Introduction to Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is outlined as a scientific investigation of phenomena by gathering quantitative information and activity applied mathematics, or procedure techniques.
Quantitative research is a research method where you gather and analyze numerical data to understand and explain various phenomena. The different types of quantitative research are survey, descriptive, experiential, correlational, and causal-comparative.
It focuses on using mathematical and statistical techniques to understand and investigate the subject. This is why the collected information must be in numerical form.
Different Types of Quantitative Research
The following are the different types of Quantitative research types with the description of each.
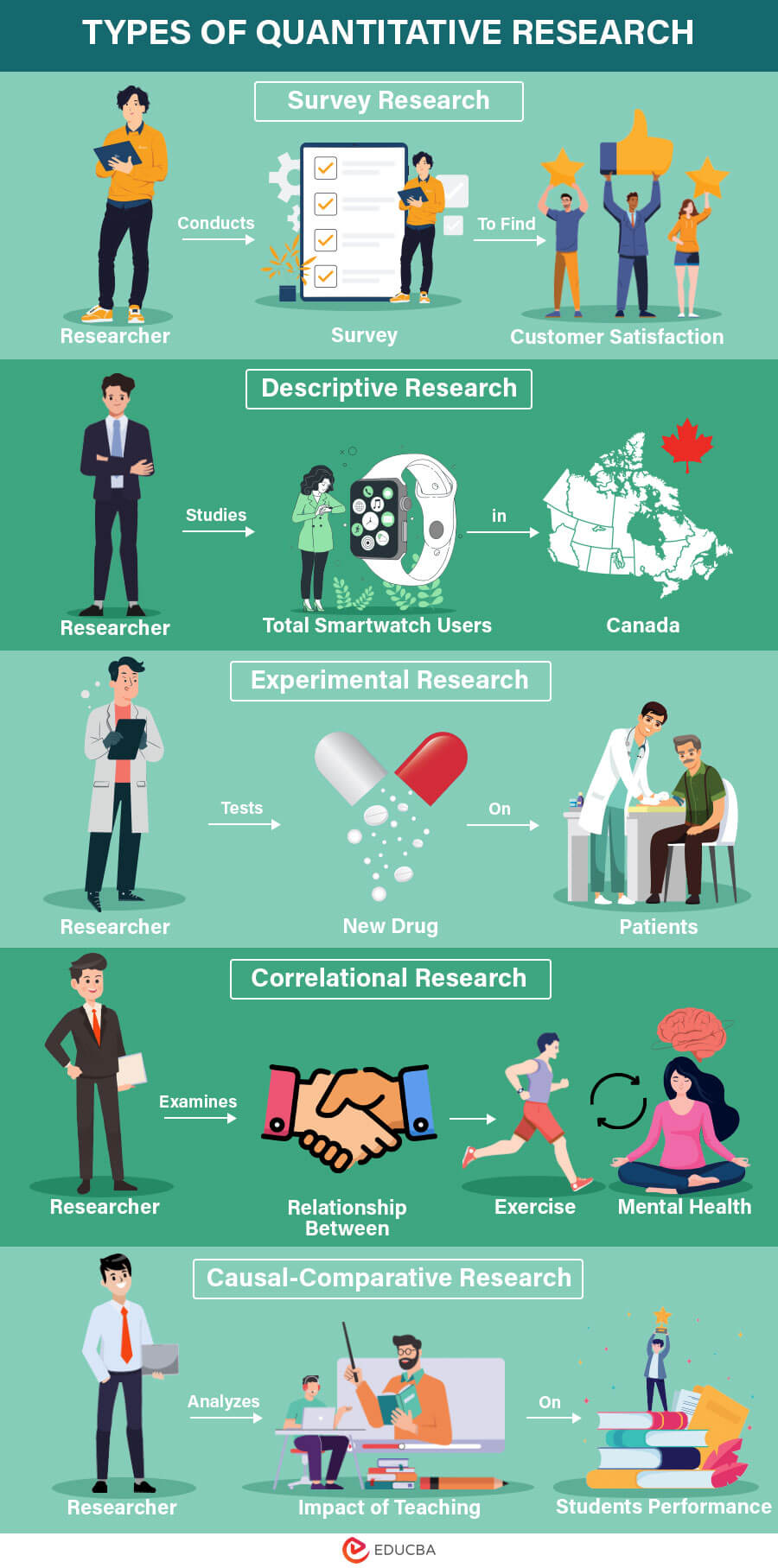
1. Survey Research
Survey Research is one of the most common types of quantitative research techniques. In this research method, you can use surveys to collect numerical data from a particular group or population. After that, you can analyze the data and explain the characteristics of the group. Both small and large organizations typically employ it for a proper understanding of their customers and to understand the merchandise and product views. It is of two types:
- Cross-sectional: In a cross-sectional survey, you collect information from a large group of people at a specific time. These are mostly useful in retail stores, education, etc.
- Longitudinal: In a longitudinal survey, you collect information from a small group of people over a long period of time, usually years. These are useful in medical trials and applied sciences.
In April 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a survey was conducted in Bangladesh to investigate sleep patterns. The researchers collected quantitative data like regular sleeping hours, age, nap durations, etc., from 9,730 participants. The results showed that age and exposure to COVID-19 had a negative effect on sleep.
2. Descriptive Research
Descriptive research aims to explain and understand the current state of things like people, places, conditions, or events. Here, the researcher’s goal is to gather general observational data without exploring the reasons behind them. Also, you don’t need to begin with a hypothesis; instead, you gather data first and then create a hypothesis if needed. Importantly, descriptive research doesn’t try to prove or disprove the hypothesis. It is mainly about creating a research hypothesis.
In September 2009, an EndoCost study was performed to find the cut-off period for diagnosis of endometriosis for the German population. The participants included 788 people who were previously diagnosed with endometriosis. The researcher analyzed data, including the time it took for individuals to report symptoms to a doctor and the time it took for a doctor to make the final diagnosis. The study concluded that a diagnosis within five years was crucial to managing the condition effectively. However, note that this is just a hypothesis.
3. Experimental Research
Experimental research, as the name suggests, uses the scientific method to establish the cause-effect relationship among a group of variables using experiments. Researchers can use multiple theories to conduct this research. The major components of experimental research are:
- A comparison group of participants who are randomly selected and assigned to experimental and control groups.
- An independent variable, referred to as the experimental variable that can be applied to the experimental group.
- A dependent variable, referred to as the effect or posttest variable that can be measured in an identical manner for all groups.
In 2022, Nicholas Epley, a behavioral scientist, conducted experimental research where he asked actors to perform random acts of kindness. Then, he asked both the actor and the receiver to fill out questionnaires to recognize the resulting patterns. It showed that people performing these random acts of kindness often underestimate how much recipients value their actions.
4. Correlational Research
Correlational research establishes a relationship between two close entities and determines how one impacts the other. For this, a researcher needs at least two separate groups. This type of research will recognize trends and patterns in data, but it does not go so far in its analysis to observe the different patterns.
In 2021, two researchers created a report based on correlation research studying how climate change affects mental health. They studied previous quantitative researches that compared an increase in climate temperature and citizen’s mental health. They found that climate change can both directly (PTSD, Anxiety, etc.) and indirectly (Sleep disorder, depression, etc.) affect mental health.
5. Casual-Comparative Research
Causal-comparative research is employed to conclude the cause-effect equation between two or more variables, where one variable depends on the opposite experimental variable. The experimenter does not manipulate the independent variable and then measures the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
From 2010 to 2019, health researchers performed causal-comparative research to see the effects of four different drugs on people with type 2 diabetes already using metformin. The experimenter gave the participants glimepiride, liraglutide, sitagliptin, or insulin glargine drug at different HbA1c levels. It was found that the drug liraglutide worked better than others in maintaining good blood sugar when HbA1c levels were above 7.0% or 7.5%.
Types of Quantitative Research Infographic
Here is a detailed infographic explaining the different types of quantitative research.
Characteristics
Here are the common characteristics of different types of quantitative research.
1. Numerical Data:
Quantitative research primarily deals with numerical data, which can be quantified and measured. Researchers use structured instruments like surveys, experiments, or observations to collect this data.
2. Large Sample Sizes:
Quantitative research typically involves large sample sizes to ensure statistical validity and generalize findings to a broader population. This allows for greater confidence in the results.
3. Statistical Analysis:
Statistical analysis plays a central role in quantitative research. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze and interpret the data, identify patterns and relationships, and draw conclusions. Common statistical techniques include regression analysis, correlation analysis, t-tests, ANOVA, and chi-squared tests.
4. Structured Research Design:
Quantitative research often employs a structured and pre-defined research design. Researchers develop hypotheses, select variables, and design experiments or surveys before data collection begins. This structured approach helps maintain consistency and rigor in the research process.
5. Generalizability:
Quantitative research often aims to generalize findings to a larger population. When conducted correctly, quantitative studies can provide insights that are applicable beyond the specific sample studied.
6. Closed-Ended Questions:
Surveys and questionnaires used in quantitative research often employ closed-ended questions with predetermined response options. This facilitates data analysis and allows for comparisons between participants.
Process
Here is a step-by-step process of performing different types of quantitative research.
Step 1: Clearly define your research problem or question.
Step 2: Conduct a literature review to identify relevant studies and theories related to your research topic.
Step 3: Develop specific hypotheses or research questions that you aim to answer through your research.
Step 4: Decide on the research design (e.g., experimental, cross-sectional, longitudinal) and your target population, and select a representative sample. Also, develop a data collection plan and choose appropriate data collection methods (e.g., surveys, experiments, observations).
Step 5: Choose valid and reliable measurement instruments (e.g., questionnaires, scales) to collect data. Make sure to test your measurement tools before actual research.
Step 6: Administer your selected data collection methods to your sample population.
Step 7: Select appropriate statistical techniques (e.g., descriptive statistics, inferential statistics) based on your research design and hypotheses. Analyze the data to test your hypotheses or answer your research questions.
Step 8: Interpret the statistical findings and summarize them to determine if they support or refute your hypothesis.
Step 9: Prepare a research report or paper that includes the research process, methodology, results, and conclusions to share your findings.
Uses
Following are some of the common uses of various types of quantitative research.
| Application | Description | Example |
| Market Research | Analyzing consumer preferences and trends | Conducting a survey to determine which smartphone brand is most popular among young adults. |
| Experimental Studies | Testing cause-and-effect relationships | Conducting a clinical trial to determine the efficacy of a new drug in treating a specific medical condition. |
| Data Analysis | Statistical analysis for decision-making | Analyzing sales data to identify the most profitable products for a retail company. |
| Performance Evaluation | Assessing the effectiveness of programs or products | Evaluating the impact of a training program on employee productivity in a corporate setting. |
| Trend Analysis | Identifying patterns and forecasting future trends | Using historical stock market data to predict future market trends and investment opportunities. |
| Risk Assessment | Quantifying potential risks and mitigations | Assessing the financial risk associated with a particular investment portfolio. |
| Health Studies | Studying disease prevalence and treatment outcomes | Investigating the relationship between smoking and lung cancer using patient data. |
| Education Research | Measuring student performance and learning outcomes | Analyzing standardized test scores to assess the effectiveness of a new teaching method. |
| Financial Analysis | Evaluating investment opportunities and risks | Calculating the return on investment (ROI) for a potential real estate investment. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Some of the key advantages and disadvantages of types of quantitative research are:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Quantitative research offers objectivity by relying on numerical data and reducing subjectivity. | Sampling issues, such as bias, can impact the reliability of findings. |
| It enables generalizability by collecting data from large, representative samples. | The approach may reduce validity by not capturing all aspects of a problem. |
| The structured approach allows other researchers to duplicate the study. | It lacks depth as it may oversimplify complex phenomena. |
| It is efficient for studying large populations or conducting surveys. | Large-scale projects can be costly and resource-intensive. |
Final Thoughts
Quantitative research is an effective method that helps us build statistically reliable insights across numerous fields. However, researchers should select the appropriate quantitative approach considering the limitations and benefits of each method. Moreover, new emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) can simplify data collection, analysis, and visualization of research outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the methods of data analysis in quantitative research?
Answer: Quantitative research uses different ways to analyze data. It uses descriptive stats, like averages and spreads, to summarize data. It also uses inferential statistics, like tests and regression, to check ideas and connections. For more complex situations, it uses multivariate methods like ANOVA and factor analysis to look at how different things interact. Researchers often use special software like SPSS or R to do these analyses.
Q2. How to interpret data in quantitative research?
Answer: Interpreting quantitative data involves looking at the statistical results and assessing the present relationships or trends. You must also discuss if the data is applicable in both theoretical and practical sense. It is also crucial to present results clearly with tables and graphs and think about any problems or biases in collecting data. When interpreting, stay objective and let the data guide you, avoiding making guesses or assumptions.
Q3. What is quantitative vs. qualitative research?
Answer: Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends. It relies on structured surveys, experiments, and statistical methods to draw objective conclusions. In contrast, qualitative research focuses on exploring the depth and meaning of phenomena through non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and open-ended questions. It aims to understand the underlying context and subjective experiences.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Quantitative Research. Here, we also discuss the introduction and different types of quantitative research, which include survey, descriptive, experimental research, etc. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –