Introduction
Ubuntu Unity, a contemporary desktop environment, is renowned for its efficiency and elegance. Developed by Canonical, it became the default interface for Ubuntu in 2011. Its intuitive design sets Unity apart, featuring a unique sidebar, a Launcher, a searchable Dash, and a top panel for global menus. It’s designed to be user-friendly, catering to newcomers and experienced users with its keyboard shortcuts and mouse navigation. Despite being replaced by GNOME in later Ubuntu versions, Unity remains popular and continues to be developed by the community, offering a distinctive, productive, and customizable experience for Linux users.
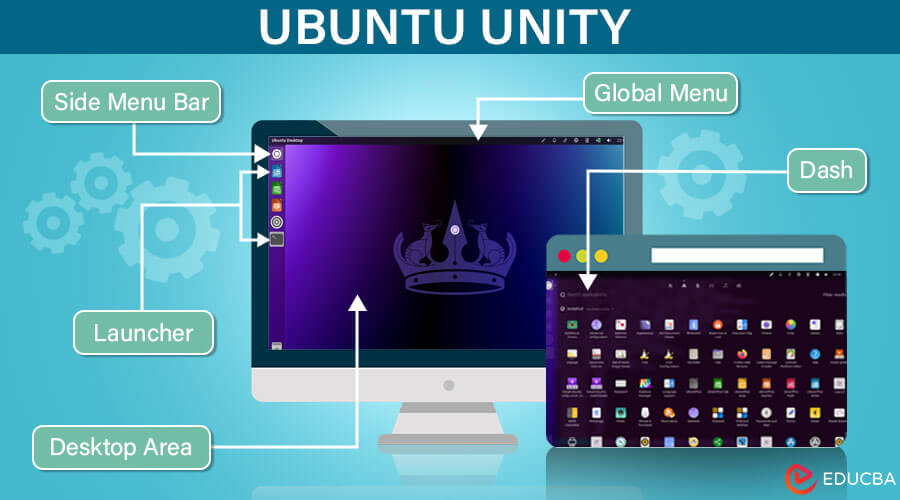
Table of Contents
What is Ubuntu Unity?
Ubuntu Unity is a desktop environment developed by Canonical Ltd. for the Ubuntu operating system. It provides a unique user interface with design elements and features that enhance usability and productivity.
Key features and characteristics
- Side Menu Bar: A multipurpose bar that includes the menu of the active application, window controls, session menu, and system notifications.
- Launcher: A sidebar that allows users to pin their favorite applications and see open applications.
- Dash: A search utility that enables users to search for local and online information.
- HUD: (Heads-Up Display) and Global Menu: Features that enhance productivity by allowing users to search through and execute menu commands without navigating the menus.
Comparison with other Ubuntu desktop environments
| Feature | Ubuntu Unity (Unity 7) | GNOME | KDE Plasma |
| User Interface | Streamlined, focused | Modern, activity-based | Highly customizable |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive | Extensive |
| Focus | Usability, beginners | Activities, workflows | Power users, features |
| Integration with Ubuntu | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
History of Ubuntu Unity
Origins of Ubuntu Unity
Unity originated as a project by Canonical Ltd., the company behind Ubuntu, to create a modern, user-friendly desktop environment. Ubuntu introduced it as the default desktop environment with the release of Ubuntu 11.04 (Natty Narwhal) in April 2011.
Evolution over different Ubuntu releases
- Ubuntu 17.04: April 2017 saw the release of the GNOME 3 desktop, but Ubuntu users or developers didn’t universally accept it.
- Unity 8 Fork: Several forks were proposed, with UBports taking over Unity 8 development and renaming it Lomiri in February 2020.
- Unity 7 Ubuntu Remix: In 2019, Canonical approved using trademarks for a Unity 7 Ubuntu remix.
- Ubuntu Unity: Rudra B. Saraswat, a Linux Foundation Certified Developer and Ubuntu team member, started Ubuntu Unity. He conducted user surveys and used the Unity 7 stock UI with minimal changes, including Nemo File Manager as a GNOME Files substitute and the GNOME Display Manager to replace the LightDM X display manager.
- Official Ubuntu Flavour: In 2022, Ubuntu Unity became an official Ubuntu flavor, starting with the 22.10 release 6.
- Unity Desktop Version: Ubuntu Unity 22.10 should feature Unity desktop version 7.6, the latest version.
- Software Center: Instead of the Software Center, Ubuntu Unity uses the excellent Synaptic for installing and uninstalling packages.
Design and User Interface
Overview of the Unity desktop layout
The designers of Ubuntu Unity focused on efficiency and elegance by centering the layout around the Launcher, a vertical bar on the left side of the screen that houses icons for frequently used applications and system indicators. At the top of the screen is the Panel, which displays the global menu and system status area. The Dash is a full-screen overlay that provides quick access to applications, files, and other content.
Key Elements:
- Dash: The Dash is a central feature of the Unity interface, serving as a unified search and application launcher tool. It provides quick access to applications, files, folders, and system settings through a searchable interface.
- Launcher: The Launcher is a vertical bar on the screen’s left side. It contains icons for frequently used applications and shortcuts to files, folders, and devices. Users can customize the Launcher by pinning their favorite applications and rearranging icons according to their preferences.
- Panel: The Panel, also known as the top bar, is situated at the top of the screen and houses system indicators, such as the system clock, network status, volume control, and notifications. It also includes menus for accessing system settings, application menus, and the Ubuntu Dash.
Customization options and settings
- Themes and Icons: Unity supports changing themes and icon sets for a personalized look.
- CompizConfig Settings Manager (CCSM): For advanced users, CCSM provides in-depth customization options for Unity’s visual effects and behavior.
- Unity Tweak Tool: Users can install the Unity Tweak Tool for advanced customization options. This third-party utility provides additional settings and options for fine-tuning the Unity desktop environment.
Advantages of Ubuntu Unity
- User-Friendly Interface for Beginners: It is renowned for its user-friendly interface, making it an excellent option for beginners and users transitioning from other operating systems. The design is intuitive, and features are easy to navigate, making the user feel at home., even if they are new to the Linux environment.
- Integration with the Ubuntu Ecosystem: Unity seamlessly integrates with the broader Ubuntu ecosystem, ensuring compatibility and cohesion across Ubuntu software and services. As Ubuntu’s default desktop environment, its core applications, system utilities, and development tools work seamlessly with Unity, which is optimized for them.
- Efficiency and Performance: Unity is designed with efficiency and performance in mind, prioritizing responsiveness and resource optimization for a responsive and smooth user experience. Its efficient utilization of system resources ensures faster boot times, snappier application launches, and smoother multitasking due to its lightweight design and streamlined workflows. This emphasis on performance is a key factor in Unity’s popularity and continued use by the Linux community.
Disadvantages and Criticisms
- Lack of Customization Compared to Other Desktop Environments: One common criticism of Ubuntu Unity is its relatively limited customization options compared to desktop environments like KDE Plasma or Xfce. While Unity offers some customization, such as adjusting the Launcher behavior and appearance or changing themes, it may provide a different level of flexibility and fine-grained control than more customizable desktop environments.
- Changes in Design Philosophy Over Time: Over its development history, Ubuntu Unity has undergone significant changes in design philosophy and direction, leading to mixed reactions from users and the Linux community. For example, the introduction of Unity with Ubuntu 11.04 represented a departure from the traditional GNOME desktop environment, which sparked debates and divided user opinions.
- Community Reactions and Feedback: Canonical’s decision to abandon Unity development in 2017 disappointed some users who felt the desktop still had potential. It led to the formation of the Ubuntu Unity community, showcasing the dedication of a user base that valued the Unity experience.
- Limited App Availability: While compatible with most Ubuntu software, some niche applications or those designed for other desktop environments require additional configuration or may not function perfectly.
- Potential Learning Curve for New Features: While the core layout remains familiar, users new to Unity 7 might need time to adjust to features like the Dash and HUD.
Ubuntu Unity in the Linux Community
Popularity and Adoption:
- Initial Success: Following its introduction in 2010, Unity became the default desktop for Ubuntu, achieving significant popularity. Its user-friendly design attracted many new Linux users.
- Shifting Landscape: The decision to switch back to GNOME in 2017 undoubtedly impacted Unity’s official adoption rate. However, a dedicated user base continues to utilize and advocate for Ubuntu Unity.
Support and development status
- Community-Driven: Following Canonical’s official discontinuation, the Ubuntu Unity community stepped in to maintain and develop the desktop environment. This passionate group ensures ongoing bug fixes, compatibility updates, and new features.
- Active Development: The Ubuntu Unity project is actively maintained, with regular releases based on the latest Ubuntu LTS (Long Term Support) versions. It ensures stability and security for users.
User testimonials and reviews
- Positive Feedback: Many users praise Ubuntu Unity’s simplicity, efficiency, and tight integration with the Ubuntu ecosystem. Newcomers to Linux often find it approachable and intuitive.
- Nostalgia Factor: For users who experienced Ubuntu with Unity in its prime, It offers a familiar and comfortable desktop environment, sparking a sense of nostalgia.
Unity vs. GNOME
| Feature | Ubuntu Unity | GNOME |
| Status | Discontinued (Last release in 2017) | Actively developed |
| Look & Feel | Focus on the launcher and global menu bar (similar to Windows) | Focus on activities overview and minimalist design |
| Navigation | Applications launched from the Launcher and search bar | Applications accessed from Activities Overview |
| Window Management | Applications tend to open maximized | More flexible window management options |
| Customization | Limited built-in customization | Extensive customization through extensions |
| Performance | Generally considered less resource-intensive | It can be resource-intensive depending on the extensions |
| Default Applications | Included Thunderbird for email | Uses different defaults (e.g., Evolution) |
| Development | No longer officially supported | Actively developed with frequent updates |
Using Ubuntu Unity
Installation process
- Download Ubuntu Unity: Visit the official Ubuntu Unity website or explore community-supported distributions that feature Unity7.
- Create a Bootable USB Drive: Utilize Rufus to create a bootable drive (for Windows) or Etcher (for Linux and macOS) to make a USB disk.
- Boot from USB: When your computer restarts, use the USB drive to boot up.
- Install Ubuntu Unity:
- Choose your language, keyboard layout, and other preferences.
- Please select the option to install Ubuntu or replace it with your existing OS.
- Follow the installation wizard, create a user account, and set up your system.
- Reboot: Once the installation is complete, reboot your system.
Getting started with basic tasks
- Launching Applications: Click the Ubuntu logo on the left-hand Launcher. It opens the Dash, a full-screen application and file launcher.
- Finding Files and Folders: Use the search bar in the top Panel or access your home folder from the Launcher.
- System Settings: Access system settings, user accounts, and network configurations from the menu in the top panel.
Tips and tricks for maximizing productivity
- Master the Keyboard Shortcuts: Learn keyboard shortcuts for frequently used actions like launching applications, searching, and opening the Dash. It can significantly boost your workflow.
- Organize the Launcher: Drag and drop icons in the Launcher to arrange them for quick access to your most used applications.
- Unity Tweak Tool: Install the Unity Tweak Tool from the Ubuntu Software Center to access additional customization options and settings for tweaking the Unity desktop environment.
Future of Ubuntu Unity
Ubuntu’s commitment to Unity development
Unity no longer serves as the default desktop environment for Ubuntu releases. Canonical continues to maintain and provide updates for Unity in the Ubuntu repositories. This commitment ensures that existing Unity users can still receive support and updates for the foreseeable future, even as the focus shifts towards GNOME and other projects.
Potential improvements and updates
- Community-Driven Enhancements: The Ubuntu Unity community remains active, providing ongoing bug fixes and compatibility updates. Based on user feedback and advancements, they might even introduce new features.
- Leveraging New Technologies: The community could integrate new technologies, such as advanced window management tools or customization options, to keep pace with evolving desktop environments.
Conclusion
Ubuntu Unity’s elegant blend of aesthetics and functionality continues as a compelling choice for users seeking a user-friendly Linux experience. While it may not be the default desktop environment in recent Ubuntu releases, its legacy lives on. Unity7’s commitment to efficiency, integration, and stability ensures that it remains a valuable option for those who appreciate its unique workflow. As the community actively contributes and Canonical maintains support, Ubuntu Unity is a testament to the diverse landscape of Linux desktop environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Ubuntu Unity suitable for beginners?
Answer: Yes, Ubuntu Unity is renowned for its easy-to-use interface, making it an excellent option for new users and users transitioning from other operating systems. Its intuitive design and centralized features simplify navigation and accessibility for new users.
Q2. What is the future of Ubuntu Unity?
Answer: While Unity is no longer the default desktop environment for Ubuntu releases, Canonical’s commitment to supporting and maintaining Unity ensures that it remains as a viable choice for users who appreciate its features and design philosophy. Additionally, the Ubuntu community contributes to Unity’s development and Evolution.
Q3. Are there alternatives to Ubuntu Unity?
Answer: Yes, alternative desktop environments are available for Ubuntu, such as GNOME, KDE Plasma, Xfce, and LXQt. Users can choose the desktop environment that best suits their preferences and workflow requirements.
Q4. Is Unity compatible with older hardware?
Answer: Unity is a portable and practical tool, which makes it an excellent choice for older hardware configurations. Even if your computer is a little older, you can still enjoy all of Unity’s benefits without having to worry about performance issues. However, performance may vary depending on your hardware specifications and your Ubuntu version.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Ubuntu Unity” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,

