Updated March 27, 2023
Difference Between VLAN vs Subnet
Both VLAN and Subnet are designed to segment or partition part of the network. And they share similarities, such as the limitation of broadcast domains or the isolation of specific sub-networks. A VLAN is a second-term layer, usually a broadcast domain. A subnet is a layer of a three-layer term. Layer 2 is where the Windows pc addresses are used. Layer 3 is the IP layer with usable IP addresses.
What is VLAN? – VLAN is a collection of computers on one or more LANs independent of their physical location, also known as virtual LANs. In other words, devices can be packed together, even if not attached to the same fiber switch. However, network hardware/software often needs to support VLAN functionality, e.g. VLAN switch is necessary for establishing a VLAN network. In VLAN, it is possible to customize the network extensively via software. In general, Layer 2 VLANs are used to distinguish broadcast domains.
What is Subnet? – A subnet is a network of IP-addresses consisting of a small group. This belongs to a larger network. Within the same Subnet, any IP address will communicate without routing tools. To order to be transparent, we should assume that Subnet is a company organization where people within the same department can speak freely without leaving their office. You must go through a route or modern Gigabit Ethernet switch with the router functionality if you want to access an address outside your subnet. As Subnet is IP address-related, it often works with layer 3.
Head to Head Comparison Between VLAN vs Subnet (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 comparisons between VLAN vs Subnet:
Key Differences Between VLAN vs Subnet
Let us discuss some key differences between VLAN vs Subnet in the following points:
- Subnetting and implementing VLANs provide managers with the ability to create medium- to large-scale networks. Essentially, the aim of the VLANs and subnetworks is similar. But it has clear functional, operational and/or deeper objectives differences.
- VLAN exists when a network hardware/Software that supports VLAN functionality is connected physically by two or more ports or grouped together. In general, a VLAN is quite similar to a real LAN. Their main difference is VLAN’s ability, without requiring the same network switch to group end stations together. In VLAN, network configuration can be done extensively through software.
- Through VLAN is a separate entity, and only a single VLAN can be reached via a router. You can use a single network using VLANs, but the whole logical network is affected if a network fails for some reason. In principle, a subnet is an IP-address group. Any address that belongs to the same subnet may be reached with no routing device.
- VLANs are very useful in improving working performance, reducing traffic and productivity in a community of IT specialist departments. Now, if your address is outside your subnet, you’ll have to go through a router just like in your VLANs. Layer 3 (IP) is a subnet that includes IP addresses.
- You divide an IP address into smaller subnets when you are subnetting. This makes a number of networks added to the system, which would always be necessary for any organization or agency.
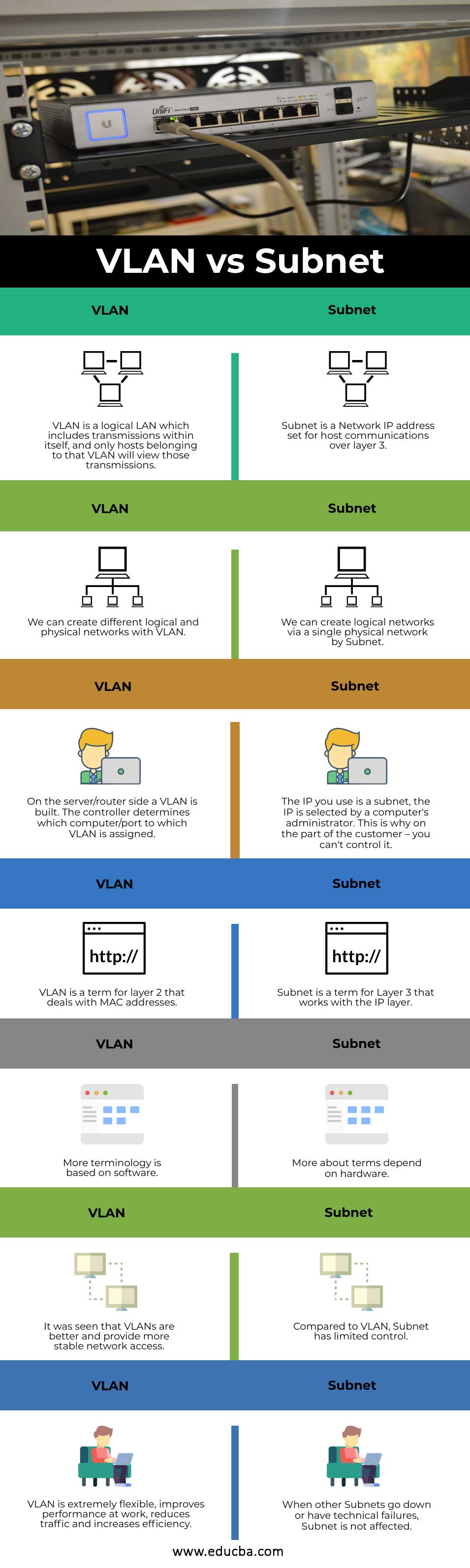
VLAN vs Subnet Comparison Table
The table below summarizes the comparisons between VLAN vs Subnet:
| VLAN | Subnet |
| VLAN is a logical LAN that includes transmissions within itself, and only hosts belonging to that VLAN will view those transmissions. | A subnet is a Network IP address set for host communications over layer 3. |
| We can create different logical and physical networks with VLAN. | We can create logical networks via a single physical network by Subnet. |
| On the server/router side, a VLAN is built. The controller determines which computer/port to which VLAN is assigned. | The IP you use is a subnet; a computer’s administrator selects the IP. This is why, on the part of the customer – you can’t control it. |
| VLAN is a term for layer 2 that deals with MAC addresses. | A subnet is a term for Layer 3 that works with the IP layer. |
| More terminology is based on software. | More about terms depend on hardware. |
| It was seen that VLANs are better and provide more stable network access. | Compared to VLAN, Subnet has limited control. |
| VLAN is extremely flexible, improves performance at work, reduces traffic and increases efficiency. | When other Subnets go down or have technical failures, Subnet is not affected. |
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen the key differences between VLAN and Subnet. VLAN is more popular than subnetting, but they are used to supplement each other more often than not. Some assume that subnetting is easier, but VLAN offers network capacity. I hope you will find this article helpful.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top differences between VLAN vs Subnet. Here we discuss the VLAN vs Subnet key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –