Updated March 27, 2023

Introduction to Validation in PHP
Validation in PHP is the process where we check if the input information in the various fields in any form such as text, checkbox or radio button, etc, submitted by the end-user in the form is correct or not using HTML code.
There are 2 kinds of validation available in PHP:
- Client-Side Validation: This type of validation is done on the web browser of the client machine.
- Server-Side Validation: The data on submission is then sent to the server machine to perform validation checks there.
Rules to Validation in PHP
There are certain rules for validation of a form and they are as follows for the following fields:
- Name: It is a mandatory field whose data contains only whitespace and letters.
- Email: It is also a mandatory field that should contain a valid email address means it should be in the format of abc@website.com.
- Website: It is an optional field and should contain a valid URL if given
- Comment: It is an optional field and is a multi-line text input where we can give long sentences.
- Gender: It is a mandatory field and should select one gender out of the female, male and other.
Types of Validation in PHP
Now let us see how to validate different types of such fields.
1. Validation of text fields
There are a few text fields from the above-said attributes such as name, email, website, and comment. The HTML code for the same is as below:
Code:
<blockquote>
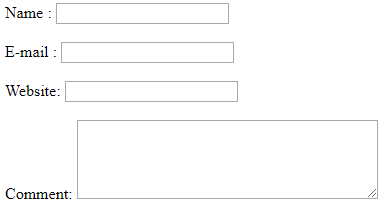
<p>Name : <input name="name" type="text" /> <br /><br /> E-mail : <input name="email" type="text" /><br /><br /> Website: <input name="website" type="text" /><br /><br /> Comment: <textarea cols="40" name="comment" rows="5"></textarea></p>
</blockquote>Output:
Explanation to the above program: Here we can customize these attribute names however we want by using different header tags and also space tags. We have shown one of the paragraph format options for this one here.
2. Validation of radio buttons
Radio buttons are basically the ones having boolean value either true or false and they are represented by a circular box kind of a thing. If the box is circled it means true and vice versa. Let us check out the HTML code to implement the same for above said “Gender” attribute.
Code:
Gender:<br /><br />
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female<br /><br />
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male<br /><br />
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="other">OtherOutput:
Explanation to the above program: By using this code we are displaying 3 options under the gender category as male, female and other. The user can circle on the required option by clicking on the circle and the option will be saved and validated.
3. Validation of form element
This method is used at the end after all the required details have been filled to submit the form. On using this HTML code the form data when submitted is sent with the “post” method. There are basically 2 attributes we need to specify while validating form element: action and method. We can convert certain HTML attributes to their respective entity names in order to prevent the form breaking when the user submits. “action” determines where the data of the form is sent on submission and “method” defines how the form’s data is submitted.
Code:
<form method="POST"
action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">Let us check an entire form of validation by combining all the different kinds of validation we learned above:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.Error {color: #FF0000;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// we are defining variables here and setting their default values to zero
$nameError = $emailError = $genderError = $websiteError = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameError = "Name is mandatory";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailError = "Email is mandatory";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["website"])) {
$website = "";
} else {
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$comment = "";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderError = "Gender is mandatory";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>PHP Form Validation Example</h2>
<p><span class="Error">* mandatory field</span></p>
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
Name: <input type="text" name="name">
<span class="Error">* <?php echo $nameError;?></span>
<br><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
<span class="Error">* <?php echo $emailError;?></span>
<br><br>
Website: <input type="text" name="website">
<span class="Error"><?php echo $websiteError;?></span>
<br><br>
Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
<br><br>
Gender:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="other">Other
<span class="Error">* <?php echo $genderError;?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<?php
echo "<h2>Your Input:</h2>";
echo $name;
echo "<br>";
echo $email;
echo "<br>";
echo $website;
echo "<br>";
echo $comment;
echo "<br>";
echo $gender;
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
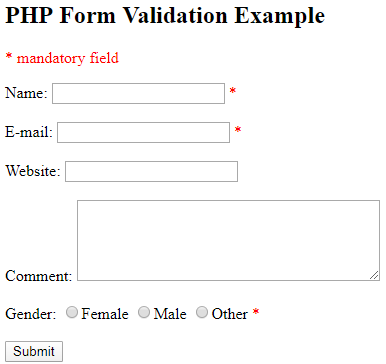
Explanation to the above program: In the above example, we have combined all the different fields available such as text field, radio buttons and also email format types. The output will be displayed in the form of a box which will be according to the specification we give in the HTML code. Upon entering the mandatory values, the same are displayed under the text “The details entered are:”. Suppose any one of the mandatory values is not given then it will throw an error message besides that particular attribute saying that it is mandatory and needs to be filled.
Advantages of Validation in PHP
- By using client-side validation we can receive feedback faster without having to switch off from the server and download another HTML page.
- Validation on the client-side also helps in saving load on the server and increases performance.
Conclusion
We have seen in this tutorial how to do validation in PHP on the client-side and how much it is essential. It helps in saving time hence allowing for more bandwidth to point out the end-user their mistake in filling the given form. However, server-side validation is also important which is done using JavaScript, etc. Hence we can finally conclude by saying that both client and server-side validations are important since they complement each other in serving the end purpose.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Validation in PHP. Here we discuss certain rules for validation, types, and advantages along with respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –