Updated June 13, 2023

Introduction to Transparent in Illustrator
Transparent in Illustrator is the most basic and essential part of Adobe Illustrator, with the possibility of adding Transparency to your artwork without noticing it. You can append Transparency to artwork by performing any of the below points:
- Reducing the opacity of objects so that the artwork lying under the object becomes perceptible.
- Making use of the opacity masks to produce disparity in Transparency.
- Making use of the blending mode to alter how colors connect among objects that overlap.
- Registering meshes and gradients that incorporate Transparency.
- Registering graphic or effects styles that incorporate Transparency, like a drop shadow.
- Importing Adobe Photoshop files that incorporate Transparency.
Even though registering transparent effects on your artwork is simple, you must interpret how transparency functions.
How to Create a Transparent Effect in Illustrator?
Transparency defines objects’ blending mode and opacity to produce opacity masks or to knock out a part of one object with the overlying part of a transparent object. Let us apply the transparency effect with a few illustrations.
Basic Transparency
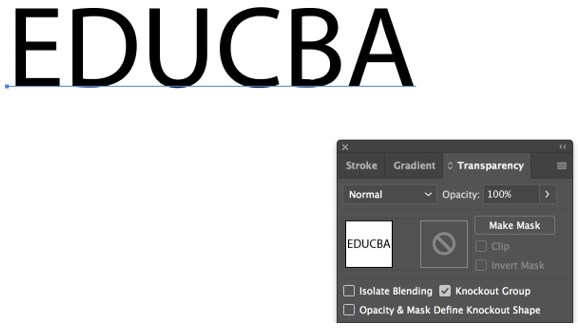
Step 1: Open Adobe Illustrator and draw or write a text on the artboard. Then click on Window and select Transparency.
Step 2: You will get a dialog box.
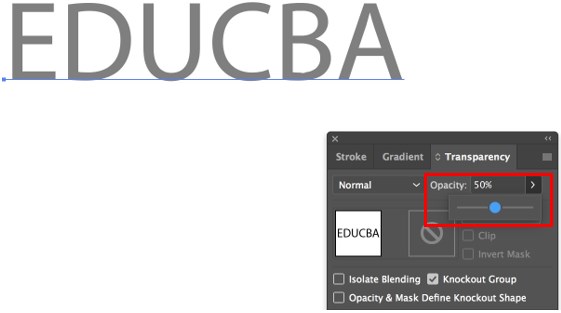
Step 3: Regulate the opacity to provide some transparency to the text. Here we are keeping it like 50%
Transparency Using Blending Mode
Step 1: Draw a rectangle on your artboard and fill it with a solid color.
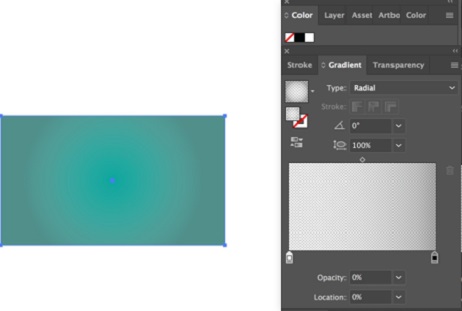
Step 2: Now duplicate the rectangle you created, place it over the original, and fill it with a black-and-white radial gradient.
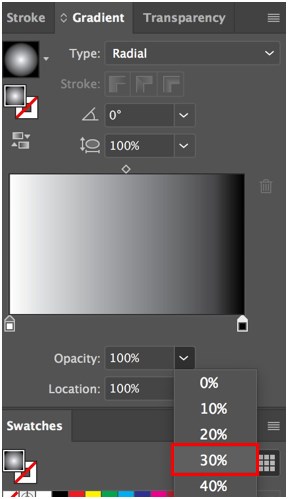
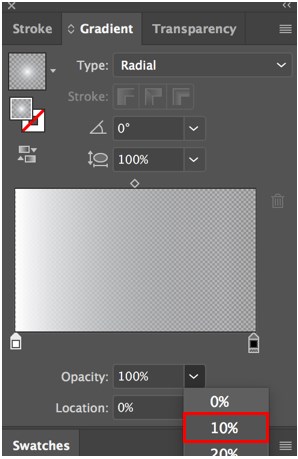
Step 3: The gradient is solid right now. Reduce the Transparency of the black bar to 30%.
Step 4: And white bar to 10%.
Step 5: When we reduce the Transparency, the behind object becomes visible, and both objects seem to blend in well, as shown below.
- The word transparency points out any alterations in opacity and blending modes.
- Blending modes manage how the colors of the groups, objects, or layers communicate with each other. They are defined as color mode-specific and achieve distinct outcomes in CMYK and RGB formats. To observe the result of blending modes, you must append a white or multi-colored element behind your artwork.
- Opacity masks permit a single object’s light and dark regions to be utilized as a mask for supplementary objects. The dark(black) inside the mask specifies regions of the masked art that will be transparent. The light(White) inside the mask specifies regions of the masked art that will be completely visible and hazy. Grays permit a scale of Transparency.
Transparency Opacity Mask
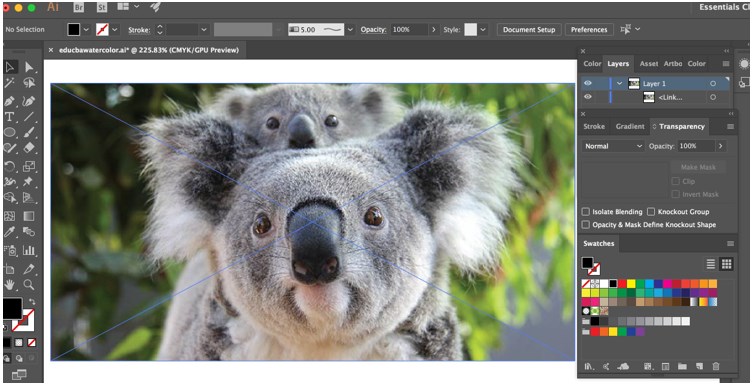
Step 1: Select any image you wish to use and paste or open it on the artwork.
Step 2: Now, create any shape you want over the image. Fill the shape with any color you wish. Next, click the type tool and insert text on your created shape.
Step 3: Select your text and cut it by pressing Command+X on Mac and Ctrl+X on Windows. Now choose your shape object and bring up the transparency panel. Once it opens, you can see two previews. The one on the left-hand side is the shape object that you have selected. On the right-hand side is the mask where you will paste your text object by pressing Command+F on Mac and Ctrl+F on Windows. Be certain that the clip option and invert mask option are unchecked. Now you can see that some of the portions of the image are visible through the text. In this way, you can achieve Transparency through opacity masks.
- You will also observe that when the mask is edited, all the other objects are locked, indicating that you are in the opacity mask mode. If you need to change other artwork elements, open the Transparency panel and click the portion representing the masked object.
- A masking object and an opacity mask can modify the artwork’s Transparency. The opacity mask gives the form through which other objects display. The masking object determines which regions are transparent and the level of Transparency. You can utilize any object that is colored or raster picture as the masking object.
Transparency can be Used to Shape a Knockout: Utilize the Opacity & Mask Define Knockout Shape alternative to create a knockout effect corresponding to the object’s opacity. In the regions of the mask near 100% opacity, the knockout effect will be sturdy; in regions with smaller opacity, the knockout effect will be less sturdy. For instance, if you utilize a gradient-masked object as a knockout, the elemental object will be removed successively. You can produce knockout forms with both raster and vector objects. This method is very functional for objects that utilize a blending mode other than normal, which is the default selection.
Conclusion
Adobe Illustrator’s advanced utilization of Transparency is laced throughout the software; you utilize Transparency not only when you register a blending mode, an opacity percentage, or an opacity mask from the transparency panel but also when you register specific types of effects such as feathers, glows and shadows or styles that incorporate those characteristics. So Adobe Illustrator provides useful latest tools to enhance your command over how you supply and print artwork that incorporates Transparency and permits you to preserve your transparency flattening settings as time-preserving presets.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Transparent in Illustrator. Here we discuss Transparency in basic, blending mode, opacity percentage, and an opacity mask with a few illustrations. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –