Updated August 3, 2023
Introduction to Networking Devices
This article will give you an insight into different Networking Devices and will provide you with a basic idea about why and how they are important in the computer world. The devices or hardware needed for communication and interaction between hardware on a network are called networking devices.
They are not simply wiring and computer. There should be some specific devices, hardware devices that can perform their distinctive roles efficiently and handle digital network connections, and these devices help do the same.
Here’s what these Networking Devices operating alone are primarily accountable for:
- Controlling Traffic: Giant networks would like to isolate and filter information traffic. Therefore, these devices come in.
- Connectivity: Different types of networks use different types of protocols, and these devices are used to provide connectivity among these
Common Networking Devices
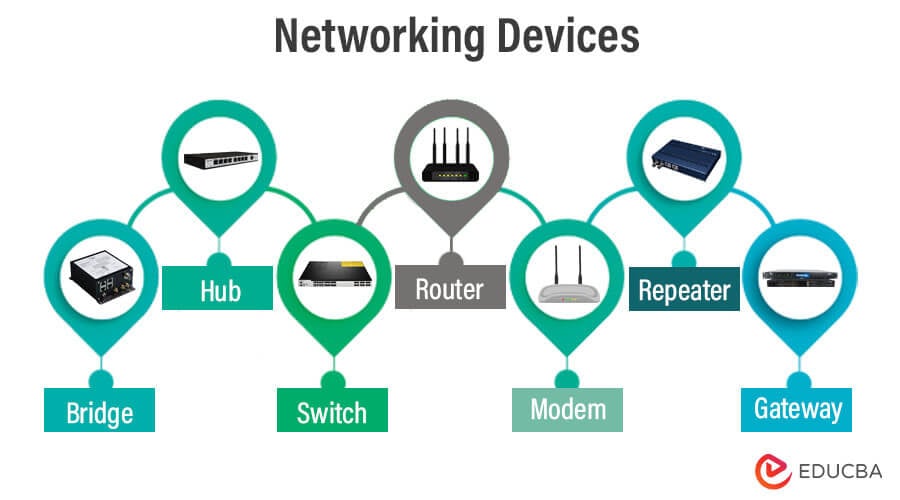
Different Types of Network Devices
- Bridge
- Hub
- Switch
- Router
- Modem
- Repeater
- Gateway
- Access Point
Let’s see the significance of the individual Networking Devices in detail-
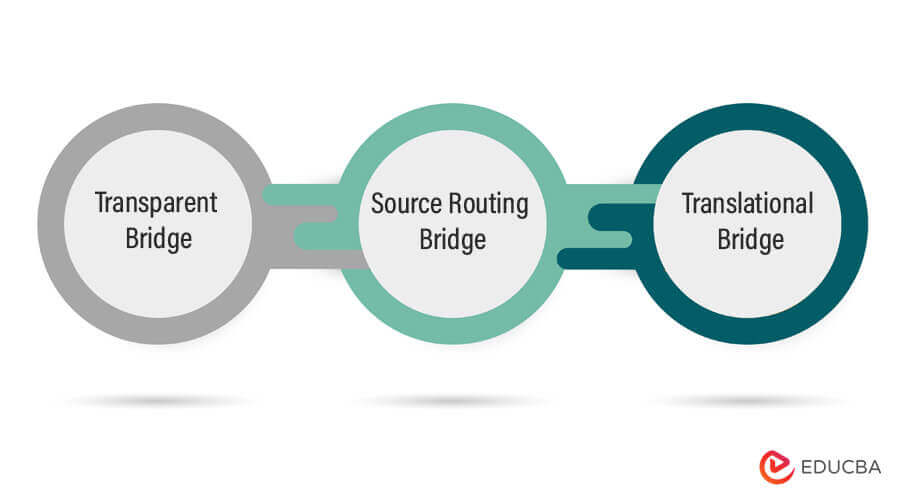
1) Bridge
A device that can forward information and is supported by a physical address is called a Bridge. In technical terms, packets are filtered and forwarded by physical address through a Bridge.
Types of bridges:
i) Transparent Bridge:
- Their network is connectionless and doesn’t support multipath routing.
- Transparent bridges are invisible to other devices on the network.
- Construct the bridging table where the MAC address will store various nodes or devices.
- It is transparent to all the network’s connected hosts.
- Keeping an eye on all the connected bridges and hosts, transparent bridge records, and maintaining the source route address of the incoming frames.
ii) Source Routing Bridge:
- The source routing bridge emphasizes connections and uses multiple paths to the exact location.
- The source Routing bridge is visible to other devices on the network.
- The source station executes the routing operations, and the frame flows through a defined route.
- It is transparent because the bridges learn the location of the destination address by the discovery frame that is spread through the entire network.
- The bridge number and address must be entered manually and should b unique; relocating the bridge can be challenging.
iii) Translational Bridge:
- Allows connection only to non-routable protocols such as local area transport(LAT), network basic input/output system(NetBIOS), and maintenance operation protocol(MOP).
- The translational bridge can be visible or invisible depending on the device’s specific implementation and configuration.
- The bridge connects two different or dissimilar types of LAN protocol, such as a Token ring or Ethernet network.
- Add or remove information depending on the traveling direction and fields from the frame according to the requirement.
- A translational bridge can configure each other’s source and destination address when switching between Ethernet and Token ring frame format.
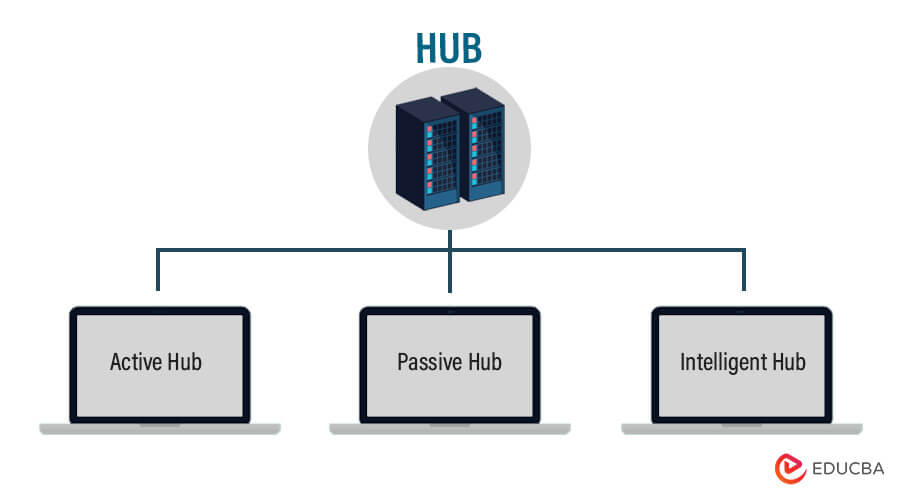
2) Hub
A network segment is formed by attaching network cables to a connectivity device. And this connectivity device is called a Hub. Hubs generally don’t filter information; instead, they conduct incoming information frames or packets to any or all the elements. Nowadays, a central switch or Hub is used by all the networks to which computers are connected.
i) Active Hub
- They can boost, relay, and clean the signals along with the network
- They don’t need power from the outside, as they have their own
- They serve each as a repeater and further as a wiring center.
- It helps to extend the maximum distance between them
ii) Passive Hub
- They collect wiring from the nodes.
- An active hub is the source of the power supply
- They do not help to extend the distance between nodes
iii) Intelligent Hub
- They provide flexible data to the system devices
- Help the controller to compose each port in the Hub and look into the traffic passing through the Hub
- They include remote management capabilities and work as an Active hub
3) Switch
- The switch is designed in such a way that it can boost its productivity.
- It is designed with a buffer.
- It is a multi-port bridge device.
- It forwards data, but before doing that, it checks errors. This makes it more efficient and improves its performance, as it only forwards the excellent and efficient packet to the correct port, which doesn’t have errors.
- It simply is a better version of a hub. As with a hub, with a switch also, the computer device is connected through one line, but the switch works smartly about where it sends the data that is coming through one of its ports.
4) Router
Data can be forwarded and filtered based on a logical address using a connective device called a Router. The IP address would be used in the case of TCP/IP networks. They play a major role in an extensive TCP/IP network. And in reality, TCP/IP routing protocols and network routers have helped the Internet to become as huge as it is today. They control traffic and keep the network productive.
5) Modem
- A Modem is somewhat of an additional attention-grabbing network device in our lifestyle. Thus if you have been noticed, you get an internet connection through a wire (different types of cables) to your house. This wire is employed to hold our internet data outside the internet world.
- However, binary data, in varieties of 0s and 1s, is generated by our computer. On the other hand, an analog signal is carried by a wire, and that’s where a modem comes in.
- A modem works as a Modulator and Demodulator both; that is, it modulates and demodulates the signal between the binary data or digital data of a computer and, therefore, the analog signal of a telephone line.
6) Repeater
- A device that, on receiving the signals, amplifies it is called a repeater. In other words, it can be said that a repeater is a device that, on receiving a signal, retransmits it at a higher level so that the signal can cover longer distances.
- For Example, within a university field, the hostels may be isolated from most school areas wherever the ISP line comes in. If the university authority desires to tug a wire between the hostels and the main field, they’ll need to use repeaters if space is more; thus, differing types of cables have limitations in terms of the distances they will carry the information.
- When these network devices take a selected configured form on a network, their configuration gets a chosen name, and this whole formation is termed Network topology. Ensure circumstances, once we add some additional network devices to a Network topology, it is known as Daisy chaining.
7) Gateway
- By the name only, we can get the meaning of it. It is a passage between the networks, connecting them so that this connection works upon completely different networking protocols. They primarily work as the middleman who takes information from a system, translates it, and then transfers it to another system.
- They are also protocol converters that may be operated at different networking layers. They are usually additionally complicated than switches and routers.
8) Access Point
While a wired or wireless link is technological in an AP, it usually means a wireless device. An AP operates on the second OSI layer, the data link layer, and can either act as a bridge that connects a standard wireless network to wireless devices or as a router that transmits data to another access point. Wireless connectivity points (WAPs) are a device used to generate a wireless LAN (WLAN) transmitter and receiver. Access points are usually separate networked machines with an integrated antenna, transmitter, and adapter.
In order to provide a link between WLAN and wired Ethernet Lan, APs are using wireless infrastructure network mode. They have several ports, which allow you to extend the network to support other customers. One or more APs may need to have full coverage, depending on the size of the network. APSAPs may also provide multiple ports that can be used to increase the network’s size, firewall capabilities, and DHCP. So, we’re getting switch-based APs, DHCP servers, firewalls, and routers.
Advantages of Networking Devices
- Working with them is seamless and superbly efficient because, whether working independently or working together, connectivity devices do a motivating job of handling your specific Internet requests simultaneously, with millions a lot of being handled each second around the world.
- So, wherever you’re and whatever computer you have been using, you can have confident networking hardware to bring the globe to your fingertips.
Conclusion
- However, having a solid understanding of the kinds of network devices accessible will help you style an engineered network that’s secure and serves your organization well.
- Thus, to confirm the continued security and availableness of your network, you must fastidiously monitor your devices and activity around them; ultimately, you’ll be able to spot hardware problems, configuration problems, and attacks quickly.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Networking Devices. Here we discuss the introduction and list of networking devices with advantages, respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –