Updated April 4, 2023
Introduction to Tokens in C
Tokens in C language is the most important concept used in developing a C program. We can say the token in the C language is the smallest individual part. Let suppose even we have a lot of words we can’t make a sentence without combining them, the same way we can’t develop the application without using tokens in C language. So, we can say that tokens in C language are the building block of C programming language.
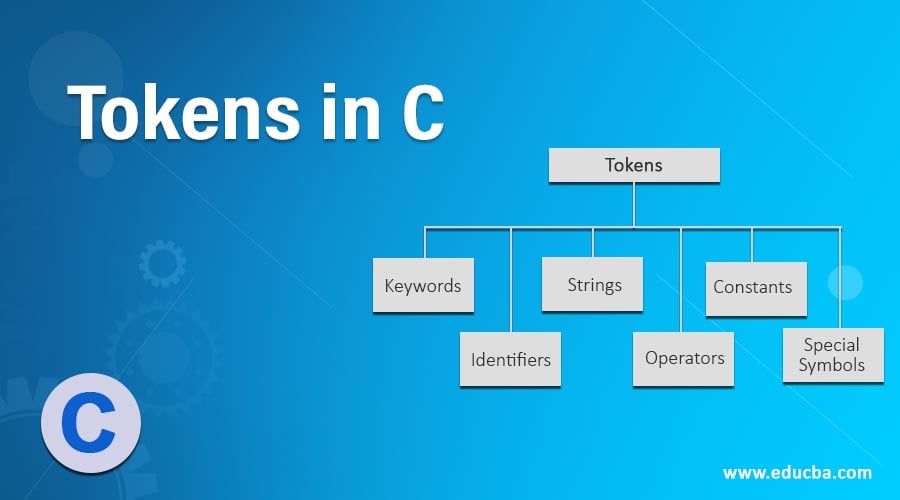
Top 6 Types of Tokens in C
C Supports 6 Types of Tokens
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Strings
- Operators
- Constants
- Special Symbols
1. Keywords
Keywords in C language are predefined or reserved keywords used to expose the behavior of the data. There are 32 keywords in C. Each keyword has its functionality to do.
Syntax:
2. Identifier
Identifier in C language is used for naming functions, variables, structures, unions, arrays, etc. The identifier is user-defined words. These identifiers can be composed of uppercase, lowercase letters, digits, underscore. Identifiers never used for keywords. Rules to construct identifiers is below
- The first character should be either alphabet or underscore and then followed by any character, digit.
- Identifiers are case sensitive as there is A and a treated as different.
- Commas and blank space are not allowed
- Keywords can’t be used for identifiers.
- The length of the identifiers should not be more than 31 characters.
- Naming convention should understandable to the user.
Syntax:
dataType _abc1= Valid
dataType 123abcZ=Invalid
dataType int=Invalid
dataType abc, ap=Invalid3. Strings
Strings in C is an array of characters having null character ‘\0’ at the end of the string. Strings in C are enclosed in double-quotes(“”) and Characters are enclosed in single quotes(”).
Syntax:
char a[10]={'1','2','3'};
char a[]="Amardeep";
char a[10]="Paramesh";4. Operators
This is used to perform special operations on data.
Unary Operator: Applied with a single operand.
Binary Operator: Applied between 2 operands.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Shift Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Misc Operator
5. Constants
A constant in C language is used to make the value fixed, we can’t change constant value.
There are 2 ways of declaring a constant:
1. Using const keyword
const variableName;2. By Using #define pre-processor
#define NAME value;Types of Constants
6. Special Symbols
- Square brackets [ ]: Used for single and multi-dimensional arrays.
- Simple brackets ( ): Used for function declaration.
- Curly braces { }: Used for opening and closing the code.
- The comma (,): Used to separate variables.
- Hash/pre-processor (#): Used for the header file.
- Asterisk (*): Used for Pointers.
- Tilde (~): Used for destructing the memory.
- Period (.): Used for accessing union members.
Examples to Implement Tokens in C
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Keywords
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries
int main()
{
//declare integer variable
int i=121;
//declare float variable
float f=11.11;
//declare character variable
char c='C';
//declare String variable in 2 ways
char s1[20]="Paramesh";
char s3[]="Paramesh";
//declare constant variable
const constant=3.14;
//declare short variable
short s=10;
//declare double variable
double d=12.12;
//displaying output of all the above keywords
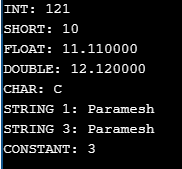
printf("INT: %d\n", i);
printf("SHORT: %d\n", s);
printf("FLOAT: %f\n", f);
printf("DOUBLE: %f\n", d);
printf("CHAR: %c\n", c);
printf("STRING 1: %s\n", s1);
printf("STRING 3: %s\n", s3);
printf("CONSTANT: %d\n", constant);
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
Switch
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries#include
//main method used for running the application
int main()
{
//decalre variable
int n;
//asking enter any choice between 1 to 4
printf("Enter any choice between 1 to 4=>");
scanf("%d",&n);
//switch case, based on choice it will gives us output
//if we did not take break each case then where ever it is true that value and rest are printf
//none are true then default value will be print
switch (n)
{
case 1:
printf("I am Paramesh");
break;
case 2:
printf("I am Amardeep");
break;
case 3:
printf("I am Venkatesh");
break;
case 4:
printf("I am Krishna");
break;
default:
printf("Opps! I am default");
}
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3
Functions
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries#include
int input(void);//declaring method
int getSquareArea(int side);//declaring method
int getCube(int cube);//declaring method
//main method used for running the application
int main()
{
int i=input();
int sArea= getSquareArea(i);
int cube=getCicrcleArea(i);
//displaying output
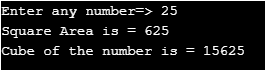
printf("Square Area is = %d\n",sArea);
printf("Cube of the number is = %d\n",cube);
return 0;
}
//method definination
//this for asking the user input
int input(void)
{
int n;
//asking the user to input
printf("Enter any number=> ");
scanf("%d",&n);
return n;
}
//method definination
//this for getting square area
int getSquareArea(int input)
{
return input*input;
}
//method definination
//this for getting cube of the number
int getCicrcleArea(int cube)
{
return cube*cube*cube;
}Output:
Example #4
Typedef
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries
#include <string.h>//Add the String library to perform string actions
//typedef for give struct keyword to user wanted keyword as like below (Courses)
typedef struct Courses {
char courseName[60];//declare character variable
float CourseFee;//declare float variable
char companyName[100];//declare character variable
int loginID;//declare integer variable
} Courses; //To make work user defined keyword we have call the keyword from here
//main method to execute application code
int main( ) {
//Taken Courses name as course( alias name)
Courses course;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy( course.courseName, "C Programming");
strcpy( course.companyName, "EDUCBA");
//Initailize float values into varaible
course.CourseFee = 5000.00;
//Initailize integer values into varaible
course.loginID=2452;
//display the output of all the declared variable below
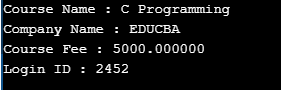
printf( "Course Name : %s\n", course.courseName);
printf( "Company Name : %s\n", course.companyName);
printf( "Course Fee : %f\n", course.CourseFee);
printf( "Login ID : %d\n", course.loginID);
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
Tokens in C language are said to the building block of the application. It can have Keywords, Identifiers, Constants, Strings, Operators, and Special Symbols. Which all are gives one complete structure the C language code.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tokens in C. Here we discuss an introduction, the top 6 types of token, and examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –