Introduction to Transmission Media
The following article provides an outline for Types of Transmission Media. Transmission Media can be defined as a means to setup a communication pathway in order to convey the information between the sender and receiver in the form of electromagnetic signal waves. It is operated using various physical elements, and so it is placed underneath the physical layer while being worked on by the physical elements from the physical layer. The network that functions using the Transmission media is the Local Area Network (LAN), where the transmitter and the receiver are present. The material used for transmission is either copper-based or fibre-based to transmit electric or light signals, respectively.
Different Types of Transmission Media
The transmission phenomenon can be explained in layman terms as it is an objective conduit between two physical elements, namely the transmitter and the receiver. This trail lane is used for sending and receiving various signals, depending on the material used for connecting the transmitters and receivers, that is, the Transmission Media.
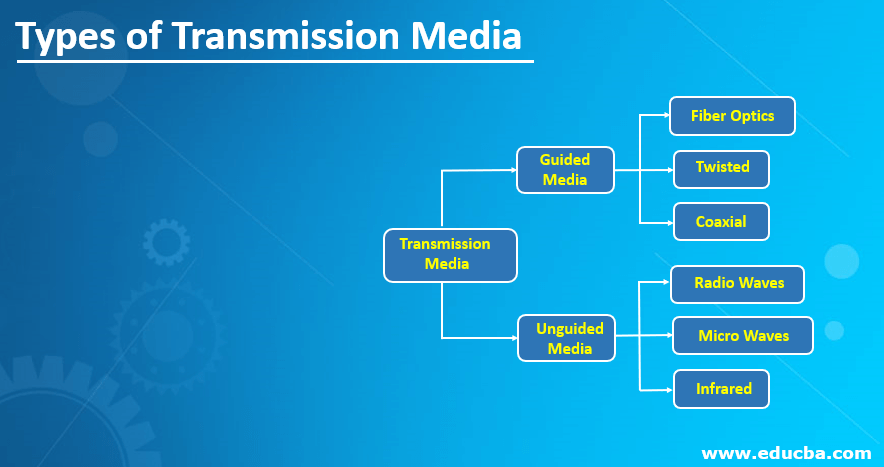
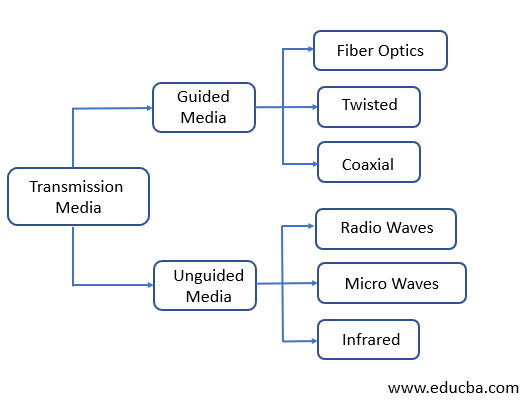
The Transmission Media are chiefly categorized as below, which can be further classified in accordance to the type and quality of the transmission.
- Guided Media
- Unguided Media
1. Guided Media
Guided Media is a type of transmission media that can be otherwise known as wired transmission. It is also termed as Bounded transmission media, as it is bound to a specific limit in the communication network. In this Guided Media, the transmission signals properties are restricted and focused in a fixed constricted channel, which can be implemented with the help of bodily wired contacts. One of the notable properties of the Guided Media is the velocity of transmission, which is observed to be at high speed. Other reasons that make the users choose guided media over unguided media are the security provided in transmission and the coverage of the network to be controlled inside a smaller geographical area.
The Guided Media transmission is further classified into three different types based on the type of connecting material used for creating the network.
They are as follows:
- Twisted Pair Cables
- Fibre Optics
- Coaxial Cables
a. Twisted Pair Cable: The Twisted Pair Cables can be defined as a cable formed by twisting two different shielded cables around each other to form a single cable. The shields are usually made of insulated materials that allow both the cables to transmit on their own. This twisted cable is then placed inside a protective layer around it for the sake of ease of use.
These Twisted pair cables are available in two different forms, where one is Shielded, and another is Unshielded.
- Shielded Twisted Pair Cable: Shielded cables are nothing but the transmission media that has exceptional casing to obstruct any or all the peripheral intrusions during the transmission process. These cables are known for their high performance that doesn’t allow signal crossings and faster transmission rates. A typical application of the Shielded Twisted Pair Cable is the telephone lines seen in domestic utilities. Like any other medium, shielded twisted pair cables have their own cons in them, which are the difficulty faced in installation, a huge volume of wires is required, and they are expensive than other cables.
- Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable: This type of cable doesn’t have the casing, as the name says, and has many qualities inversely proportional to the shielded cable type. These cables are a less expensive, effortless installation process, with faster transmitting abilities. It also lets outer interferences, which leads to lesser performance qualities.
b. Optical Fibre Cable: Optical Fibre Cables can be defined as the cables made of glass material, which uses the light signals for transmission purposes. The reflection principles are used for light signal transmission through the cables. It is known for letting bulky data to be transmitted with higher bandwidth and lesser electromagnetic interferences during transmission. Since the material is not corrosive in nature and it is weightless, these cables are preferred over twisted cables in most cases. A few of the disadvantages are the complications in maintenance or installation, expensive and the costs higher than other types of transmission media.
c. Coaxial Cable: Coaxial Cables are made of plastic layering on the outside and two conducting material placed in parallel to one another while being wrapped in individual insulating layers around them. It is used for transmitting data with dedicated cables or a single cable cracked into different bandwidths, and they are termed referred to as Baseband mode and Broadband mode, respectively. A well-known application of this type of cable is for providing television network in the houses. A few of the advantageous qualities of this type of cable are exceptional bandwidth range, simple installation or maintenance, and not as expensive as other cable types. Whereas the Coaxial Cable can form a single cable network, and if it fails, the network is disordered completely.
2. Unguided Media
As the name says, Unguided Media is not a guided media, which simply means that the network created using this type of transmission media cannot be bound to a certain physical plan. It can be defined as a wireless transmission media with no physical medium to provide the connection to the nodes or servers in the network. The electromagnetic signal waves are transmitted in the air across a larger geographical area, and so it is less secure than the guided media.
This type of transmission media is further classified into three types with respect to the signals used for the transmission.
a. Radio Waves: Radio waves are the simplest form of transmission signals, which doesn’t involve any complicated steps to create and transmit. This signal generally ranges between 3 KHz and 1 GHz of frequency, and the signal types can be of AM and FM signals. The main application of this transmission media is the cordless phones for domestic or official usage and the radio devices used as an element in mass media communication. These Radio waves can be of Terrestrial or Satellite method of communication.
b. Micro Waves: Micro Waves are the type of transmission media that uses antennas as the main element for sending and receiving the data. The area coverage provided by these signals directly related to the elevation of the antenna placement. The signal range for this type of transmission is between 1 GHz and 300 GHz, which are usually used for mobile phone and television networks.
c. Infrared: Infrared is another way of transmitting the data inside a small area, which cannot pass through the obstacles and doesn’t give –in for interference. These waves come in a range of 300 GHz to 400 THz and can be used for wireless peripheral devices like mouse, remotes, keyboards, printers, etc.
Conclusion
Transmission Media are the essential constituents to setup a flawless network, which can operate on its own without any glitches in sending and receiving the data across the network. Without a medium to transmit the contents inside a network, the network setup cannot be complete and cannot become a completely functioning system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Transmission Media. Here we discuss the introduction and different types of transmission media, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –