What is Universal Life Insurance?
Universal life insurance (UL) is a lifetime protection policy that promises death benefits whenever the insured dies. It is in contrast to term life insurance which guarantees protection only for a specific period (5 to 75 years). UL also builds a cash value account for the individual, where the surplus money from the premiums grows with monthly interest.
For example, Mrs. Patricia purchases a UL policy of $1,000,000 and deposits a yearly premium of $15,000. The company reduces $5,000 (fees) from the premium and adds the $10,000 to the cash value account. The cash value account grows with time and accumulates $50,500 (assuming 1% yearly interest) in 5 years. Suppose Patricia passes away, so her family will receive the benefits ($1,000,000) but not the $50,500. However, if she closes the policy before she dies, they will receive the $50,500. The benefit is that as it is a lifetime policy, her family will get the reimbursement even if she passes away later (Eg. 101 years).
Universal life insurance allows lower or raised premiums within firm limits. However, it also offers rarer guarantees than whole life insurance. After the death of the insured, their inheritors obtain either a single tax-free payment or can select periodic (monthly or annual) payments.
Key Highlights
- Universal life insurance is life insurance that includes an investment savings scheme and requires small premiums
- The various types of UL are guaranteed, indexed, variable, and traditional
- Death benefit and cash value account are its two crucial components
- One of the significant benefits is that there are no tax allegations for policyholders who borrow from their policy’s accrued cash value.
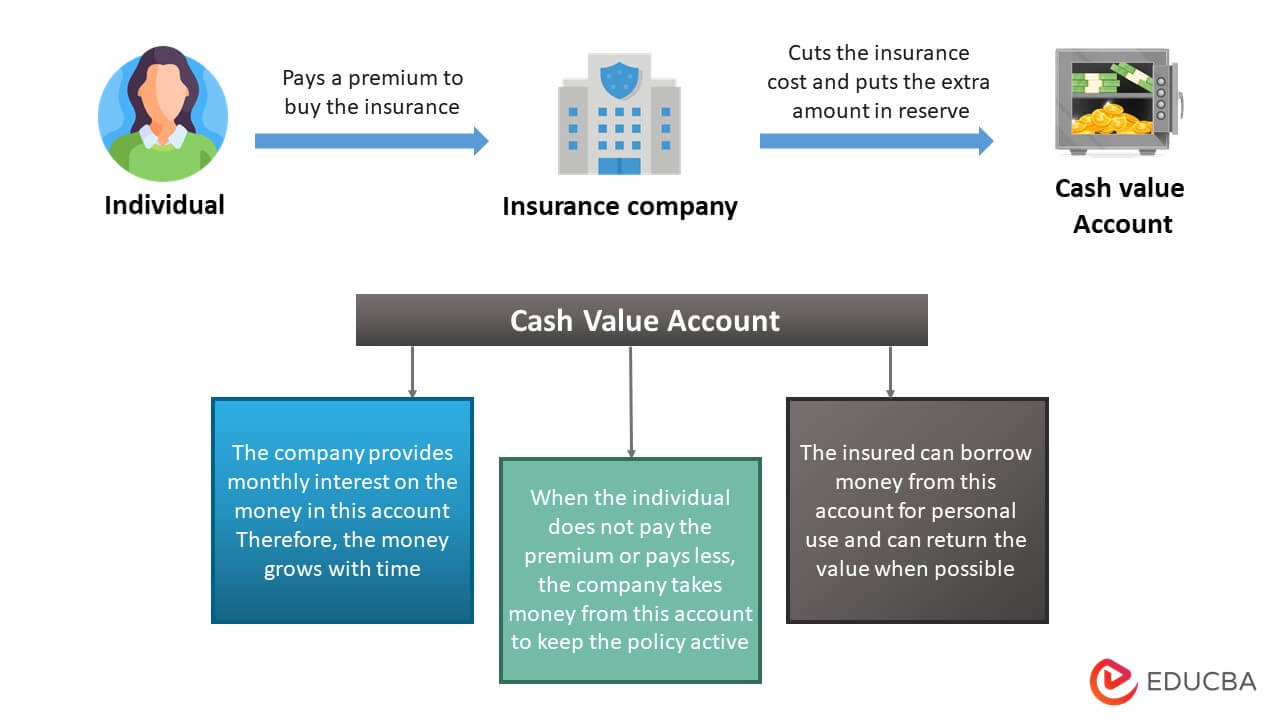
How Universal Life Insurance Works?
- Once the person buys the insurance and pays a premium, the insurance company reduces the administrative fee and the insurance cost from it and transfers the rest to the cash value account
- The cash value account is a savings account where the excess money is accumulated, and the company provides monthly interest on it. Therefore, it grows with time
- In case the person is unable to make the premium payments, the company will extract the amount from the cash account to keep the policy valid
- If the policy is active during the insured’s demise, the inheritors only obtain the life insurance disbursement, as the surplus funds in the cash account go to the insurance company
- However, if someone chooses to terminate the policy while they are still alive, they receive most or all of accrued cash from the cash value account.
Universal Life Insurance Types
Traditional or Non-Guaranteed:
- The traditional policy offers the basic UL approach, but the policy may lapse if the holder makes any changes to the contract
- However, this policy is a good option if one wishes to save premiums.
Variable:
- It allocates the cash value into indexes, stocks, money markets, or accounts
- Also, they diversify the investments, ensuring rapid growth, though the amount you receive has a cap.
Indexed:
- It builds cash value that lasts for the entire life
- This policy allows cash value growth through an equity index account
- One must only choose this fund if they understand the stock market well or work with a reliable financial advisor.
Guaranteed:
- This policy offers premium payments and a death advantage that will not change over time
- It is an extension of the traditional policy, as it has all essential benefits with the assurance that the policy will not lapse.
Components of a Universal Life Insurance Policy
Death Benefit:
- After the insured person passes away, the policy beneficiaries receive the death benefits
- For several policies, the insurance company retains the cash account. However, according to the plan, the beneficiaries can claim the cash account money.
Cash Value Account:
- When one makes premium payments, a percentage of that money funds the death benefit while the extra amount goes to the cash value
- In some cases, when the insured cannot pay the premium, the company takes money out of the cash value
- The holder can borrow capital from this account or keep it for their inheritors.
Benefits of Universal Life Insurance
- There are no taxes on current income or interest because the cash value cultivates on a tax-deferred basis. However, taxation can depend on various elements of the policy
- It allows alteration and modification of the premium amount unless it is enough to retain the policy
- The policy starts from the first day and works till the death of the insured person, ensuring that the beneficiaries receive the benefits
- It has an in-built cash value that cultivates over time and produces interest.
Universal Life Insurance vs. Term Life Insurance vs. Whole Life Insurance
| Universal Life Insurance | Term Life Insurance | Whole Life Insurance |
| Universal Life Insurance is a life insurance that offers its holders flexibility in paying premiums, a death benefit, and a cash value account | Term Life Insurance is a death benefit policy that pays the inheritors of the policyholder for a definite period | Whole Life Insurance is permanent life insurance with a cash savings component |
| Insurance premium prices may change with interest and as the holder ages, but it is primarily inexpensive | As it expires, the policyholder can either change the policy to permanent coverage, apply for its renewal for another term, or let the policy lapse | It is considerably expensive as it presents guaranteed benefits for the insured’s lifetime |
| It permits borrowing against cash in savings, which grows tax-deferred over the lifetime. | These policies do not have savings components like the other two. It has only guaranteed death benefits. | It does not allow the insured to take a loan from the cash account. |
Universal Life Insurance Taxation
- As long as the cash account receives consistent addition of cash, it sustains tax-free development
- Once the holder withdraws these funds, taxes will be levied on the amount the person takes
- Suppose a person borrows from the cash value account and pays back the whole amount. This amount will be tax-free.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It accumulates a cash value that is available to the policyholder for use during their lifetime | The policyholder has to bear various costs and fees to enjoy its benefits |
| It offers flexibility in paying premiums as long as they are enough to keep the policy active | If one fails to maintain the premiums and the cash value, consequently, the policy will lapse |
| The policyholder can increase the death benefits, consequently gaining more benefits for the inheritors | Sometimes lower premiums result in a decrease in death benefits, which leaves a lesser amount for inheritors |
Conclusion
Universal life insurance is mostly for high-income recipients seeking lifelong coverage with flexible monthly premiums and a variable death benefit. However, the policy is complex compared to other insurance policies, like term insurance. Therefore, before purchasing a policy, one must adequately assess the policy.
FAQs
Q1. What is universal life insurance?
Answer: A universal life insurance policy provides the insured lifetime protection rather than for a specific period. It also ensures a cash value savings benefit. Additionally, it gives policyholders a choice to pay flexible premiums.
Q2. Which is a better option, whole or universal life insurance?
Answer: Universal life and whole life insurance are alike in most aspects, and both are outstanding options to help safeguard your family. The significant difference that makes UL insurance slightly beneficial is its premium flexibility. Thus, it can be accommodating for low-income families.
Q3. How can I cash out my universal life insurance policy?
Answer: You can cash out your policy in three ways. You can withdraw the cash either in whole or in installments. Furthermore, you can raise loan money against your cash account with a nominal interest credit. Another method is to surrender the policy.
Q4. What is universal life insurance’s disadvantage?
Answer: The most significant disadvantage of UL is that one must pay premiums on the face value irrespective of the amount of cash value the policy holds. Due to flexible premiums, the insured may get fewer death benefits if they pay lower premiums.
Recommended Articles
This article explains universal life insurance’s meaning, types, benefits, components, and more. Here are a few articles to learn more about it,