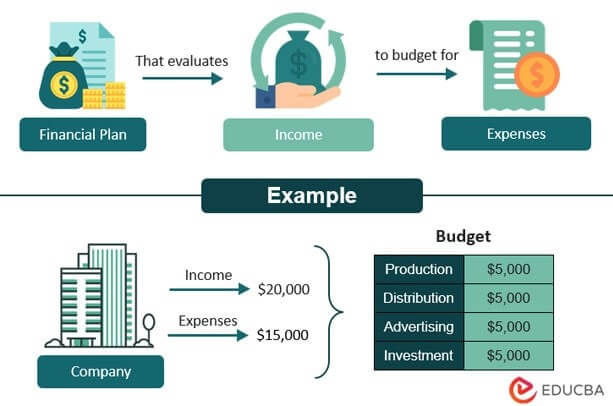
What Budgeting Means?
Budgeting is a strategic planning process that businesses use to plan how they will spend their money in the future. To make a budget, businesses look at how much money they made (revenue) and spent (expenses) in the past and use that information to predict how much money they will make and spend in the future.
For example, a software company might make a budget to plan how much money they will spend on developing new products, advertising their products, and running their business.
A resulting budget is a tool that helps management make informed decisions, avoid overspending, achieve financial goals, and more.
Explanation
A budget acts as a financial roadmap outlining a company’s expected revenue, expenses, and cash flow for a specific period. It estimates a business’s future needs in aspects like production, working capital, capital expenditure, and more. Moreover, companies can create budgets for an entire financial statement or only specific components.
The finance team prepares the budget and presents it to the management for decision-making. Effective budgeting can help a company achieve its goals by enabling it to allocate resources efficiently, identify potential areas of improvement, and make informed decisions. The budget also provides insights into the financial health of the organization. Thus, the budget preparer must consider internal and external factors impacting the budget.
Process
Here is the Stepwise process of budget preparation:
Step #1: Objective
The budget preparation starts with defining the objectives the organization wishes to achieve. It can be cost savings, exploiting new market segments, or launching new products/services.
Step #2: Management of Resources
As each objective requires specific resources, management must determine the availability of these resources before preparing the budget. Thus, they must identify and manage the resources necessary to accomplish these objectives.
Step #3: Estimation
Since budgets depend on estimates, having a solid foundation for these measures is crucial to ensure they are realistic and achievable. These estimates are usually based on past experiences or modified to fit future prospects.
Step #4: Approval
After preparing the budget, the budgeting committee presents it to higher management for approval. Thus, the committee should perform a detailed review of all assumptions to justify the figures presented in the plan.
Step #5: Disbursal of Funds
After the budget’s approval, the committee sends the details to the finance team to disburse funds. As finance is the lifeblood of any organization’s activities, fund distribution across units is essential to ensure they meet their targets.
Step #6: Control, Watch & Evaluate
Moreover, distributing funds alone is not enough. The management must monitor whether everyone is following the plan correctly and make any necessary amendments based on the actual position. Frequent evaluations are also crucial to achieving the organization’s goal of growth and development.
Real-World Budgeting Example
Coca-Cola Case Study
Coca-Cola, one of the largest global beverage companies, has built budgets that have played a key role in its success. They set realistic goals on revenue and expenses while planning their budget and creating effective financial plans to achieve those goals.
For instance, their focus on sustainability while creating a budget has yielded positive results for the company. In 2019, Coca-Cola announced its “World Without Waste” initiative, which states that the company will collect and recycle the equivalent of every bottle they sell by 2030. With that purpose, it invested $100 million in a new recycling plant in the Philippines and partnered with other organizations to improve worldwide recycling infrastructure. Moreover, it also invested in new recycling technologies and improved its packaging materials.
As a result, Coca-Cola has increased the recycled content in its packaging and reduced its carbon footprint. Thus, through its budgeting process, Coca-Cola was able to allocate the necessary resources to achieve these sustainability goals.
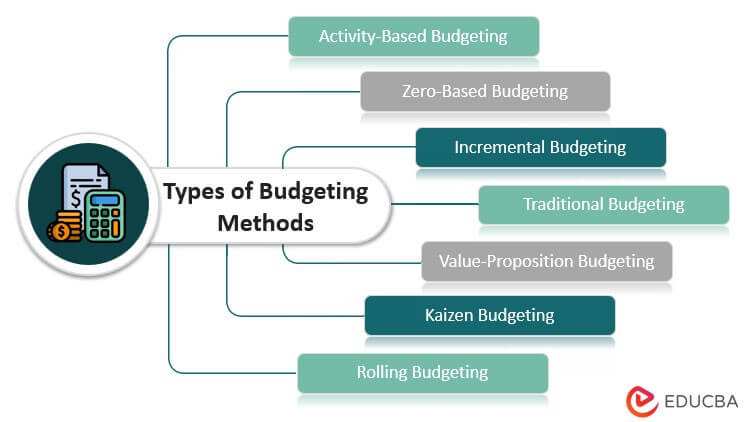
Types of Budgeting Methods
Here are a few types of budgeting methods:
1. Activity-Based Budgeting
In this method, the firm identifies all of its activities, like production, distribution, advertising, etc., along with its level of operation. Then it allocates a cost to each activity based on its past consumption. Finally, the firm prepares a budget by combining the estimated costs of each action.
Example: Every year, AlignGood Pvt. Ltd. spends $15,000, $25,000, and $20,000 on production, distribution, and marketing, respectively. Thus, they set their current budget at $60,000.
2. Zero-Based Budgeting
In this method, the company must create the budget from scratch each year, with no reference to previous budgets. They must evaluate and justify each cost expense before finalizing its value.
Example: A shoemaker, Lily, had a budget of $40,000 last year. However, this year, she starts the budget at zero and reevaluates all her costs before making a new plan.
3. Traditional Budgeting
In contrast to zero-based budgeting, the companies can take the previous year’s budget as a base in the traditional method. They can use the same activities and costs or can reevaluate them if they deem it necessary. In such cases, they only need to justify expenses exceeding the previous budget.
Example: BestTech Ltd. has an annual budget of $100,000 (inclusive of all activities and goals). While reevaluating the plan in 2023, there were no additions, so they used the same budget.
4. Incremental Budgeting
It is similar to the traditional method, as the firm can use the previous budget or the company last year’s financial performance to build a budget. They just make adjustments to the budget in response to the current circumstances.
Example: Oscar had a budget of $30,000 in 2022. In 2023, he has a new goal of buying a car. Thus, with little changes, he adjusts his $30,000 budget to $37,000 to accommodate his new goal.
5. Kaizen Budgeting
The Japanese word “kaizen” means “change for the better.” This method primarily focuses on cost-reduction strategies for businesses. It is a practice where the team constantly analyzes the spending and reallocates the finances if required. It helps the firm cut costs while producing high-quality goods/services.
Example: Tremblay Ltd. has a budget of $500,000 in Jan 2023. However, they bought a machine in March to reduce labor and increase production. They reallocate the budget to save $50,000, making the new budget $450,000.
6. Value-Proposition Budgeting
In value-proposition budgeting (priority-based budgeting), the company’s financial team evaluates the budget to recognize any unnecessary expenses. They redesign and reassign the finances if the prior allocation does not yield a positive outcome.
Example: Gray&White Ltd. built a $250,000 budget in 2022. However, it did not give the expected results, so in 2023, they removed certain unnecessary expenses, bringing the budget down to $180,000.
7. Rolling Budgeting
In this method, the business adds a new budget for every accounting period once the previous accounting period ends. Suppose a company has a budget for 12 months; after the first month, they have a remaining budget plan of 11 months. Now, they can add one month’s plan to the budget to keep it consistently complete (12 months.)
Example: Georgia has a 12-month budget from March 2023-March 2024. As soon as March 2023 ends, she adds the financial plan for April 2024 to the budget to maintain the 12-month cycle.
Purpose
The following are the objectives for creating budgets:
- Forecasting: It forecasts potential financial issues, future losses, or monetary risks and aids organizations in mitigating them.
- Planning: It helps the company build a plan of action to achieve its desired goals and objectives.
- Control: It allows firms to control resource management, production planning, organizational tasks, cost activity, and department efficiency.
- Evaluation: It helps businesses choose the best monetary policies by mapping all the firm’s possible choices regarding money.
- Communication: It offers a way of clearly communicating the company’s financial goals and the corresponding plan of action.
- Authorization and Delegation: Firms can easily assign staff responsibilities depending on the budgeting goals and retain the power to authorize important transactions for those responsibilities.
- Coordination: It assists departments in reaching their target goals by resolving any conflicts inside or outside a department.
- Motivation: It enables HRs to attract and retain top talent and motivate the existing staff to work harder by providing bonuses and incentives.
Differentiate Between Budgeting, Forecasting, and Planning
|
Particulars |
Budgeting | Forecasting |
Planning |
| Meaning | It involves setting financial targets for a specific period, typically a year, and then developing a plan to achieve those targets. | Forecasting involves predicting future financial performance based on historical data and trends. | Planning involves creating a roadmap for achieving broader business goals. |
| How does it help decision-making? | It outlines the expected revenues, expenses, and profits for the coming period and guides financial decision-making throughout the year. | It estimates future revenues, expenses, and profits for a specific period based on past performance to help businesses with decision-making. | Planning creates a roadmap for achieving business goals, including financial targets and other objectives. |
| Purpose | It focuses on setting financial goals and creating a plan to achieve them. | Forecasting helps businesses anticipate future changes and adjust their strategies accordingly. | It sets the overall direction for the organization, defining its mission and vision. |
| Time-period | Companies create a long-term budget that rarely changes. | Forecasting is frequently changing with the company’s and industry’s current circumstances. | Depending on the firm’s needs, it can be both short-term and long-term. |
| Based on | Budgeting uses revenues, expenses, cash flows, working capital requirements, capital expenditure, etc. | It uses the industry’s historical data & trends, the company’s past performance, and future expectations. | It uses the businesses’ short-term and long-term goals. |
Principles
The principles of budgeting are as follows:
- Suitable Method: Businesses must use budgeting methods that sign with their organizational design and help them create an effective, functional, and practical budget.
- Annuity: Companies should also create new budgets annually and at the start of their financial year.
- Inclusiveness: Budgets should be collaborative and include input and feedback from all stakeholders, executive employees, departments, and management.
- Accuracy: Companies should build comprehensive monetary plans that cover all financial activity aspects using realistic income and expense estimates.
- Transparency: The management should be transparent and open about the budget with all departments to enhance communication and coordination.
- Organizational Goal: The company must make its financial and monetary goals clear and well-defined before planning a budget.
- Flexibility: Budgets must be adaptable to changing business circumstances like goals, so firms should regularly monitor and adjust their budgets.
Tools
1. Spreadsheet:
Businesses can develop a basic budget on a spreadsheet to track their income and expenses, using programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
2. Apps:
Numerous free and paid applications help individuals track expenses, set financial goals, and get warnings for overspending, etc.
3. Internet banking:
Use online banking services by banks to examine account balances, keep tabs on spending, and set up automatic bill payments.
4. Envelope:
It is a traditional method using envelopes to separate the cash for various expenditure categories. After spending the money in the envelope, they can’t make purchases there.
5. Online Software:
Some online websites and software can assist in tracking expenses, managing assets, and assembling a thorough budget.
6. Pen and paper:
Several individuals also use the method of manually recording income and expenditures in a notebook or planner.
Budgeting Rules
Apart from businesses, individuals use budgeting to plan their expenses and meet their financial goals. Following are the rules that individuals can follow to make an effective financial plan.
|
Rule |
Breakdown |
Purpose |
| 50/30/20 | Needs: 50% Wants: 30% Savings: 20% |
The most common rule states that people should spend on survival at the same time, on living life while saving minimally. |
| 30/30/30/10 | Housing: 30% Utility: 30% Wants: 30% Savings: 10% |
It can be beneficial for people looking to create a balance between investments and expenses. |
| 50/40/10 | Needs: 50% Savings: 40% Wants: 10% |
It helps people who want to save quicker for upcoming goals, as they spend the least on wants. |
| 70/20/10 | Expenses: 70% Debt: 20% Wants: 10% |
This rule is for those who are budgeting to settle numerous debts. |
| 50/15/5 | Expenses: 50% Retirement: 15% Short-term Goal: 5% Else: 30% |
It is for people wanting to save for retirement or an upcoming short-term goal. They can even enjoy the financial freedom of spending 30% on what they desire (wants, savings, etc.). |
| 80/20 | Expenses: 80% Savings: 20% |
This rule is for individuals who do not want to restrict their finances too much. It also includes people who do not differentiate wants from needs. |
Budgeting Apps for Individuals
|
App |
Unique Features |
Price |
| Mint | Set financial goals Sync bank accounts Get reminders on bills |
Free version with limited features Subscription for $4.99 a month |
| Goodbudget | Sync bank accounts Allows splitting transactions Gives insight reports |
Free version with limited features Subscription for $7 a month |
| Quicken Simplify | Create a custom dashboard Get alerts on bills Automate bill payments |
30-day free trial Subscription for $5.99 a month |
| Pocketguard | Get detailed analytics Prepares a debt plan Gives saving and spending tips. |
Free version with limited features Subscription for $7.99 a month Lifetime subscription at $79.99 |
| YNAB | Sync bank accounts Provides loan calculator Analyze using reports |
34-day free trial Subscription for $14.99 a month |
Tips
- Focus on goals: Base the budgeting process on “why” rather than “how.” It means you should set goals like paying off debt or building an emergency fund rather than “spend $100 on groceries and $50 on dining,” etc.
- Set realistic goals: The financial goal you set for the year should be realistic and achievable. Keep your expectations in check with your current financial position.
- Distinguish short and long-term: It is crucial to separate short-term goals like saving for rent and long-term goals like planning for retirement.
- Categorize your expenses(fixed and variable): Divide expenses into fixed costs (rent and car payments) and variable costs (groceries, entertainment). It assists in prioritizing necessary spending and identifying areas to save money.
- Track Spending: Ensure not to overestimate your income or undervalue your expenditures. One can track their transactions and payments for a few months to understand their spending habits.
- Monitor your progress: Monitor your financial goals by regularly monitoring spending.
- Adjust the budget: As life circumstances change, the budget should be flexible and adaptable to reallocating finances.
Advantages and Disadvantages
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It gives the management an idea of previous performances, helping them achieve the organization’s overall objective. | There might be bias involved while building a budget, as predicting business finances on projection takes a lot of work. |
| It aids management in reviving the company if it leads to bankruptcy. | It may set higher expectations for the employees, resulting in poor outcomes for the organization. |
| Communication between the personnel and other departments is facilitated by it. | Tight budgets can slow down business expansion. |
| It can improve coordination among an organization’s various components. | Tight and rigid budgets can restrict creativity. |
Final Thoughts
Budgeting is an essential tool for financial planning that can help individuals and businesses avoid financial pitfalls that can eventually lead to bankruptcy. Thus, it is crucial to regularly review and adjust budgets to reflect changes in income, expenses, and financial goals. Overall, budgeting is important because it helps you to take control of your finances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Importance of Budgeting?
Answer: The key reasons why budgeting is essential are as follows:
- It aids in planning and prioritizing business spending, helping control spending, and identifying areas to cut back on unnecessary expenses.
- It also improves understanding of cash flow and financial position and develops financial discipline, helping individuals make informed financial decisions.
- Businesses can use it to define long-term financial goals and work towards achieving them.
- It provides a clear picture of a company’s financial situation and aids in the early detection of potential financial problems.
- It also gives firms a framework to work with and allocate resources effectively and helps save money for investments and manage debts.
Q2. What are the main Objectives of Budgeting?
Answer: The main objectives of budgeting is to effectively plan and allocate financial resources and keep spending under control. Businesses also rely on budgets to serve as a foundation for decision-making and to ensure they meet their financial goals. It can also help firms identify opportunities for improvement and cost savings.
Q3. What are the Best Budgeting Courses?
Answer: Several budgeting courses are available online and offline to help individuals and businesses learn its techniques, tools, and best practices. Popular budgeting courses also teach learners how to create and use budgets effectively.
Q4. Why is it called a Budget?
Answer: The word “budget” is derived from the old French word “bougette,” which means “small bag.” In the 18th century, the British government presented its financial plans in a leather bag, or “budget.” The term “budget” has since come to refer to any financial strategy.
Q5. Who introduced the Budget?
Answer: Sir Robert Walpole, Britain’s first Prime Minister, used a budget for public finance for the first time in 1717. He used a budget to keep government spending and taxation under control. The modern budgeting process, as we know it today, was developed by the United States government in the early twentieth century.
Q6. Explain the prominent Budgeting Ratios.
Answer: Budgeting ratios are financial metrics that companies use in budgeting to assess a company’s financial success.
1. Cash Ratio: It determines a company’s liquidity, helping management create adequate budgets considering the prospect of liquidating its assets.
2. Debt Ratio: It indicates a company’s leverage level and determines how much it is paying to repay debt, which helps the company create an accurate budget.
3. Asset Turnover Ratio: It calculates how much income a business generates, which gives the firm an idea of where to start its budgeting process.
4. Net Operating Ratio: It helps businesses identify the production costs behind revenue generation and plan budget strategies accordingly.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Budgeting? Here we also discuss the definition, purpose, and budgeting process, along with its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –