Updated July 12, 2023
What is EBITDA?
It stands for Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortization. When a company prepares financial statements, margin, and the number of EBITDA is the interesting item in the income statement to judge the profitability of the business. It refers to earnings for any business which comes solely from the operations of the business and it comes after gross profit and deduction of various overheads, selling, and distribution expenses.
It is simply calculated by adding back the non-cash expense i.e. depreciation and amortization, to the company’s operating income.
Types and Components
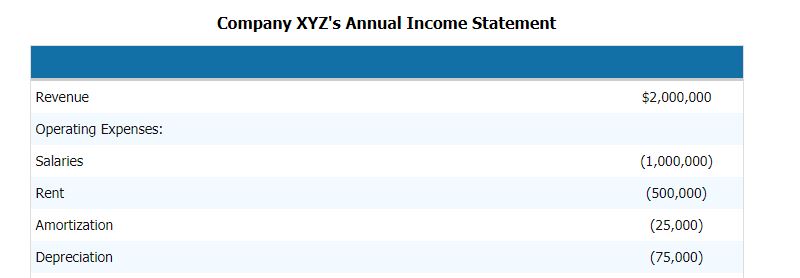
To calculate the EBITDA of the company, we need to follow the following steps. Below is an example of the income statement of the company, including the components, which will give us a clear picture of the components.
To compute the EBITDA of the above company, we need to deduct all the operating and non-operating expenses of the company from the revenue.
Hence revenue – operating expenses – salaries – rent – amortization – depreciation
By deducting this, we can arrive at the EBITDA component
- EBITDA = $2,000,000 – $1,000,000 – $500,000 – $25,000 – $75,000
- EBITDA = $400,000
Hence the component is revenue, operating expenses, salaries, rent, depreciation and amortization, and other direct and indirect expenses.
EBITDA Formula
Alternatively, we can calculate backward also by adding the interest and the non–cash expense component to EBT, i.e., earnings before tax, or PBT, i.e., profit before tax
So the formula will be
Examples / Calculation
Company RMZ Corp prepares their income statements per the U.S. GAAP and the Income statement for 2003 – 2004, as shown below. Calculate the EBITDA and the margin of the company for the fiscal year.
| Revenue | $1,000 |
| Salaries | $400 |
| Rent | $135 |
| Overheads | $150 |
| Contract Cost | $112 |
It can simply be calculated by deducting all the direct and indirect expenses that the business has incurred from the revenue it has generated during that fiscal year. So the calculation is as follows,
EBITDA = 1000 – 400 – 135 – 150 – 112
So, EBITDA = 203
EBITDA Margin = EBITDA / Revenue
= 203 / 1000
EBITDA Margin = 20.3%
Advantages
The following are the advantages:
- This is the most important line item of the business, which is why it is widely used for financial and peer group analyses.
- It is the only line item that tells the analyst the strength of the business, and it tells whether the business can recover all the expenses it is incurring to generate revenue. It is also used for internal management reporting and discussion, and analysis.
- This also tells the management and the executive of the business how well it is generating the revenue to recover the cost incurred if the EBITDA of any business is negative. It becomes an alarming situation for the business to operate.
Disadvantages
- It is widely used in valuation techniques, especially when using the discounted cash flow method, and it can also give misleading results at times because each company can report in a different manner and have its separate definition.
- It is also misleading sometimes when annual financial reports use different accounting principles to calculate or compute the cost components of their business. In that case, the companies under comparison don’t become alike; hence EBIT is now widely used.
Limitations
- It has a limitation that it does not account for changes in working capital. Liquidity also fluctuates because of interest, taxes, and capital expenditures.
- Determine how difficult it would be to turn assets into cash. This could highlight low liquidity, but we have different liquidity measures and ratios.
Conclusion – What is EBITDA?
Hence, by just looking at the margin or the number, the business should not judge the company’s financial strength and weakness. Furthermore, a detail analysis of the profit line items of the company should be done to do a complete analysis and a good analysis.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to EBITDA. Here we discussed the Advantages, Disadvantages, Limitations, Types, Components, and also Examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –