Updated March 6, 2023
Difference Between Ubuntu and Fedora
Ubuntu is a Linux-based operating system. It is created for computers, smartphones, and network servers. The system is developed by a UK based organization called Canonical Ltd. All the principles applied to develop the Ubuntu software are based on the principles of Open Source software development. Fedora is a Linux distribution created by the community-supported Fedora Project and sponsored by Red Hat. Fedora comprises software distributed under several free and open-source licenses and targets to be on the leading edge of such technologies. Fedora is the upstream source of the economic Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution.
What is Ubuntu?
Ubuntu is offered in three official releases: Ubuntu Desktop for personal computers, Ubuntu Server for servers including the cloud, and Ubuntu Core for the Internet of things devices plus robots. The latest releases of Ubuntu occur every six months, while long-term support (LTS) releases happen every two years.
Ubuntu is designed by Canonical and the community in a meritocratic governance model. Canonical gives free guaranteed security updates and support for all Ubuntu release, beginning from the release date and until the release reaches its predesignated end-of-life (EOL) date. Canonical produces income through the sale of premium services associated with Ubuntu. Ubuntu is the most popular operating system for the cloud; moreover is the reference operating system for OpenStack. The significant features of Ubuntu are, The desktop version of Ubuntu supports all the normal software on Windows such as Firefox, Chrome, VLC, etc. Also, It supports the office suite called LibreOffice.Moreover, Ubuntu has an inbuilt email software called Thunderbird, which provides the user access to email such as Exchange, Gmail, Hotmail, etc.
What is Fedora?
The release of Fedora 21, three separate editions are currently available: Workstation, focused on the personal computer, Server for servers, and Atomic focused on cloud computing. As of February 2016, Fedora has an assessed 1.2 million users, including Linus Torvalds, creator of the Linux kernel.
Fedora has a reputation for focusing on innovation, integrating the latest technologies beginning on and working intimately with upstream Linux communities. Making changes upstream instead of especially for Fedora assures that the modifications are available to every Linux distributions. The default desktop background in Fedora is GNOME, and the default user interface is the GNOME Shell. Different desktop environments, including KDE Plasma, Xfce, LXDE, MATE, and Cinnamon, are available and can be installed. In October 2018, Red Hat announced that KDE Plasma was no longer supported in Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Fedora’s forthcoming updates.
Head To Head Comparison Between Ubuntu and Fedora (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Ubuntu vs Fedora:
Key Differences Between Ubuntu and Fedora
Both are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major difference :
- Ubuntu is the most common Linux distribution; Fedora is the fourth most popular. Fedora is based on Red Hat Linux, whereas Ubuntu is based on Debian.
- Software binaries for Ubuntu vs Fedora distributions are incompatible. Both Ubuntu vs Fedora distributions release the latest version every 6 months, but there’s a contrast in their long-term support models — Ubuntu gives support for 18 months later a version is issued and also releases LTS (or Long Term Support) versions every two years that are supported for 5 years. Fedora, on the other hand, offers a shorter support span of only 13 months. This supports leading-edge software because it frees Fedora developers from some backward compatibility restraints; however, it also makes Fedora a poor product development option (e.g., embedded systems) or web servers. There are other contrasts among Ubuntu vs Fedora, such as bundled apps, the desktop environment, and the distribution size.
- Fedora gives the GNOME desktop, whereas Ubuntu relies on Unity. Both share some things, yet for the most part, they’re quite different user experiences.
- The significant contrast here is that the original Red Hat Linux originally divided into Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, while Debian is still a whole, separate entity from Ubuntu, which carries packages from one of Debian’s branches.
- Both Ubuntu vs Fedora offer spins. For instance, you can get Fedora with KDE or Ubuntu with KDE. Things differ, yet Fedora mainly embraces separate desktop environments, similar to KDE, while Ubuntu moves these projects to others to manage.
Ubuntu vs Fedora Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison among Ubuntu vs Fedora:
| The basis of comparison |
Ubuntu |
Fedora |
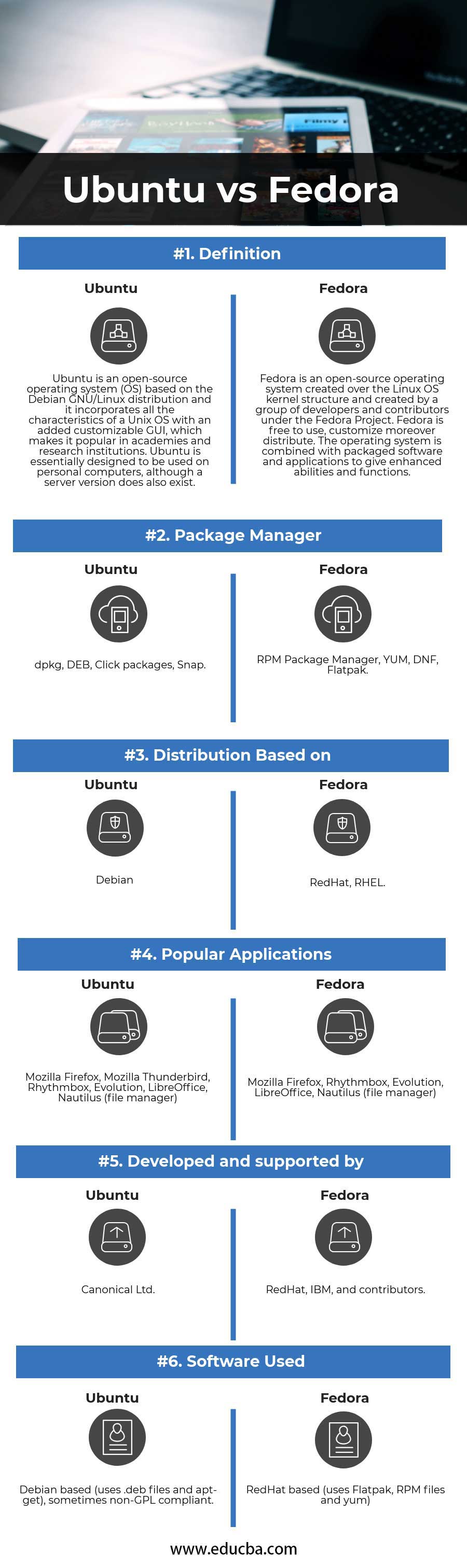
| Definition | Ubuntu is an open-source operating system (OS) based on the Debian GNU/Linux distribution, and it incorporates all the characteristics of a Unix OS with an added customizable GUI, which makes it popular in academies and research institutions. Ubuntu is essentially designed to be used on personal computers, although a server version does also exist. | Fedora is an open-source operating system created over the Linux OS kernel structure and created by a group of developers and contributors under the Fedora Project. Fedora is free to use, customize moreover distribute. The operating system is combined with packaged software and applications to give enhanced abilities and functions. |
| Package manager | dpkg, DEB, Click packages, Snap | RPM Package Manager, YUM, DNF, Flatpak |
| Distribution Based on | Debian | RedHat, RHEL |
| Popular Applications | Mozilla Firefox, Mozilla Thunderbird, Rhythmbox, Evolution, LibreOffice, Nautilus (file manager) | Mozilla Firefox, Rhythmbox, Evolution, LibreOffice, Nautilus (file manager) |
| Developed and supported by | Canonical Ltd. | RedHat, IBM, and contributors |
| Software used | Debian based (uses .deb files and apt-get), sometimes non-GPL compliant | RedHat based (uses Flatpak, RPM files and yum) |
Conclusion
In short, Both Ubuntu vs Fedora perform excellent desktop distributions. Their use cases also ecosystems are moderately different, though. Ubuntu comes from the Debian family, and it’s the initial operating system developed by Canonical. Ubuntu’s varied announcement cycle makes it slightly of a jack of all trades, and it can fit approximately any use case. Fedora is Redhat’s testbed, and it’s an excellent option for developers and administrators working with Redhat systems. It has a much thinner ecosystem furthermore would feel out of place on anything yet a desktop either workstation.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to the highest distinction among Ubuntu vs Fedora. Here we additionally consider the Ubuntu vs Fedora key differentiation by infographics and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –