Updated July 20, 2023

What are Types of Financial Statements?
The financial statements are critical reports as it describes the financial condition of a business. These are prepared by the management of the business to describe the financial position of the business for a given financial period and can be broadly classified as the income statement, balance sheet, cashflow statements, and statement of owner’s equity.
Explanation
The financial statements of the business or an organization helps in sharing the financial position of the business to the creditors, investors, and analysts. They then shortlist broad attributes drawn from the financial statements and thereby derive meaningful inferences. Such inferences would then result in actions as planned by the stakeholders.
The financial statements can be broadly classified as balance sheet, income statement, cashflow statements, and statements of owner’s equity. These can be prepared on a quarterly basis, monthly basis, semi-annually basis, and on an annual basis. They are to be prepared as per the guidelines placed in the accounting principles as laid down by the regulatory authority. In lay man terms, they should be prepared in the standardized form so that such statements can be easily with the other financial statements of business that are a part of the organization.
Generally, the balance sheet would describe the financial position of the business as to how they stand in terms of assets and liabilities. The income statement describes the profitability of the business and provide an explanation of the income streams generated by the business. The cashflow statement describes the exact cashflow position of the business that is how the inflows and outflows of cash happens in the business from the prior period to the current period.
Types of Financial Statements
The types can be described as shared below: –
1. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet describes the financial position of the business and it delivers critical and important insights on how the investments of the company or business are in place. Such information and insights could be both on tangible and intangible investments and assets. The balance sheet also provides information pertaining to the debt and equity mix. It can be described as the financial statements which is regarded as the final outcome resulting from on all financial statements.
The balance sheet is prepared using the below equation:
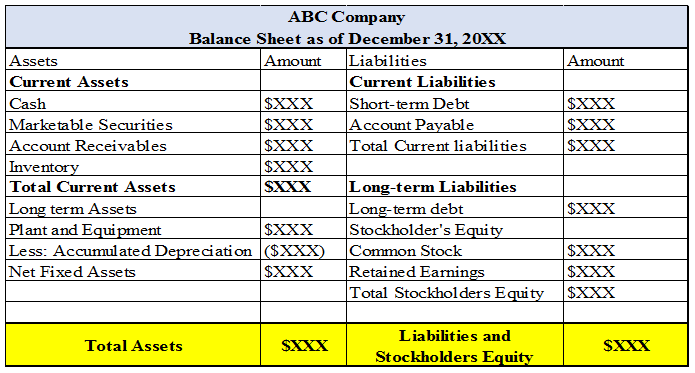
The following can be regarded as the example of the balance sheet as displayed below:
At the asset section, there is the presence of cash, marketable securities, account receivables, Inventory, Plant properties, and Equipment. Generally, cash signifies the amount the business has on hand or it has placed in the checking accounts. The marketable securities can comprise of mutual funds, stocks and bonds which can be converted to cash within one to two business days. The account receivables can be termed as the amount that the business owes from their clients when they sell items on credit. Inventories can be classified as the items that the business intend to sell.
Similarly, on the liabilities section, the business may hold short-term liabilities such as short portion or the current portion of long-term debt. The current portion of debt can be described as the amount that the business has to service in the current financial period. The long-term debt can be described as the amount that the business has to retire over several financial period of its lifecycle. Similarly, it may comprise of account payable which are amount that the business is liable to pay to the suppliers from whom they have taken raw materials on credit.
2. Income Statements
The balance sheet normally prepared and presented is on as on date. It provides the overall snapshot of the liability’s positions, asset position, and debt to equity mix. It does not describe the overall profitability that the business achieved and how they achieved their business growth. The income statement, therefore, becomes important and it is the second statement that the investors sought to access so as to gain insights on the profit numbers as shared by the income statements. Therefore, the income statement reports sales, expenses, profits both before and after tax, and any losses that the business may incur. The operational expenses may comprise of Salaries, rent, telephones, and internet, taxes, water bills, sales and marketing costs, taxes, stationaries, etc.
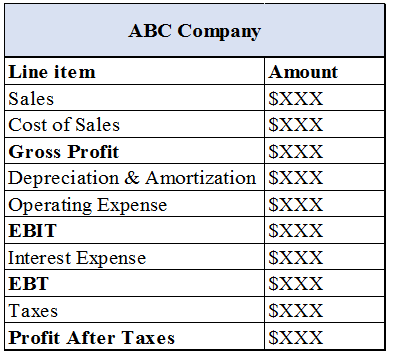
The following is the example of the income statement:
Therefore, a general income statement comprises of sales. From Sales, the cost of goods sold or cost of sales is deducted to arrive at the gross profit. From the gross profit, operational expenses and depreciation are deducted to arrive at earnings before interest and taxes. From the earnings before interest and taxes, interest expense is deducted to arrive at earnings before taxes. Finally, the taxes are deducted to arrive at the profit after taxes.
3. Cashflow Statements
The statement of cashflows generally describe the overall cash outflow and cash inflow that the business experiences during the financial period. This helps the investors and creditors ascertain that the business has enough to service its expenses and handle their purchases. The cashflow statements are broadly described in terms of operating cashflows, cashflows from financing activities, and cashflows from the investing activities.
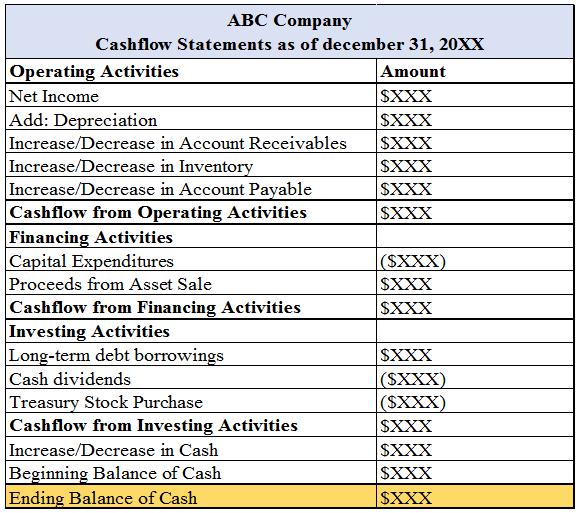
The cashflow from operations generally begins with the adding up of non-cash expense into depreciation followed by the changes in assets and liabilities position. The cashflow from the financing activities describes the changes in the cashflows arising due to retiring or raising funds from debt and equity as well as reporting of distributions and contributions. The cashflow from investing activities describes the changes in the cashflows arising from purchase and sales of fixed assets. The following is the example of cashflow statements as displayed below:
4. Statements of Equity
The statement of equity is of utmost importance to the existing as well as to the potential shareholders of the business. It basically describes the changes that happen in the levels of retained earnings of the business. The computation of the net worth of the business is done by subtracting the debt of the business with the equity of the business.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Financial Statements. Here we also discuss the 4 different types of financial statements with detail explanation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –