Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Tkinter Listbox
Tkinter Listbox widget is used to display a list of items of which all are text items having the same font and color. The user can choose more than one item from the list to be displayed depending on the widget’s configuration. The Listbox is initially empty when it is created and requires insertion of more than one lines of text which can be done using the insert method for which an index and string must be given as arguments of which index is the item number in the list and string is the text item to be displayed.
Listbox uses the following syntax:
w = Listbox(master, option,..)The master represents the parent window, and the option is the list of options that can be used for the widget, and options are the key-value pairs separated by commas.
Tkinter Listbox Widget
The most commonly used list of options for the widget are:
- bg: Behind the label and indicator, the normal background color is displayed.
- bd: This represents the border size around the indicator. Its default value is two pixels.
- cursor: When the mouse is moved over the Listbox, a cursor appears, and that is this cursor.
- font: This represents the font of the text present in the Listbox.
- fg: This represents the color of the text in the Listbox.
- height: This represents the number of lines in the Listbox. The default value for the number of lines is ten.
- highlightcolor: This represents the focus highlight color when the focus is in the widget.
- highlightthickness: This represents the focus highlight thickness.
- relief: The border shading effects is selected as three dimensional by relief. The default value for relief is SUNKEN.
- selectbackground: This represents the background color to be used while displaying the text that is selected.
- selectmode: This specifies the number of items that can be chosen, and the effect of mouse drag on the selection
- Browse: This is the default setting. One line from the Listbox can be selected. If an item is clicked and dragged to some other line, the chosen line goes along with the mouse.
- Single: Only one line can be selected, and the mouse cannot be dragged; wherever the button one is clicked, that corresponding line is chosen.
- Multiple: The number of lines that can be selected at once is not fixed. Selection can be determined by clicking on any line and its toggling.
- Extended: The number of adjacent groups of lines that can be selected at once is not fixed and is selected by dragging the last line from clicking on the 1st line.
- width: This represents the width of the character present in the widget. The default value of the widget is twenty.
- xscrollcommand: The horizontal scrollbar linked to the Listbox widget allows the user to horizontally scroll the Listbox.
- yscrollcommand: The vertical scrollbar linked to the Listbox widget allows the user to vertically scroll Listbox.
There are several methods that can be implemented on Listbox objects, they are:
- activate(index): The line which is specified by the index passed as an argument is selected.
- curselection(): The selected elements line numbers starting from zero is put into a tuple and is returned by the curselection() method. An empty tuple is returned if there is no selection.
- delete(first, last=None): The indices in the range [first, last] are deleted using this option. The single line having the first index is deleted if the second argument is omitted.
- get(first, last=none): The lines consisting of the text whose indices from the first line to the last line is contained in a tuple and is returned. The text of the line similar to the first line is returned if the first argument is omitted.
- index(i): The portion of the Listbox that is visible is positioned in such a way that the top of the widget consists of a line with index i.
- insert(index, *elements): More than one lines in inserted into the Listbox keeping the line marked by the index above all the lines. If new lines are to be added to the listbox’s end, END must be used as the first argument.
- nearest(y): The index of the line that is visible and which is nearest to the y coordinate Listbox widget’s y relative is returned.
- see(index): The place of the Listbox is adjusted so that the index referred lines are visible.
- size(): The count of lines in the Listbox is returned.
- xview(): The horizontal scrollbar’s command option is set to the xview() method to make the Listbox horizontally scrollable.
- xview_moveto(fraction): When the Listbox is scrolled, the leftmost fraction of the longest line’s width in the listbox is present outside the left side of the Listbox. The range of the fraction is [0,1].
- xview_scroll(number, what): This method is used to horizontally scroll the Listbox. What argument uses either UNITS, which scrolls with respect to characters or PAGES, which scrolls with respect to pages by the listbox’s width. The number of times to be scrolled is told by the number argument.
- yview(): The command option of the vertical scrollbar is set to yview() method to make the Listbox vertically scrollable.
- yview_moveto(fraction): When the Listbox is scrolled, the top fraction of the longest line’s width in the Listbox is present outside the left side of the Listbox. The range of the fraction is [0,1].
- yview_scroll(number, what): This method is used to vertically scroll the Listbox. What argument uses either UNITS, which scrolls by characters or PAGES, which scrolls by pages by the listbox’s height. How many to scroll is told by the number argument.
Example on Tkinter Listbox
Below is the example of Tkinter Listbox:
Python program using Tkinter Listbox to display a list of items.
Code:
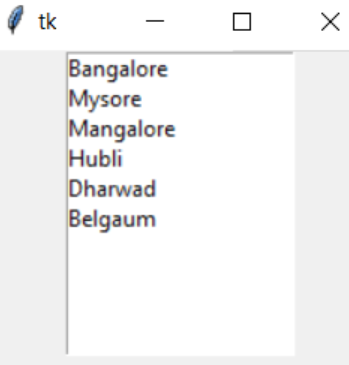
from tkinter import *
import tkinter
top1 = Tk()
lb = Listbox(top1)
lb.insert(1, "Bangalore")
lb.insert(2, "Mysore")
lb.insert(3, "Mangalore")
lb.insert(4, "Hubli")
lb.insert(5, "Dharwad")
lb.insert(6, "Belgaum")
lb.pack()
top1.mainloop()Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tkinter Listbox. Here we discuss a brief overview of the Tkinter Listbox Widget, attributes, methods, and examples of Tkinter Listbox. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –