have a charge sheet.
- If you caused the damage, the other person files the FIR, and vice versa
- Contact the insurer, notify them of the damages, and give them all the necessary details. One might need to provide proof if they were not at fault
- Afterward, the case goes to the court, where the judge decides if the claim is valid. If the claim passes, the judge chooses the coverage amount for the damages
- The injured may also present repair receipts to claim as per their requirement.
Third-Party Insurance vs. Comprehensive Insurance
| Third-Party Insurance | Comprehensive Insurance |
| It is a liability insurance covering damages the insured may cause to a third party. | The policy covers the damages to the third party and the insured. |
| It is inexpensive, as it does not provide coverage to the insured | It is the most expensive, as it offers additional coverage |
| It covers damages to the other person’s car, property, and themselves in case of injury | It covers damages to the insured, their automobile, property, and third party. It may also cover natural disasters and theft |
| It is a necessary legal requirement for all automobile owners. | It is an optional policy, where the policyholder may choose from various coverage plans. |
Benefits
- It provides adequate cover for all damages/loss to the third party and their property.
- It is cheaper than most insurance plans
- It is flexible, and the insurance company is less likely to decline it
- It can protect businesses in case of a lawsuit related to their products and services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it protects the insured party and covers the damage they may cause to someone else’s property. It is helpful when a company hires an outside contractor. It can also be useful when an individual rents their property to a third party. This type of insurance is usually a requirement by law, and it’s common in many countries.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is the disadvantage of third-party insurance?
Answer: The primary drawback of this insurance is that it does not provide compensation for the insured’s automobile. It also does not repay for damages to any belongings in the vehicle during the accident.
Q2. What are first-, second-, and third-party in insurance?
Answer: In a third-party insurance policy, the buyer is the first party, while the insurance provider is the second party. The third party is any other person apart from the insured and the insurer. When the other person suffers damage/loss because of the insured, they are known as a third party.
Q3. What is the difference between third-party insurance and comprehensive insurance?
Answer: Third-party insurance is basic car insurance and covers damage to your vehicle and any other vehicles involved in an accident. Comprehensive insurance, on the other hand, is a detailed coverage plan. Along with the third party, it covers damage to your vehicle and theft or vandalism.
Q4. What is the claim amount of third-party insurance?
Answer: The claim amount can vary per the policy and the damages. However, on average, the claim can be around $100,000 to $300,000 for personal and property liability. In addition, $25,000 for medical and the driver.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about Third-Party insurance. We describe its definition, types, coverage, benefits, etc. To learn more, visit the following links,