Updated March 23, 2023

What is Timer in Java?
Timer in Java is available in java. util package extends Object class and implements Serializable and Cloneable interfaces. The timer class contains methods that are used to perform timing-related activities. Timer Class in Java is used for performing time-related scheduling of tasks. Java threads use the Timer class’s methods to schedule a task like executing a section of code after some instant of time, repeated execution of code after some predefined time. Each Timer object is bound to a separate background running thread which is responsible for executing all tasks associated with the thread. It is to be noted that the timer class in java is thread-safe; that is, at a time, only one thread can execute the Timer class method. Also Timer class makes use of binary heap as an underlying data structure to store tasks.
Syntax of Timer in Java
Here is a basic syntax of how the Timer class is used in java:
Syntax:
// create a class extending TimerTask
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
//define run method
public void run()
{
// Write Code to be executed by Timer
}
}
class MainClass{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//create timer instance
Timer timer = new Timer();
// create Timer class instance
TimerTask task = new TimerHelper ();
// call timer method
timer.schedule(task, 3000,6000);
//first argument is timer object
// second argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be first executed
// Third argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be executed regularly.
}
}Explanation of the above syntax: The syntax shows how a Timer class is used in java. Using a timer class involves creating a class extending TimerTask and defining the run method in it. The run method contains logic that needs to be executed on a time-driven basis. Below is the Timer class declaration:
public class Timer extends Object
implements Serializable, CloneableMethods of Timer Class in Java
Now we will see what different methods and fields available in the java Timer class are. Here is the list of commonly used methods available in Timer class:
| Method Name | Description |
| public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date date) | Schedules a task to be executed on the defined date. |
| public void schedule (TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long timeperiod) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time after which the task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
| public int purge() | Used for removing all canceled tasks from the timer’s queue. |
| public void cancel() | Cancel’s the timer. |
| public void schedule(TimeTask task, long delay) | Schedules the task to be executed after the specified time in milliseconds. |
| public void schedule(TimeTask task, long delay, long period) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time in milliseconds after which task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
| public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long timeperiod) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time after which the task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which the task will be executed regularly. |
| public void scheduleAtFixedRate (TimeTask task, long delay, long period) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time in milliseconds after which task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
From the above-stated methods, we have found two methods that are similar in working but different in the name; they are schedule and scheduleAtFixedRate. The difference between the two is that in the case of fixed-rate execution, each execution is scheduled in accordance with the initial execution. If there is a delay in execution, then two or more executions will occur in quick succession to overcome the delay.
Constructors in Timer Class
The timer class contains four constructors for instantiating timer object.
- Timer(): Creates a new Timer Object.
- Timer(boolean isDaemon): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread specified to run as a daemon.
- Timer(String name): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread name.
- Timer(String name, boolean isDaemon): This method is a combination of the above two constructors.
One of the above four listed constructors can be called depending on our requirements.
Examples of Implementing Timer in Java
Below is the example of Timer in Java:
Example #1
To start things, let us see a basic example of Timer class. In this example, we will demonstrate the use of the schedule method of the Timer class.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask timerhelper = new TimerHelper();
timer.schedule(timerhelper, 3000, 2000);
}
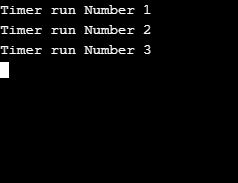
}Explanation of the above code: The above code will execute the run method for the first time after 3 seconds as the first argument is 3000, and after every 2 seconds, the run method will be executed regularly. Here is the output that will be displayed:
Output:
Example #2
In this example, we will see how to terminate a timer thread after a given number of timer runs.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
if(counter ==3){
this.cancel();
System.out.println("Now Cancelling Thread!!!!!");
return;
}
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask helper = new TimerHelper();
helper.schedule(task, 3000, 2000);
}
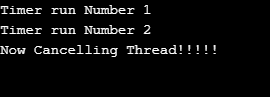
}In the above example, the timer will cancel after the three times run method is called using the timer class’s cancel method.
Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Timer in Java. Here we discuss what is Timer in Java, different methods available in java, with four constructors and examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –