Updated September 22, 2023
Introduction to Motherboard
The motherboard is a circuit board for the computer system, called a logic board or mainboard. In the computer system, the biggest component is the motherboard, which controls all the components of the computer system and establishes a link between all components. The motherboard connects components such as ROM, CPU, RAM, PCI slots, USB ports, and other peripherals. It also attaches devices like a DVD drive, hard drive, mouse, and keyboard to the controller. The computer system starts using the motherboard, and these components act as the backbone for starting the system.
Table of Contents
How does Motherboard work?
A motherboard acts as a computer’s central nervous system, coordinating interactions between hardware components for seamless operation. It provides physical and electrical connections for critical components and facilitates data transfer. The central processing unit (CPU) is placed on the motherboard and acts as the computer’s brain. The motherboard’s CPU socket connects the CPU to the rest of the system, allowing it to execute instructions and perform calculations. Memory modules, such as RAM, are inserted into specific slots on the motherboard. These provide fast, temporary storage for data that the CPU needs for immediate tasks.
The motherboard manages data transfer between the CPU and RAM to ensure rapid access to information. Expansion slots on the motherboard allow additional components like graphics, sound, and network cards to be added to the system. These slots enable the CPU to communicate with these peripherals. The motherboard also provides power to various components through connectors, ensuring they receive the correct voltage and current. Input/output ports on the motherboard enable devices like USB drives, monitors, and keyboards to connect to the system. The motherboard functions as a critical communication hub, facilitating data transfer, power distribution, and interaction between the CPU, memory, and various peripherals, enabling the computer to function as a cohesive unit.
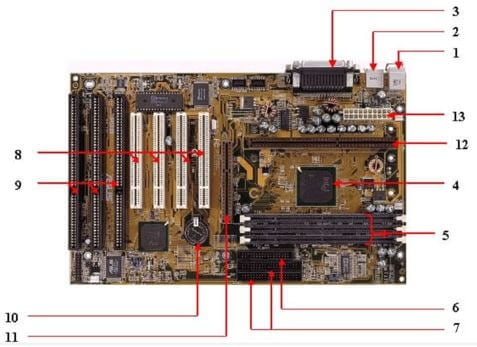
Components of Motherboard
In the below section, some of the important components of the motherboard are defined below:
1. Keyboard and mouse
There are mainly two types of mouse and keyboard connectors. The first connector is known as PS/2 & the second connector is known as USB.
2. Universal Serial Bus (USB)
The USB port is used for connecting the computer system. Various devices are connected to the USB port in the computer system, like a keyboard, mouse, camera, scanner, printer, and other devices. The main use of a USB port is to connect the peripheral devices and computer motherboards. The peripheral device connected to the computer system can be inserted or removed without system restarts, which can be the main advantage of a USB port.
3. Parallel port
The old printers used in the past used the parallel port to connect with the computer system. In the parallel port, multiple wires send or receive various data bits simultaneously. On the other hand, serial ports use only one wire at a time. In the parallel port, 25 pins female DB-type connector is used.
4. CPU chip
The central processing unit is the processor that controls all computer system functions. The central processing unit controls the overall flow of tasks and functions. For the computer system, the central processing unit is called the brain of the computer system.
5. RAM slots
The RAM slots connect the RAM (memory) in the computer system. There are mainly two RAM slots in the general computer system, but sometimes, there can be four-plus slots in the motherboard to increase the computer system’s memory.
6. Floppy Controller
The older motherboard chip contains a 34-pin ribbon cable connecting the computer system with a floppy drive. In this ribbon cable, one end is directly connected to the computer system, and one end is connected to the motherboard.
7. IDE controller
The integrated drive electronics, also known as ATA or Parallel ATA, represent the type of component responsible for hard drive control. In today’s computer systems, there is no support for IDE controllers.
8. PCI slot
The full form of PCI is a peripheral component interface. The PCI slot primarily serves as the insertion point for a computer’s expansion cards. It can also connect other PCI devices such as sound cards, network cards, video cards, modems, and other peripherals. In today’s computer system, support for PCI expansion slots is not there.
9. ISA slot
Industry-standard architecture (ISA) defines a standard architecture for expansion buses. The ISA slot serves as a connection point for input devices and modems.
10. CMOS Battery
The CMOS battery stores the BIOS settings on the motherboard. The CMOS battery can also store the time and data in it.
11. AGP slot
The AGP (Accelerated Graphics slot) is a type of computer slot used to attach the video card to the system. This slot facilitates high-speed data transfer.
12. CPU slot
The CPU slot connects the central processing unit to the computer system’s motherboard.
13. Power Connectors
These connectors supply power to the motherboard. The main power connector is typically a 24-pin ATX connector, and there may be additional connectors for CPU power.
14. Southbridge/northbridge: The Northbridge and Southbridge are chipsets on a motherboard. The Northbridge handles high-speed connections like RAM and graphics, while the Southbridge manages slower I/O functions like USB and SATA.
15. BIOS/UEFI Chip: The BIOS or UEFI chip stores firmware and settings for the motherboard. It initializes hardware during the boot process and manages system settings.
16. FDC (Floppy-Disk Controller): FDC, or Floppy-Disk Controller, is a hardware component that manages data transfer to and from floppy disks in older computer systems.
17. Cooling Connectors: Headers for CPU and system fans and temperature sensors allow you to monitor and control the system’s cooling.
18. Clock Generator: A clock generator is a hardware component that produces precise timing signals to synchronize and regulate the operation of various components within a computer or electronic device.
Factors of Motherboard
The main form factor for the motherboard is size and shape. The other factors are physical layout, mounting holes, and board organization.
Some of the form factors are as follows:
1. ATX
In this type, developers defined standard locations for the mouse, keyboard, input/output devices, video connectors, and other devices. In 1990, they developed the ATX form factor. They relocated the expansion slot in this form factor, providing separate spaces to connect it with the motherboard.
2. Micro-ATX
The benefit obtained from the Micro-ATX is the same as the ATX form factor. The main difference lies in improving the system design to reduce the overall cost of the component as we reduce the motherboard size in this form factor. We achieve this reduction in size by decreasing the number of I/O slots on the motherboard.
Micro ATX, short for Micro Advanced Technology Extended, is a compact motherboard form factor commonly used in desktop computers. It measures 9.6 x 9.6 inches (24.4 x 24.4 cm) and is smaller than the standard ATX motherboard. Despite its reduced size, Micro ATX motherboards typically feature most of the same components and connectivity options, making them a popular choice for smaller PC builds with limited space. However, performance and expandability are still important.
3. Baby AT
Introduced in 1995, the Baby AT motherboard form factor, short for Advanced Technology Extended, represented an evolution of the earlier AT form factor. It aimed to accommodate more advanced hardware components and offered improved layout and compatibility. These motherboards, which were smaller in size, gained popularity in the mid-1990s. However, ATX motherboards eventually replaced them, providing even more advancements in terms of expansion and connectivity options.
4. DTX
A DTX motherboard is a compact motherboard form factor, smaller than ATX and microATX but larger than Mini-ITX. It typically measures 8.5 x 9.6 inches (21.6 x 24.4 cm) and is designed for small form factor (SFF) PC builds. DTX motherboards balance space-saving and expandability, accommodating a few expansion slots and components while fitting into smaller PC cases. They suit budget and mid-range gaming or general-purpose computing setups in compact builds.
5. NLX
NLX, New Low-Profile Extended, represents a compact and versatile form factor for computer motherboards. Designers conceived it to offer a smaller footprint while retaining compatibility with standard desktop components. NLX motherboards have low height and horizontal orientation, making them suitable for space-constrained environments. This form factor enjoyed popularity in the late 1990s and early 2000s but has since seen replacement by other form factors like ATX and Mini-ITX in modern computer systems.
6. Mini STX
Mini STX, for Mini Socket Technology Extended, represents a compact motherboard form factor for small form factor PCs. It measures 147 x 140 mm, making it smaller than Mini-ITX but larger than Intel’s NUC. Mini STX motherboards typically support desktop-class CPUs, providing more power than NUCs. They offer limited expandability due to their size but are ideal for compact and efficient PC builds, particularly in scenarios where space is a premium.
7. Flex ATX
This form factor is designed for small form factor (SFF) and mini PCs and is a compact computer motherboard. It measures 9 x 7.5 inches (approximately 229 x 191 mm) and is smaller than standard ATX and microATX motherboards. Flex ATX motherboards have a reduced size and feature set, making them suitable for space-constrained environments while supporting basic computing needs. They typically have limited expansion slots and connectors compared to larger motherboard form factors.
8. Extended ATX
This form factor is larger and specifically designed for high-performance desktop computers and workstations. It measures 12 x 13 inches (30.5 x 33 cm) and offers more space for additional components, such as multiple graphics cards, RAM modules, and storage devices. E-ATX motherboards provide extra room for advanced cooling solutions and support for various CPU and memory configurations, making them suitable for demanding tasks like gaming, content creation, and professional applications.
9. Standard ATX
Many computer motherboards and power supplies widely use the Standard ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) form factor. It measures 12 x 9.6 inches (30.5 x 24.4 cm) and has defined specifications for component placement and connectors. ATX motherboards typically offer a range of features and expansion slots, making them suitable for various computing needs. The ATX power supply units provide stable power to the components. Overall, the ATX form factor has become a standard in the PC industry, ensuring users’ compatibility and ease of assembly.
Uses of Motherboard
The motherboard is the primary component in the computer system responsible for connecting all its various components, enabling it to perform many tasks and functions. It functions as the system’s backbone, combining all components into a single circuit board to facilitate operations. A motherboard comes at a considerable cost, and in the event of damage, the user must invest a substantial amount in purchasing a new one for the computer system. This central device, the motherboard, connects and regulates the flow of all devices within the computer system.
Features of Motherboard
- Motherboards have connectors for USB, SATA, and audio ports to link peripherals, storage, and audio gear.
- The motherboard holds firmware (BIOS or UEFI) responsible for starting up hardware and adjusting system settings during boot-up.
- These slots allow for the installation of various expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
- Motherboards have connectors for different storage devices, like SATA ports for hard drives and SSDs and M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs.
- Motherboards contain one or more chipsets that manage data flow between CPU, RAM, storage, and other components.
- Overclocking support
- Multi-GPU support
- Onboard Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
- RGB lighting
- USB-C and Thunderbolt ports
- ARGB (addressable RGB) lighting
Advantages of Motherboard
Here are some advantages of a motherboard:
- Central Hub: Motherboards serve as the central hub of a computer, connecting and enabling communication between all essential components.
- Compatibility: They ensure compatibility between CPU, RAM, storage, and other hardware components.
- Expansion Slots: Motherboards provide slots for adding expansion cards like GPUs, sound cards, and network adapters.
- Ports: They offer various ports for connecting peripherals like USB devices, monitors, and audio equipment.
- BIOS/UEFI: Motherboards host the BIOS/UEFI firmware, enabling system initialization and configuration.
- Power Distribution: They distribute power to all components, ensuring stable operation.
- Form Factors: Motherboards come in different form factors to fit various computer cases.
- Overclocking: Some motherboards support overclocking, allowing users to boost CPU and RAM performance.
- Diagnostic Features: Many motherboards include diagnostic LEDs and error codes to troubleshoot hardware issues.
- Customization: They offer customization options for enthusiasts, such as RGB lighting and advanced BIOS settings.
FAQs
Q1. What are onboard Wi-Fi and Bluetooth?
Answers: Onboard Wi-Fi and Bluetooth allows the computer to connect to wireless networks without needing an external adapter.
Q2. What is RGB lighting?
Answers: RGB lighting enables the motherboard and other components to illuminate with different colors.
Q3. What is the best motherboard for me?
Answers: 1) Compatibility 2) Features 3) Form factor 4) Price
Q4. What is overclocking?
Answers: Overclocking is increasing the CPU’s or other components’ clock speed. This can improve performance, but it can also increase heat and instability.
Conclusion
A motherboard is a circuit board in a computer system that connects all components of the computer system. It serves as the backbone of the computer system and comes in various formations based on budget, needs, requirements, and speed. The motherboard functions as a central hub where it connects multiple computer devices.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is a Motherboard. Here, we discuss an introduction to Motherboard and an explanation of its components, factors, and uses. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –