Difference Between WebLogic and JBoss
WebLogic is a server software application that runs on a middle tier among back-end databases and associated applications and browser-based thin clients. WebLogic is a leading e-commerce online transaction processing (OLTP) platform developed to connect users in a distributed computing environment moreover to promote the integration of mainframe applications with distributed corporate data and applications. JBoss is a part of Red Hat that gives assistance for the WildFly open-source application server program (formerly termed JBoss AS) and related middleware services. JBoss is an open-source choice to commercial offerings from IBM WebSphere and SAP Net Weaver. Red Hat JBoss products are accessible through a subscription prototype that includes technical support plus long-term maintenance.
What is WebLogic?
WebLogic server is based on Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE), the standard platform used to develop Java-based multi-tier enterprise applications. J2EE platform technologies were developed through BEA Systems’ efforts and different vendors in collaboration with the principal developer, Sun Microsystems. Because J2EE applications are standardized modules, WebLogic can automate several system-level tasks that would otherwise have necessitated programming time. The principal characteristics of WebLogic server include connectors that make it possible for any legacy application on any client to interoperate with server applications, Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) components, resource pooling, plus connection sharing that make applications highly scalable.
An administration console with a user interface performs management tasks more efficiently, and characteristics such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) support for the encryption of data transmissions and authentication, moreover, authorization mechanisms, make applications and transactions secure. Oracle WebLogic Server is a Java EE application server currently produced by Oracle Corporation. Oracle gained WebLogic Server when it purchased BEA Systems in 2008. Oracle WebLogic Server forms a section of Oracle Fusion Middleware portfolio plus supports Oracle, DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL Enterprise, and different JDBC-compliant databases.
What is JBoss?
The JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (or JBoss EAP) is a subscription-based/open-source Java EE-based application server runtime platform used for developing, deploying, and hosting highly-transactional Java applications also services. The JBoss Enterprise Application Platform is a division of the JBoss Enterprise Middleware portfolio of software. Because it is Java-based, the JBoss application server functions over platforms; it is available on any operating system that supports Java.
JBoss developed the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform, presently a division of Red Hat. JBoss EAP gives two operating modes for JBoss EAP instances: standalone server or managing the domain. The standalone server operating mode represents operating JBoss EAP as an individual server instance. The managed domain operating mode enables the management of multiple JBoss EAP instances from a particular control point. In addition, JBoss EAP includes APIs plus development frameworks for fast-developing secure plus scalable Java EE applications.
Head To Head Comparison Between WebLogic and JBoss (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 difference between WebLogic vs JBoss
Key Difference Between WebLogic and JBoss
As you can see, there is much difference between WebLogic vs JBoss. Let’s look at the top difference –
- A JBoss application server is a free moreover open-source product. While Oracle develops the WebLogic application server.
- The newest version of the JBoss server supports Java EE 6 Web Profile. Whereas the latest announcement of the WebLogic server only supports Java EE 5.
- Configuration and administration are much easy in JBoss, but a UI is not provided. Furthermore, WebLogic is an expensive product; it has various features that are not provided in JBoss. For instance, WebLogic’s web-based administrator console can be practiced for the configuration of JMS, Data Sources, and security settings, etc.
- It is possible to change console requirements depending on the specifications in WebLogic, as Self Console 7001 is involved, but since JBoss is dependent on Tomcat Server, this is not permissible in JBoss.
- Various ways of deployment are possible in Web Logic, while Ant alone could be used for deployment in JBoss, and it is pretty fast and easy.
