What are Total Liabilities?
Total Liabilities are the total amount of money a business or an individual owes to third parties like lenders, government, vendors, etc., in the form of interest expenses, deferred tax, and accounts payable, respectively.
They are legal commitments that a business makes to pay a specific sum to other entities in the future as a result of business operations.
Key Highlights
- Total liabilities are all debts and obligations a company or person owes to third parties.
- It has three types: Short-term, long-term, and other liabilities.
- It is present on the balance sheet of a company’s financial statements.
- Among various formulas, the most common is adding the short-term, long-term, and other liabilities.
Table of Contents
Types
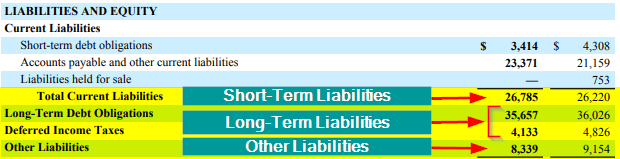
1. Short-Term/Current Liabilities:
These are short-term obligations that a company has to pay within one year. These include accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses, among others.
2. Long-Term/Non-Current Liabilities:
Long-term liabilities represent obligations the company may settle over an extended period (more than one year). They encompass long-term debt, deferred tax liabilities, long-term bonds, and more.
3. Other Liabilities:
This category includes various obligations that are not debt. These can range from accounts payable, accrued expenses, pension obligations, etc.
Position in the Balance Sheet
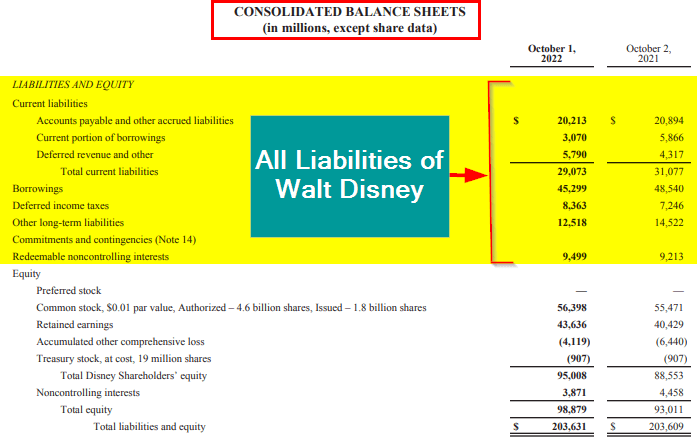
You will find liabilities typically on a company’s balance sheet after assets. For example, in Walt Disney’s 2022 Annual Report, if we see the balance sheet, we can find that it had total current liabilities of $29,073.
There are other liabilities, too, such as borrowings ($45,299), deferred income taxes ($8,363), other long-term liabilities ($12,518), and redeemable noncontrolling interests ($9,499).
(Image Source: Walt Disney Annual Report 2022)
How to Calculate Total Liabilities?
Calculating these liabilities involves the following step-by-step process.
- The company must separate its debts and liabilities into short-term, long-term, and other liabilities.
- Find total current liabilities by adding amounts for accounts payable, short-term loans, accrued expenses, and any other obligations due within the next year.
- Sum up the amounts of all the long-term liabilities, like long-term loans, bonds, and other debts, with maturity dates beyond one year.
- If there are any other liabilities, total them under others.
- Use the formula to calculate total liabilities.
Excel Examples
Let us see how to calculate total liabilities using the formulas mentioned above.
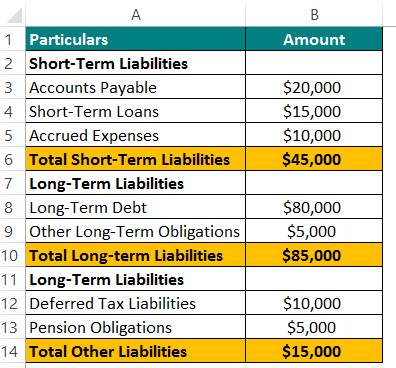
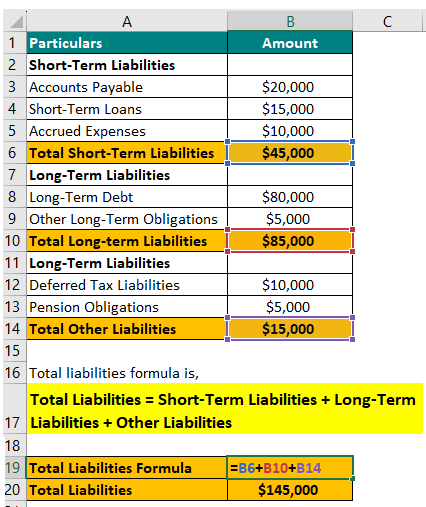
Example #1
Let’s say a company, XYZ Ltd., has the following financials.
Use the below formula,
Total Liabilities = Short-Term Liabilities + Long-Term Liabilities + Other Liabilities
= $45,000 + $85,000 + $15,000 = $145,000
So, company XYZ Ltd. has $145,000 in liabilities.
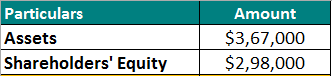
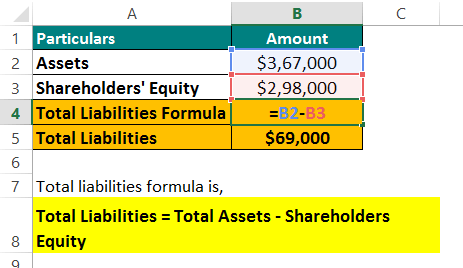
Example #2
Let’s say a company, ABC Corp, has $367,000 in assets and shareholders’ equity of $298,000 in 2022. Calculate its liabilities.
Given,
Solution:
Let’s find the liabilities using the following formula,
Total Liabilities = Total Assets – Shareholders Equity
= $367,000 – $298,000 = $69,000
Thus, ABC Corp has $69,000 in liabilities.
Total Debt vs. Total Liabilities
Here are some key differences between both of them:
| Aspect | Total Debt | Total Liabilities |
| Definition | The total amount of money a company borrows through loans, bonds, or other forms of debt. | The total financial obligations and debts a company owes to external and internal parties. |
| Inclusions | Includes only the debt portion of liabilities, typically long-term and short-term debt. | Encompasses all financial obligations, including both long-term and short-term obligations. |
| Purpose | Indicates the company’s borrowing to finance its operations, capital projects, or other needs. | Provides a broader picture of the company’s overall financial obligations and solvency. |
| Interest Payments | Requires regular interest payments on the debt. | It may or may not include interest payments, depending on the type of liability. |
Calculator
Use the following calculator for the calculations.
| Short-Term Liabilities | |
| Long-Term Liabilities | |
| Other Liabilities | |
| Total Liabilities = | |
| Total Liabilities = | Short-Term Liabilities + Long-Term Liabilities + Other Liabilities |
| = | 0 + 0 + 0 = 0 |
Final Thoughts
Effectively managing these liabilities is vital for long-term sustainability. High liabilities signal financial stress, while well-structured liabilities can support growth and innovation. In conclusion, monitoring and managing liabilities are essential for a healthy financial position.
Recommended Articles
This is a comprehensive article on the overall liabilities of a company where you can learn what it means, its formulas, how to calculate, and examples. We have also explained where you can find liabilities for a company. For more similar resources, check these articles: