Introduction
Among the most widely used Linux distributions is Ubuntu. It offers two primary editions: Ubuntu Server and Ubuntu Desktop. Although the core foundation is the same for both editions, they tailor each for distinct purposes and user environments. Ubuntu Desktop provides a user-friendly graphical interface, while Ubuntu Server lacks one by default. Selecting the appropriate edition of Ubuntu is critical for achieving optimal performance and functionality.
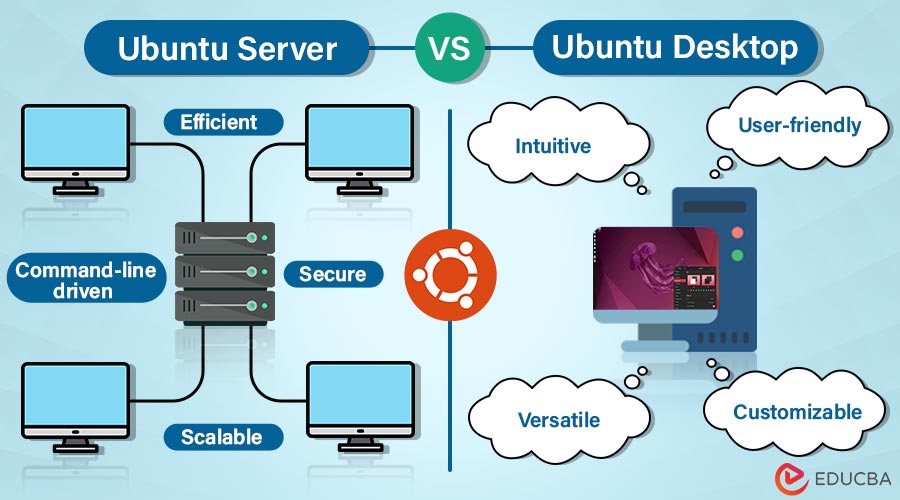
Table of Contents
Ubuntu Desktop
Overview of Ubuntu Desktop edition.
Ubuntu Desktop is the version of Ubuntu Linux specifically designed for personal computers, laptops, and workstations. It provides a comprehensive and user-friendly computing environment suitable for various tasks, including productivity, multimedia, web browsing, and development.
Features and functionalities for desktop users.
- User-friendly graphical interface (GNOME): Ubuntu Desktop has a modern and intuitive GUI, typically GNOME by default. GNOME offers a clean layout with a taskbar, menus, and windows for easy mouse and keyboard navigation.
- Default applications and software availability: Unlike Ubuntu Server, Ubuntu Desktop has various pre-loaded applications to meet your everyday needs. These applications include:
- Web browser: Firefox a default web browser, providing a secure and fast platform for web browsing and online activities.
- Office suite: LibreOffice is a powerful and feature-rich suite that allows creating, editing and saving documents, spreadsheets, and presentations in Microsoft Office file formats.
- Email client: Thunderbird, a popular email application, lets you manage your email accounts and stay connected.
- Multimedia players: VLC media player comes pre-installed and offers excellent support for playing a wide range of audio and video formats.
- Productivity tools: A calendar application, archive manager, note-taking application, and many other productivity tools are available to streamline your workflow.
- Hardware compatibility: Ubuntu Desktop boasts excellent hardware compatibility due to its large community and active development. Modern computer components work seamlessly with Ubuntu; additional drivers are readily available.
- Regular software updates and security patches: Ubuntu Desktop receives punctual software updates and patches, ensuring you have up-to-date features, bug fixes, and protection against vulnerabilities.
User-friendly graphical interface (GNOME).
- Personal Use: Ubuntu Desktop is an excellent choice for individuals seeking a stable, secure, and user-friendly operating system for personal computing tasks such as web browsing, email, document editing, multimedia consumption, and casual gaming.
- Office Work: Ubuntu Desktop provides a reliable platform for office productivity tasks, including creating documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and managing emails. Its compatibility with Microsoft Office file formats through LibreOffice ensures seamless collaboration in office environments.
- Development: Software developers and programmers widely favor Ubuntu Desktop due to its robust development tools., extensive software repositories, and compatibility with popular programming languages
- Multimedia Production: Ubuntu Desktop supports multimedia creation and editing with applications like GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) for graphic design, Audacity for audio editing, and OpenShot or Kdenlive for video editing.
Below is the image of how Ubuntu Desktop looks like (GUI format)
Ubuntu Server
Overview of Ubuntu Server edition.
Ubuntu Server is a variant of Ubuntu Linux specifically tailored for server environments. It offers a dependable and scalable platform for hosting services, managing infrastructure, and deploying applications in data centers, cloud environments, and enterprise settings.
Purpose-built for server environments.
Unlike Ubuntu Desktop’s focus on user interaction, Ubuntu Server prioritizes efficiency and stability for running server applications.
- Purpose-Built for Server Environments: Ubuntu Server focuses on server deployments’ stability, security, and performance. It offers features and optimizations optimized for running server workloads efficiently.
- Minimal Installation Footprint: Ubuntu Server adopts a minimal installation footprint, including only essential components and dependencies required for server operations. This streamlined approach ensures efficient resource utilization and reduces unnecessary overhead.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI) by Default: Unlike Ubuntu Desktop, which features a graphical interface, Ubuntu Server primarily utilizes a command-line interface (CLI). It enables administrators to perform system configuration, management tasks, and automation efficiently through the terminal.
- Lack of Graphical Interface for Optimized Resource Usage: Ubuntu Server minimizes resource consumption by omitting a graphical interface, making more system resources available for running server applications and services. This approach enhances performance, reliability, and security in server environments.
This is how Ubuntu Server looks like (without GUI)
Package Selection and Server-Specific Tools
Ubuntu Server includes a curated selection of packages and tools tailored for server deployments, such as:
- Web Servers: Apache HTTP Server, Nginx
- Database Servers: MySQL, PostgreSQL
- Cloud Infrastructure: OpenStack, Kubernetes
- Containerization: Docker, Podman
- Monitoring and Management: systemd, SNMP, Nagios, Zabbix
- Security: SSH, iptables, SELinux, AppArmor
Additionally, Ubuntu Server provides access to a vast repository of server-specific software packages and tools, allowing administrators to customize and extend the server’s functionality as needed.
Use Cases and Target Audience:
- Web Servers: Ubuntu Server is well-suited for hosting websites, web applications, and web services. Its robust performance, security features, and support for popular web server software make it a preferred choice for web hosting providers and developers.
- Database Servers: People commonly use Ubuntu Server to deploy and manage database servers, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc. Its stability, scalability, and compatibility with database management systems make it an ideal database administration and development platform.
- Cloud Deployments: Ubuntu Server is widely adopted in cloud computing environments, including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Its support for cloud orchestration tools like OpenStack and Kubernetes and reliability and scalability make it suitable for building and managing cloud infrastructure.
- Enterprise Applications: Ubuntu Server is utilized in enterprise environments to run mission-critical applications, manage enterprise databases, and support business operations. Its stability, security updates, and long-term support (LTS) releases cater to the needs of enterprise IT infrastructure.
Performance and Resource Utilization
Resource Usage:
- CPU:
- Ubuntu Desktop’s graphical interface consumes significant CPU resources for rendering visuals and animations.
- Ubuntu Server, lacking a GUI, dedicates CPU power primarily to server tasks, leading to potentially better performance under heavy workloads.
- Memory (RAM):
- Ubuntu Desktop requires more RAM to run the GUI and various pre-installed applications smoothly. Ubuntu recommends a minimum of 4GB RAM, but we suggest 8GB or more for a comfortable experience.
- Ubuntu Server has a much lower memory footprint due to its minimal installation. The base system can run on as low as 512MB of RAM, although the requirement depends on your installed server applications.
- Disk Usage:
- Ubuntu Desktop comes pre-loaded with various applications, resulting in a larger installation size than Ubuntu Server’s minimal footprint.
- However, disk usage on both systems depends heavily on the additional software you install.
Impact on System Performance
- Workload: Ubuntu Desktop optimizes desktop computing tasks such as web browsing, document editing, multimedia playback, and gaming. It provides a rich user experience but may consume more system resources. Ubuntu Server, designed for server workloads, prioritizes efficiency and scalability, ensuring optimal server application and service performance.
- Hardware Configuration: The Hardware specifications, including CPU, memory, storage, and network connectivity, can influence the performance of Ubuntu Desktop and Server. High-performance hardware can mitigate resource constraints and enhance both editions’ overall performance.
- Environmental Conditions: System load, concurrent tasks, network traffic, and environmental temperature can affect system performance. Proper system monitoring, tuning, and optimization practices can help mitigate performance bottlenecks.
Security
Security Features and Considerations.
- Regular Security Updates:
Ubuntu Desktop and Server benefit from Ubuntu’s regular security patch release cycle. These updates address vulnerabilities in the core system and installed packages, ensuring your system stays protected against known threats.
- Package Management System: Ubuntu’s APT (Advanced Package Tool) package management system simplifies software installation and updates. It also verifies software packages for authenticity and integrity, mitigating the risk of malware installation.
Vulnerability management and patching.
- Automatic Updates: Both editions offer the option to enable automatic updates for security patches. It ensures your system receives the latest security fixes promptly.
- Security Audits: Regularly running security audits using tools like Lynis or OpenVAS can identify potential security weaknesses in your system configuration.
- Manual Patching: For advanced users, manually checking for and applying security patches through the terminal provides granular control over the update process.
Default firewall settings
- Ubuntu Desktop: Ubuntu Desktop has a basic firewall by default, using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). This firewall is less robust than those typically used on servers but can provide some protection against unauthorized network access.
- Ubuntu Server: Ubuntu Server typically ships without a firewall pre-configured. It allows administrators to customize firewall rules based on the specific server’s needs.
Best practices for securing Ubuntu Desktop and Server installations.
- Strong Passwords: Use a solid and unique password for all user accounts.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Identify and disable any system services or applications you don’t use. It minimizes the attack surface and potential vulnerabilities.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Assign users the minimum privileges necessary to perform their tasks. It limits the damage caused by compromised accounts.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure you have automatic updates enabled for both the operating system and installed software to receive the latest security patches promptly.
- Regular Backups: It allows you to recover your data in case of a security incident. Make regular backups of your important data in a safe place.
Software Management
| Feature | Ubuntu Desktop | Ubuntu Server |
| Pre-installed Applications | Variety of applications for everyday use | Minimal software |
| Default Repositories | “main” and “universe” | “main”, “universe”, and server-specific repositories |
| Package Management Tools | Graphical (Ubuntu Software Center) | Command-line (APT) |
| Software Availability | More comprehensive range, including desktop applications | Server-specific software |
| Update Management | Automatic or manual | Automatic or manual |
| Upgrade Process | Easier, potentially graphical | More manual configuration might be required |
Community and Support
The Ubuntu community is renowned for its size, welcoming nature, and dedication to helping users of all experience levels.
Overview of the Ubuntu community and support resources.
- Forums: The official Ubuntu Forums (ubuntu-support-community-support) is a vibrant platform for users to ask questions, share solutions, and engage in discussions. Here, you can find dedicated forums for Desktop and Server users, allowing you to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Documentation: Ubuntu boasts extensive and well-maintained documentation covering various topics. The official Ubuntu Documentation Center (help.ubuntu) provides detailed guides, tutorials, and explanations for installing, configuring, and troubleshooting Ubuntu.
- Community-driven Help Channels: Several community-driven platforms offer support for Ubuntu users. Stack Exchange, a network of question-and-answer communities, has a dedicated section for Ubuntu (askubuntu), In which individuals can ask any inquiry and get assistance from experienced users and developers.
- Official Support Options: While Ubuntu is a free and open-source operating system, official support options are available for those requiring more comprehensive assistance. Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, offers various commercial support plans for Desktop and Server editions. These plans typically involve guaranteed response times, access to dedicated support engineers, and extended security updates.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability in both Desktop and Server environments.
- Ubuntu Desktop: Although massive scalability is not inherent to Ubuntu Desktop, you can achieve a certain extent of scalability by upgrading hardware components such as CPU, memory, and storage.
- On the other hand, Ubuntu Server is built with scalability in mind and excels at handling increased workloads and user demands. You can achieve this scalability in several ways:
- Horizontal Scaling (Adding More Machines): Scaling horizontally involves adding more server machines to distribute the workload. It is ideal for web servers handling increased traffic or database servers managing growing data volumes.
- Vertical Scaling (Upgrading Hardware): Similar to Desktop, you can upgrade hardware resources (CPU, memory) on existing server machines to handle heavier workloads.
- Virtualization: Leveraging virtualization software like KVM or LXD allows you to run multiple VMs (virtual machines) on a single physical server. It virtualizes resources and enables efficient utilization of hardware for various server applications.
Ability to scale resources based on workload demands.
- Ubuntu Desktop: There is a limited ability to adapt to significant workload increases. Adding hardware can help, but it’s not as efficient or cost-effective as scaling on Ubuntu Server.
- Ubuntu Server: Offers the flexibility to scale resources by adding more machines, upgrading hardware, or utilizing virtualization. It allows you to dynamically adjust resources based on fluctuating workloads.
Ease of deployment and management in large-scale environments.
- Ubuntu Desktop: Deployment and managing multiple Desktops can be cumbersome and time-consuming, especially in large organizations.
- Ubuntu Server: Server deployment and management tools like Ansible or Puppet can automate configuration and software installation on multiple servers, simplifying large-scale deployments and ongoing server management.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct Ubuntu version depends on understanding your primary computing needs. Are you looking for a user-friendly operating system for everyday tasks on your computer? Or do you need a robust and secure platform to host websites, manage databases, or run other server applications? Ubuntu offers two distinct flavors, Desktop and Server, each catering to specific requirements. By understanding the strengths and functionalities of each edition, you can make an informed decision and choose the Ubuntu that best suits your project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can I use Ubuntu Desktop as a server?
Answer: While it’s technically possible to use Ubuntu Desktop as a server by installing server-oriented software and configuring it accordingly, Experts recommend using Ubuntu Server for server deployments because of its minimal installation footprint, optimized resource usage, and built-in server features.
Q2. How often are security updates released for Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Servers?
Answer: Ubuntu follows a predictable release cycle with a new Long Term Support (LTS) version every two years in April. These LTS versions receive security updates for five years.
Q3. Based on workload demands, can I scale resources in Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Server?
Answer: Individual users can upgrade Ubuntu Desktop with additional hardware resources to improve performance. Ubuntu Server provides built-in scalability features and resource management capabilities for dynamic scaling based on workload demands in server environments.
Q4. Can I run graphical applications on the Ubuntu Server?
Answer: While Ubuntu Server does not include a graphical desktop environment by default, it’s possible to install and run graphical applications on Ubuntu Server by installing the necessary components and configuring remote desktop or X11 forwarding.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Ubuntu Server vs Ubuntu Desktop” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,