WebLogic vs JBoss Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison among WebLogic vs JBoss
| The basis of comparison | WebLogic | JBoss |
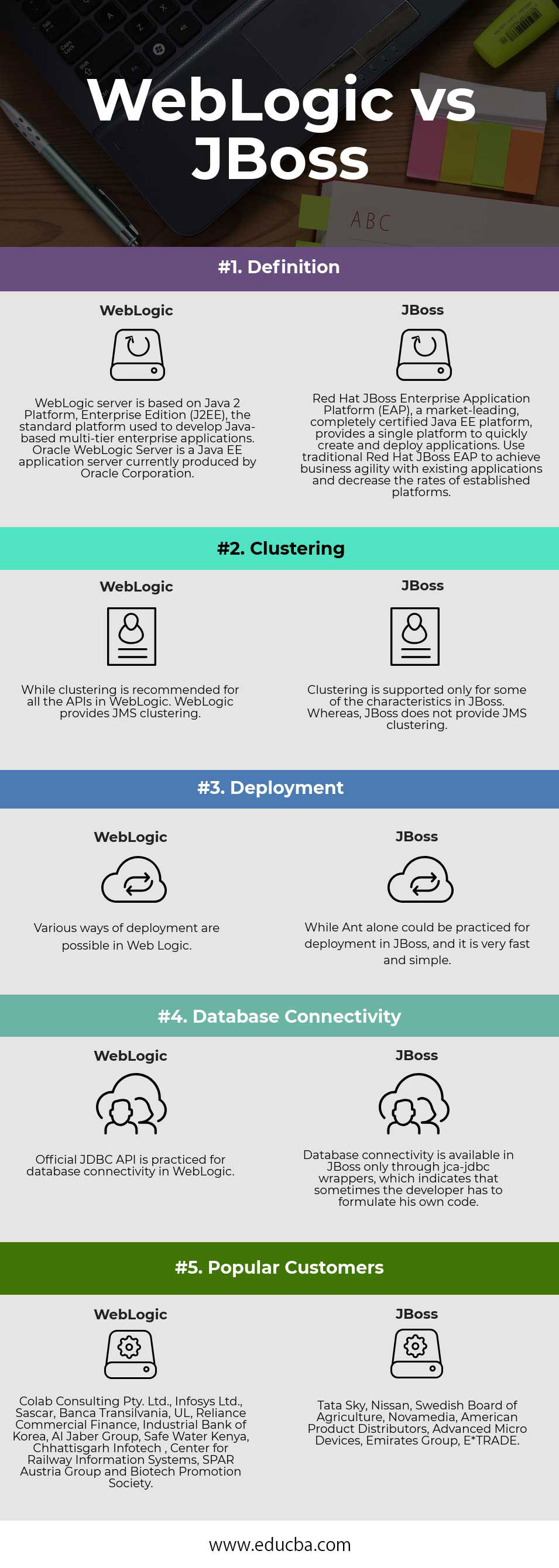
| Definition | WebLogic server is based on Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE), the standard platform used to develop Java-based multi-tier enterprise applications. Oracle WebLogic Server is a Java EE application server currently produced by Oracle Corporation. | Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP), a market-leading, completely certified Java EE platform, provides a single platform to quickly create and deploy applications. Use traditional Red Hat JBoss EAP to achieve business agility with existing applications and decrease the rates of established platforms. |
| Clustering | While clustering is recommended for all the APIs in WebLogic. WebLogic provides JMS clustering. |
Clustering is supported only for some of the characteristics in JBoss. Whereas JBoss does not provide JMS clustering. |
| Deployment | Various ways of deployment are possible in Web Logic. | While Ant alone could be practiced for deployment in JBoss, and it is very fast and simple. |
| Database Connectivity | Official JDBC API is practiced for database connectivity in WebLogic. | Database connectivity is available in JBoss only through jca-JDBC wrappers, which indicates that sometimes the developer has to formulate his own code. |
| Popular Customers | Colab Consulting Pty. Ltd., Infosys Ltd., Sascar, Banca Transilvania, UL, Reliance Commercial Finance, Industrial Bank of Korea, Al Jaber Group, Safe Water Kenya, Chhattisgarh Infotech, Center for Railway Information Systems, SPAR Austria Group and Biotech Promotion Society | Tata Sky, Nissan, Swedish Board of Agriculture, Novamedia, American Product Distributors, Advanced Micro Devices, Emirates Group, E*TRADE |
Conclusion
Application servers play a significant role in modern enterprise computing by working as the platform for the development, deployment, moreover integration of enterprise applications. Application servers promote common functions, such as connection, security, also integration. This enables developers to concentrate only on the business logic. Two of the modern Java EE-based application servers are WebLogic and JBoss application servers. Typically, WebLogic is used in huge enterprises, while small/midsize businesses prefer JBoss.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to the top difference between WebLogic vs JBoss. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –