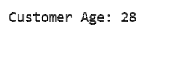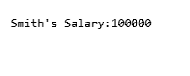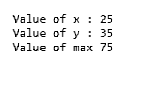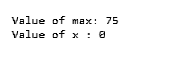Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to Variables in C#
In C#, a variable is a name that we give to the memory location and every variable has a specified type that specifies the type of values that can be stored in a variable. All the variables should be declared before they are in use; every variable has a specific type that decides the size and range of variables. To perform any operation on variables it is essential to define a variable with a particular data type to specify the type of data that the variable can hold in our application. Let’s see a few basic things about variables,
- Variables are nothing but a name given to data value.
- Variables can hold the value of particular data types, for example, int, string, float and so on.
- Declaration and initialization of variables are in separate statements.
- Variables can be defined by multiple separated by a comma and also in single and multi-line till the end of the semicolon.
- Values must be assigned to a variable before we make use of it; otherwise, it will show a compile-time error.
- The value of a variable can be changed at any time until the program accessibility.
How to Declare Variables in C#?
There are some rules to declare C# Variables:
- We must define a variable name with the combination of numbers, alphabets and underscore.
- Every variable name should start with alphabets or underscore.
- There should not be any white space allowed in between the variable name.
- Variable names should not contain any reserve keywords like int, char, float and so on.
The syntax for variable definition in C#
<data_type> <variable_name>;
<data_type> <variable_name>=value;
<access_specifier><data_type> <variable_name>=value;Here the <data_type> is a type of data in which the variable can hold the types they are an integer, Sting, float and so on. <variable_name> is the name of a variable that holds the value in our application and <value> is assigning a specific value to the variable and finally <access_specifier> is used to give access permission for the variable. They are some suitable methods to describe the variable names in c# programming language.
int name;
float value;
char _firstname;You can also initialize a variable at the time of definition as follows,
int value = 100;How to Initialize Variables in C#?
To assign a value to a variable called initialization, variables can be initialized with an equal sign by the constant expression, variables can also be initialized at their declaration.
Syntax:
<data_type> <variable_name> = value;Or
variable_name = value;For example,
int value1=5, value2= 7;
double pi= 3.1416;
char name='Rock';Types of Variables in C# with Examples
There are several types of variable, such as
- Local Variables
- Instance Variables or Non – Static Variables
- Static Variables or Class Variables
- Constant Variables
- Read-only Variables
1. Local Variables
A local variable defined within a method or block or constructor. Once the variable is declared, those variables exist only within the block and we can access these variables only within the block. The variable is created when the function is called or the block is entered and it will be demolished once after existing from block or while the call returns from the function.
In the sample program, the variable “customer_age” is a local variable to the function GetAge(). The compiler will generate an error, once we apply the variable customer_age outside GetAge() function.
Sample Program – Local Variables
using System;
class CustomerEntry
{
public void GetAge()
{
int customer_age=0; // local variable
customer_age= customer_age+28;
Console. WriteLine("Customer Age: "+ customer_age);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
CustomerEntry _customerObj=new CustomerEntry();
_customerObj.GetAge();
}
}Output:
2. Instance Variables or Non – Static Variables
Instance variables are called the non-static variables; the instance variables are declared in a class but declared outside of any method, block or constructor. These variables are created once the object of a class created and it will destroy when the object becomes destroyed. For instance variables, we can use the access specifiers.
In the program, the instance variables are markEnglish, markMaths. We can create multiple objects each of the objects have its copy of the instance variable.
Sample Program – Instance Variables
using System;
class StudentMarks {
// instance variables
int markEnglish;
int markMaths;
int markPhysics;
public static void Main(String[] args) // Main Method
{
StudentMarks obj1 = new StudentMarks (); //Object creation 1
obj1. markEnglish = 90;
obj1. markMaths = 80;
obj1. markPhysics = 93;
StudentMarks obj2 = new StudentMarks (); //Object creation 1
obj2. markEnglish = 95;
obj2. markMaths = 70;
obj2. markPhysics = 90;
Console.WriteLine("Marks Obtained from first object:");
Console.WriteLine(obj1. markEnglish);
Console.WriteLine(obj1. markMaths);
Console.WriteLine(obj1. markPhysics);
Console.WriteLine("Marks obtained from second object:");
Console.WriteLine(obj2. markEnglish);
Console.WriteLine(obj2. markMaths);
Console.WriteLine(obj2. markPhysics);
}
}Output:
3. Static Variables or Class Variables
A static variable is created at the beginning of the program execution and destroys at the end of the execution. Static variables are also called as class variables. For accessing static variables, we no need to create an object of the class; we can simply access the variable as,
Class_name.variable_name;A static variable is declared using the keyword static within a class or outside any method or constructor.
Sample Program – Static Variable
using System;
class Employee
{
static double empSalary;
static string empName="Smith";
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Employee.empSalary=100000; // accessing the static variable
Console. WriteLine(Employee.empName+ "'s Salary:" + Employee.empSalary);
}
}Output:
4. Constants Variables
Constant variables are similar to the static variables, once initialized and the one-time life cycle of a class and it does not need the instance of the class for initializing or accessing. The constant variable is declared by using the ‘const’ keyword, these variables cannot be altered once it declared, and it should be initialized at the time of the declaration part only.
Sample Program – Constant Variable
using System;
class Program_A
{
int x= 25; // instance variable
static int y= 35; // static variable
const float maxValue =75; // constant variable
public static void Main()
{
Program_A classObject= new Program_A(); // object creation
Console.WriteLine("Value of x : " + classObject.x);
Console.WriteLine("Value of y : " + Program_A.y);
Console.WriteLine("Value of max " + Program_A. maxValue);
}
}Output:
5. Read-Only Variables
A read-only variable is declared using the keyword ‘read-only‘ and those variables cannot be altered like constant variables. The constant variable is an unchanging value for the entire class whereas read-only is a permanent value for a specific instance of a class. There is no compulsion to initialize a read-only variable at the time declaration, it can be initialized under constructor. The default value set to the variable is 0.
Sample Program – Read-Only
using System;
class Program_B
{
const float maxValue =75; // constant variable
readonly int x; // read-only variable
public static void Main()
{
Program_B classObject= new Program_B(); // object creation
Console.WriteLine("Value of max: " + Program_B. maxValue);
Console.WriteLine("Value of x : " + classObject.x);
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Finally, you have known about how variables allow you to store data in different ways. In this article, we learned about how to declare and initialize variables and how to make use of it. I hope this article would have helped you out with the working process of variables.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Variables in C#. Here we discuss what are variables in C#, how do we declare variables, how do we initialize variables, and finally what are different types of variables in C# with their examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –