Updated July 26, 2023
Introduction to Unadjusted Trial Balance
An unadjusted trial balance is a list of all the general ledger balances without making any adjustment entries. It serves as a foundation for adjusting entries and analyzing financial statements. It helps to confirm that all debits are equal to credits and identify any errors. All the accrual adjustments are made to get an adjusted trial balance.
Format of Trial Balance
The unadjusted trial balance consists of three columns: the first column includes account names, the second column represents debits, and the third column represents credits. The accounts are generally listed following the balance sheet order, with assets and liabilities before income and expenses. Assets and expenses are recorded on the debit side, while liabilities and incomes are recorded on the credit side.
Steps to Prepare an Unadjusted Trial Balance
- Balances from all the ledger accounts are taken, and the trial balance format is to be prepared.
- Enlist the accounts and write the balances in respective debit and credit columns.
- Calculate the total balance of the debit and credit side
- If the total of both sides is the same, the trial balance is mathematically correct. If the same is not tallied, look for errors and reasons and correct the same.
Example of Unadjusted Trial Balance
Examples of Unadjusted Trial Balances are as follows:
Example #1
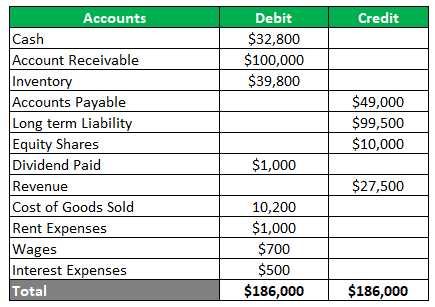
A company trading in metals wants to prepare a trial balance from the below ledger balances- Cash $32,800, account receivable $100,000, inventory $39,800, accounts payable $49,000, long-term liability $99,500, equity shares $10,000, the dividend paid $1,000, revenue $27,500, cost of goods sold $10,200, rent expenses $1,000, Wages $700 and interest expenses $500. Also, one month’s wages amounting to $100 are not provided for in the ledger account. Prepare a trial balance before and after adjustment.
Solution:
The unadjusted trial balance is as under-
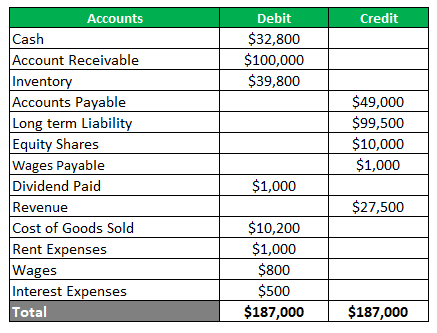
Now the adjustment entry for an accruing one-month wage would be passed. This will increase the wage expense and create a new liability of wages payable. The adjusted trial balance will be as under.
Uses of Trial Balance
Trail balance has numerous uses depending on the requirements of the end user. A few of them are as below:
- Provides a base for making adjustments
- Helps in an audit by providing an audit trail
- It defines the credibility of transactions
- It is also an aid to management in having control over business transactions.
Advantages
- Ensures that debits are equal to credits
- Helps in identifying errors in journalizing or posting
- Helps in finding errors in the general ledger
- Provides a base for the preparation of financial statements
- Provides a summary of balances in one place
- Helps in checking the mathematical accuracy of accounts
Disadvantages
- It doesn’t authenticate that all the transactions are recorded in books
- There are still chances of errors even if the trial balance columns tally
- It cannot find any missing entries from journal or ledger
- It cannot ascertain an error in passing the original entry
- There are chances of offsetting errors
- An error of commission or omission cannot be ascertained
- It doesn’t validate the error of the principle
- It cannot find the error in the reversal entry
Conclusion
- An unadjusted trial balance is crucial for making financial statements and helps identify errors so that corrective measures can be taken.
- It is a worksheet of ledger balances with credit and debit columns to check mathematical accuracy.
- It ensures that there are no mathematical errors, but there can be an accounting error.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Unadjusted Trial Balance. Here we discuss the Formant, Uses, examples, advantages, and disadvantages of Trial Balance. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –