Updated August 10, 2023
Introduction to VLOOKUP Error
We all know how to apply and application of Vlookup function. And we have seen various ways to use the Vlookup function in previous articles. We are all also somewhere and sometimes see different error messages which could and couldn’t be able to resolve it. Vlookup Errors are errors that may happen for different reasons. The basic and most common reasons are incorrect range, no match, and special characters in the lookup range as well in the lookup cell. This article will show the different types of Vlookup Errors and the logic behind those errors.
How to Use VLOOKUP Error?
Below are the most commonly occurring Vlookup Errors.
- #N/A Error
- #Value! Error
- #Name? Error
- #REF! Error
MS Excel has a standard way to prompt the errors it is happening in the cells while applying any of the Excel functions, which is by putting the HASH sign (“#”) before that. We all have seen this; we rarely have noticed. Above mentioned errors are some of them. Every error has a different meaning and reason to occur, which we will see in upcoming examples.
Examples of VLOOKUP Error
Lets us discuss the examples of VLOOKUP Error.
Example #1
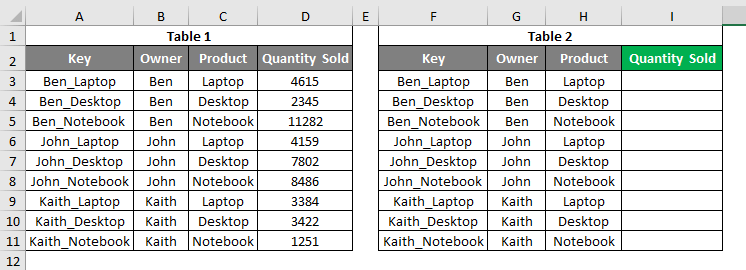
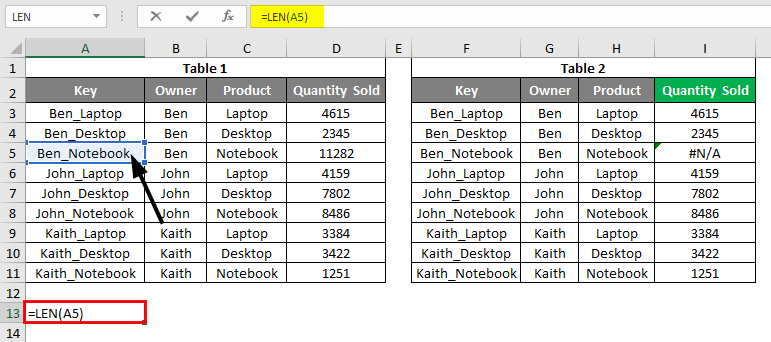
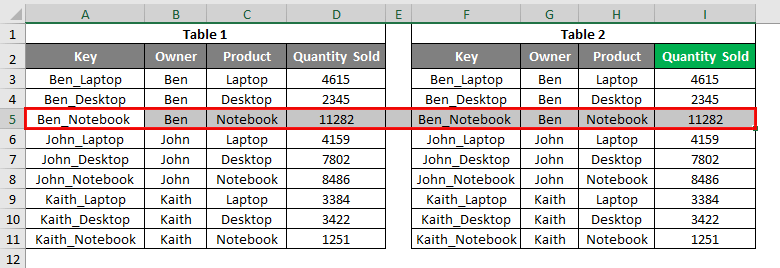
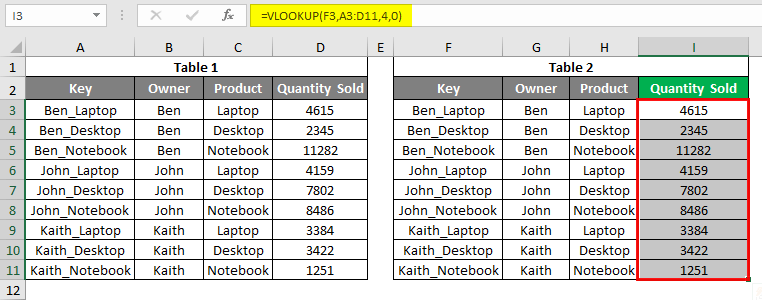
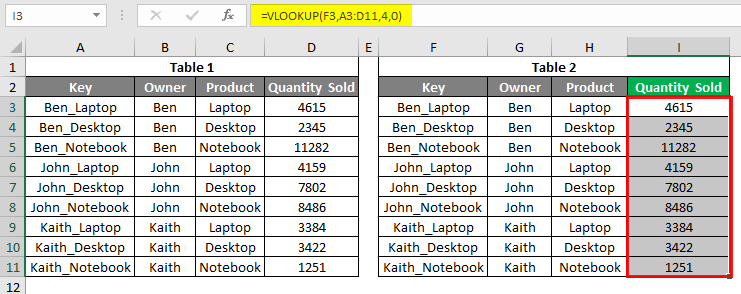
In this example, we will see the first and most common type of error, #N/A. For this, we have some sample data, as shown below. As we can see, we have 2 tables. The first table has the Sales data for some electronic products like laptops, desktops, notebooks, and tablets, and the second table is the table where we will be looking up the value from the first table. We have created a common key by combining OWNER and PRODUCT columns, separated by an underscore (“_”).
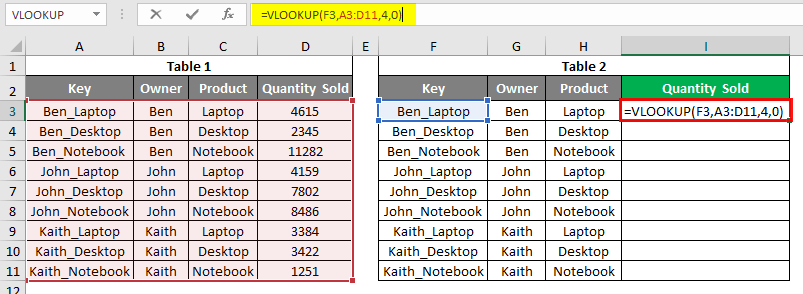
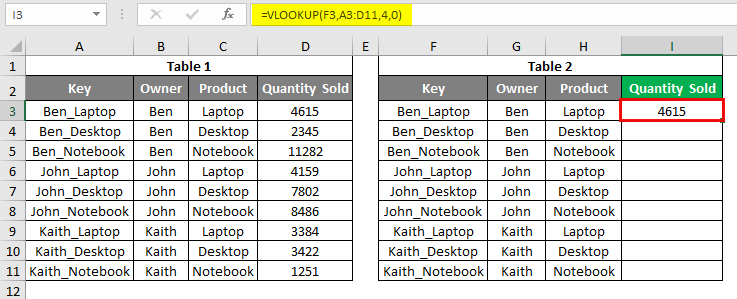
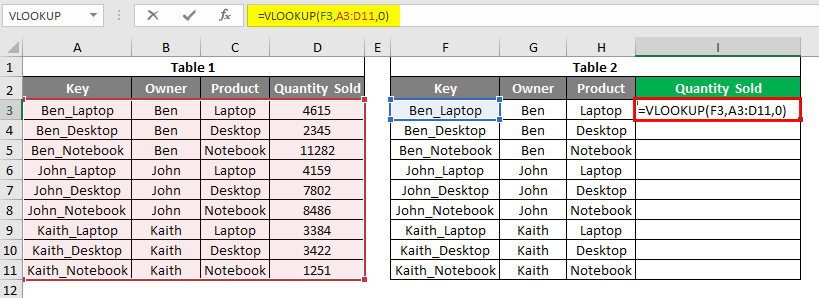
Let’s apply the Vlookup in cell I3. Apply the vlookup using the range and lookup cell as shown below. As shown below, the Lookup cell is F3, our Key of Table2, the lookup range selected from Table1.
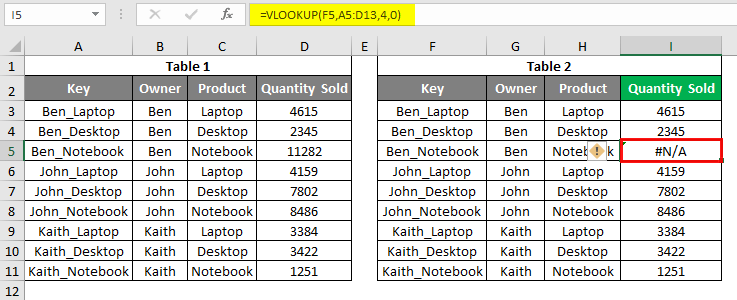
Once we drag the applied function, we will see that for cell I5, and we got an error as #N/A.
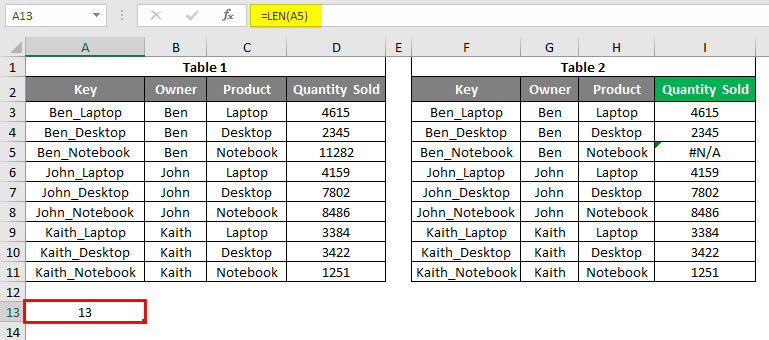
To find the reason behind this, there are 2 possibilities. We may have some space or special characters in lookup cell F4 or the first column of the Lookup range. To find this, we can check the length of both the cell of the same row using the LEN formula. We have used the LEN function by selecting the cell of row 5. Below is row 13.
After using LEN Formula in cell A13, the output is shown below:
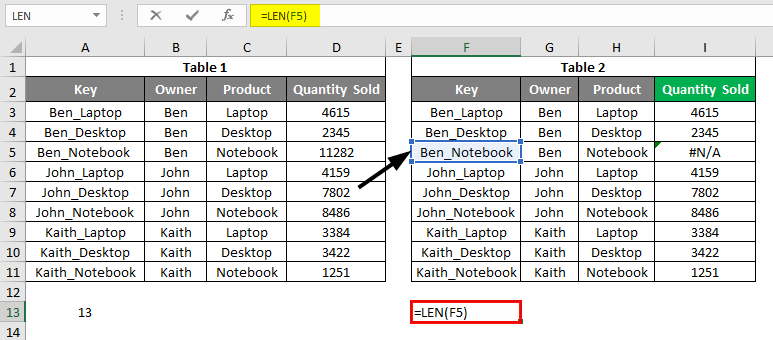
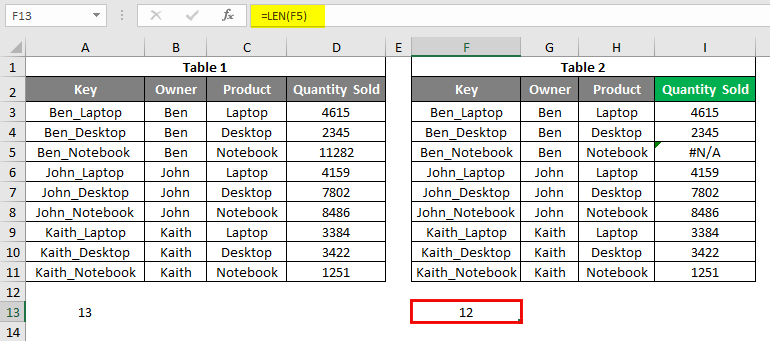
LEN Formula use in cell F13.
After using the above formula, the output is shown below:
If we Clear or Delete that extra space or special character from cell A5, we will get the Quantity sold for Ben_Notebook for Table 2, as shown below.
Example #2
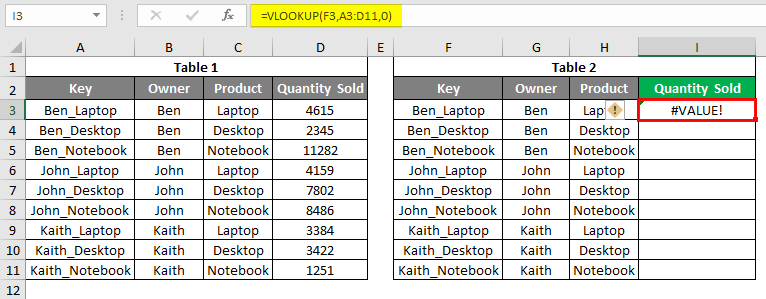
In this example, we will see the Vlookup error #VALUE! This happens due to incorrect syntax or missing syntax values while applying Vlookup. We will be using the same data which we have seen in example-1. Let’s apply the vlookup at cell I3 and not choose any syntax value. Let’s say it is Col_Index_num, as shown below.
And if we press enter to exit from the syntax, we will see that cell I3 will have an error as #VALUE!
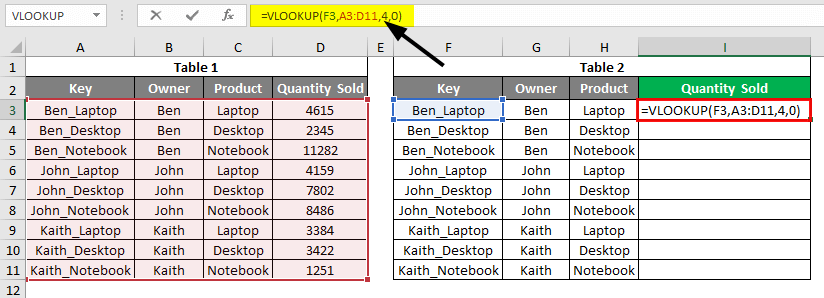
To rectify this, choose the missing Column Index Number in the syntax as 4 and Enter.
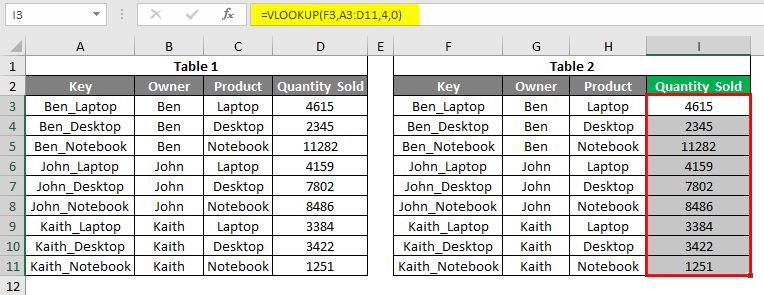
We will see that now the values are looked up properly.
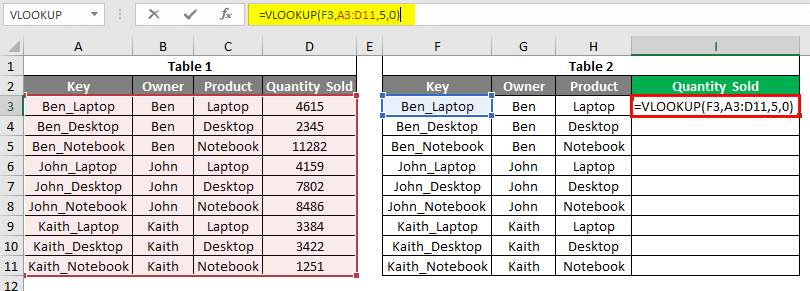
Example #3
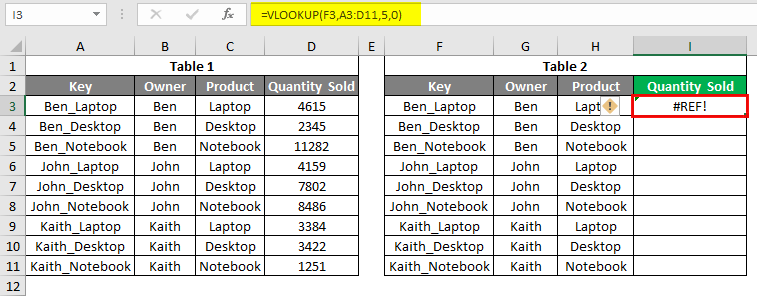
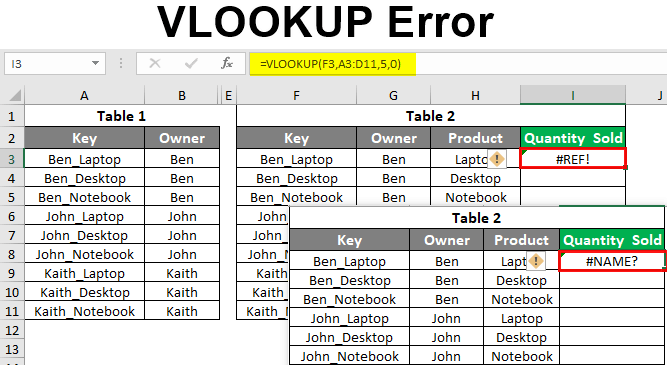
In this example, we will see the Vlookup error type #REF!, which happens due to the selection incorrect Column index number, exceeding the limit beyond the selection. In cell I3, we have applied the Vlookup function choosing everything as we have seen in the above example, but the column index number is now selected as 5, as circled below.
Once we press Enter key to exit from the syntax, we will get the error message #REF!
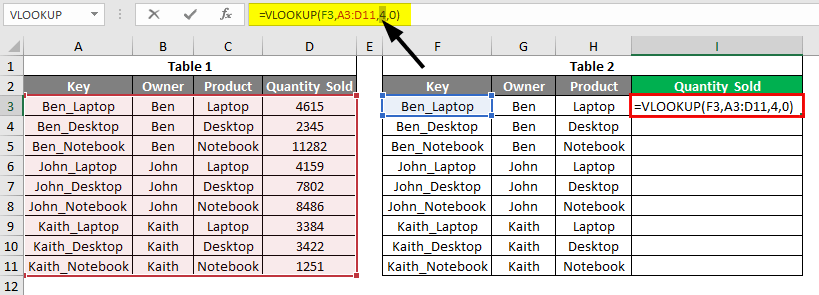
If we correct the column index number from the 5th to the 4th position, we will get the right value looked up.
Once we exit, we will notice the value there.
Example #4
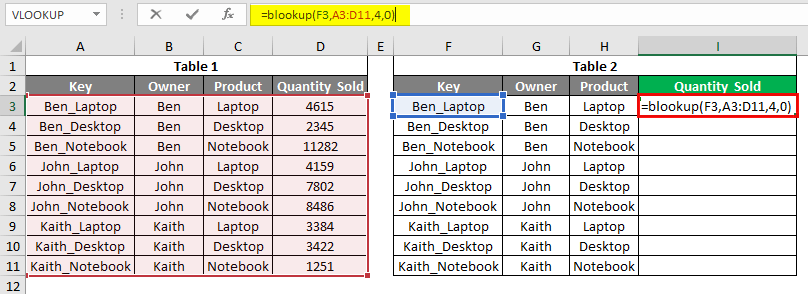
Vlookup error #NAME? We get this when we select all the right positions and cells in syntax but mistakenly type the wrong name of the syntax. As per my experience, I mostly type the function CLEAN instead of VLOOKUP. We will use the same data and select a different function with the syntax of Vlookup. Here intentionally chose BLOOKUP instead of VLOOKUP with the same syntax.
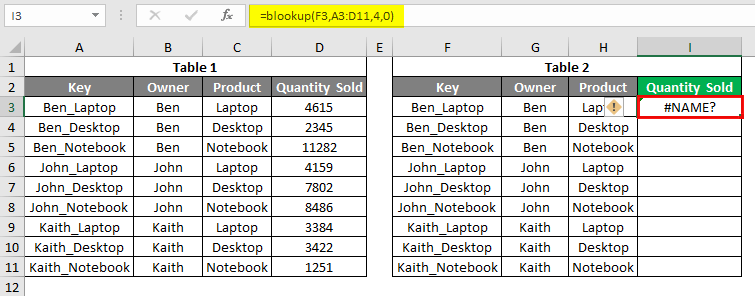
And once exit from the syntax, we will get #NAME? Error as shown below.
To rectify this error, we must select the right function with the right syntax, as we have selected BLOOKUP instead of VLOOKUP.
Pros of Vlookup Error
- It is very important to know the different errors available in Excel for the Vlookup function.
- Vlookup Errors are not limited to the above-shown variations.
Things to Remember
- #N/A error occurs due to the absence of a lookup value.
- #NAME? The error occurs due to incorrect function selection but keeping the right syntax.
- #REF! error occurs due to incorrect selection of column index number.
- #Value! The error occurs when we miss any of the syntax sequences.
- We must know all possible types of errors that happen in the VLOOKUP function so that we would be able to rectify them whenever it is required.
- We can calculate the formula using Evaluate Formula option available Formulas menu ribbon under the Formula Auditing section.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VLOOKUP Error. Here we discuss How to Use VLOOKUP Error, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –