Updated February 24, 2023
What are Treasury Bills?
The term “treasury bills” (TB) refers to the type of money market instruments issued by a nation’s government in the form of a promissory note with the guarantee to repay on a future pre-decided date. These financial instruments are inherently short-term with a maximum tenure of 364 days and are primarily issued as zero coupons, i.e., at a discount to their par value. They are also popularly known as T-bills or G-secs (Government securities).
Explanation
Typically, the money raised through Treasury Bills is used by the government for funding various public projects, such as the construction of highways and schools. Given that the government backs these instruments, they are considered one of the safest and most conservative investments. Although most treasury bills are held until maturity, few investors resell them in the secondary market before maturity to book short-term interest gains.
Features
Now, let us look at some of the salient features of (TB):
- These can either be issued in dematerialized form or physical form (promissory note).
- They are issued at a particular minimum price and in the exact multiples thereof.
- They are issued at a discount and redeemed at par value.
- They are issued for a minimum tenure of 14 days, up to 364 days.
- They are highly liquid and traded in both primary and secondary financial markets.
- They are considered to have zero risk of default, given that the government backs them.
- For (TB), a year has a total day count of 364 days.
How to Purchase Treasury Bills
The (TB) can be purchased in any one of the following ways:
- Non-Competitive Bid: In this case, the investors buy Treasury Bills at a discounted rate based on the average auction price.
- Competitive Bidding Auctions: In this case, the investors bid specific discount rates at which they are willing to purchase the Treasury Bills. Bids with the lowest discount rates are accepted first, then the bids at the next lowest rate are accepted, and the process continues until all the treasury bills are sold.
- Secondary Market: Treasury Bills can be purchased or sold on the secondary market or traded through mutual funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) that also deal in previously issued bills.
Example of Treasury Bills
Let us look at the example of the US Treasury Department auctions that issue Treasury Bills throughout the year. On October 29, 2020, the department published 13-week and 26-week Treasury bills worth approximately $114.5 billion at an auction rate of 0.1%, i.e., the discounted price of $99.9for a $100 par value.
Source: US Treasury Department
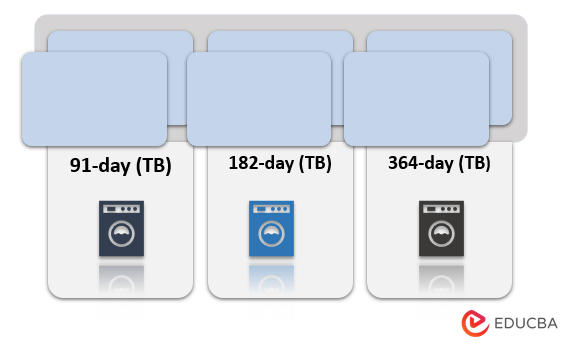
Types of Treasury Bills
(TB) can be primarily classified in terms of its holding period. Although there can be many different variants with different issuance frequencies, the primary three types available are:
- 91-day (TB): These bills are auctioned every week, and they mature after the expiry of 91 days from their date of issuance.
- 182-day (TB): These bills are auctioned every alternate week, and they mature after the expiry of 182 days from their date of issuance.
- 364-day (TB): These bills are auctioned every alternate week, and they mature after the expiry of 364days from their date of issuance.
Who Should Invest?
(TB) are considered suitable for all investors irrespective of risk appetite or financial market knowledge. It can serve as a secure investment option and dilute the overall portfolio’s risk for investors who intend to diversify their investments. Companies, firms, trusts, banks, financial institutions, provident funds, insurance companies, and state governments usually invest in treasury bills.
Factors that Impact Treasury Bills
Several factors impact the price of (TB), and some of the major ones are:
- Monetary policy: The interest rates of (TB) usually move in sync with the rate (Fed Funds rate) determined based on the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. As such, the price of treasury bills is influenced by the Fed’s monetary policy.
- Maturity period: The price of (TB) is impacted by its maturity period. Bills with extended maturity periods offer a higher return as it means the additional risk for the investors.
- Market sentiment: In an expansionary market, (TB) is less attractive and priced lower. However, treasury bills command a higher price when the market is volatile, as they are considered safe.
- Inflation rate: The prevailing inflation rate can affect the price of (TB). The actual return should be at least positive to attract investors’ interest and drive the price.
Uses of Treasury Bills
Like any other organization, governments also require funds to carry out operations. The revenue earned through taxes is one of the significant sources of cash inflow for the government; hence to carry out public welfare projects, they need to issue various debt instruments, and (TB) is one of them. Further, the funds raised through (TB) meet short-term requirements and reduce the country’s overall fiscal deficit.
Advantages
Some of the significant advantages of (TB) are as follows:
- Given that the government backs them, they are considered the safest investment option with zero risk of default.
- The government primarily uses it to fund public welfare projects that benefit society.
- They offer a stable investment option during economic uncertainty or market volatility.
- They are highly liquid and can be traded in primary and secondary markets.
Disadvantages
Some of the significant disadvantages of (TB) are as follows:
- Because of the lower risk, they offer lower returns.
- They don’t provide any regular income until maturity.
- The earnings on (TB) are taxable.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that a treasury bill is one of the safest forms of investment options available in the market. It is an ideal investment option for risk-averse investors and investors who wish to reduce portfolio risk through diversification.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Treasury Bills. Here we also discuss the introduction, how to purchase treasury bills, along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –