What is Economics – Study of the Production
Simply stating, Economics is the study of the production and consumption of goods and the transfer of wealth to produce and obtain those goods. It helps in explaining how people interact within markets to get what they want or achieve certain goals. Economics is a driving force of human interaction, hence studying it often reveals why people and governments behave in particular ways.
People often use their resources to improve their welfare and well-being. Well-being includes the satisfaction they gain from the products and services, time spent in leisure and with family, community as well as in jobs and the security and services provided by the government.
In short, economics includes the study of labor, land, investments, money, income, and production, and taxes and government expenditures. Thus various economists measure well-being, to learn how it may increase over time, and to evaluate the well-being of the rich and the poor. The most well-known book in economics is the “Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of The Wealth of Nations”, which is written by Adam Smith. Although the behavior of individuals is important, economics also reports the collective behavior of businesses, industries, governments, and countries. Microeconomics is thinking about how individuals make decisions. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, considers aggregate outcomes. These two viewpoints are essential in understanding most economic phenomena.
Career in Economics
A degree in Economics can lead to many career options. For being a professional economist a postgraduate degree is usually required. The majority of Economics students after graduation obtain employment in various sectors like banking, accountancy, tax advice, actuarial work, insurance, and trading, etc.
Various Job Positions offered are
- Environmental Economist
- Research analyst – Economics
- Policy Economist
An Economist is involved in Researching and analyzing economic trends, issues and data. He then uses this research to produce forecasts & reports. This reports forms as a basis for advising clients like companies, financial institutions, & public bodies. This helps in providing them with economic information for use in forming policy or strategy.
Employers for Economics
- Government Services
- Investment banks
- Insurance companies
- Stockbrokers
- Consultancies
- Manufacturing & commercial companies
- Local authorities
- International organizations
- Universities.
Educational Qualification for economics
DEGREE: Degree in Economics normally required.
POSTGRADUATE STUDY: Master’s degree in Economics recommended.
Skill requirement for an Economist
- Understanding of economics concepts and principles
- understanding of economic theory and modeling approaches
- proficiency in quantitative methods
- Communication and Interpersonal skills
- Analytical skills
Learn various techniques to analyze economic trends. Master to analyze savings, investments and risks. Provide advice to aid managerial planning and decision making.
Economics Basics
In order to study economics, we first need to understand the concept of
- Scarcity
- Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
- Demand and Supply
- Elasticity
- Utility
1. Scarcity
Scarcity refers to the tension between limited resources and unlimited wants and needs. Resources for an individual may include time, money and skills. Whereas for a country, limited resources include may natural resources, capital, labor force, and technology. Because all of the resources are limited in comparison to all of our wants, individuals and nations have to decide on what goods and services they can buy and which ones they must sacrifice. Hence people and economies must make decisions of how to distribute their resources.
2. Macro and Microeconomics
Macro and microeconomics are the two points from which the economy is observed.
Macroeconomics considers the total output of a nation. It also looks at the way nations allocate their limited resources of land, labor, and capital in an attempt to maximize production levels in order to promote trade and growth for future generations. Some of the key subjects which are dealt with in macroeconomics include:
- Long-term Economic growth
- Business Cycles
- Inflation
- Global economic linkages
- Macroeconomic Policies
Microeconomics looks into comparable issues, but on the level of the individuals and firms. It inclines to be more scientific in its approach. Microeconomics studies how individuals and firms respond to changes in price.
3. Demand and Supply
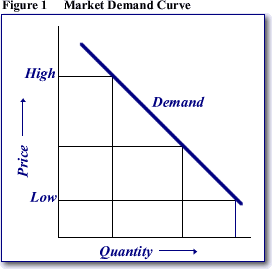
Demand and Supply is the backbone of a market economy and perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics.
Demand denotes how much quantity of a product or service is desired by buyers. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are ready to buy at a certain price. Thus demand relationship denotes the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
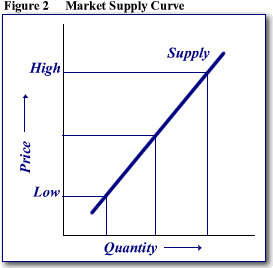
Supply signifies how much the market can offer. The quantity supplied denotes the amount of goods that the producers are willing to supply while receiving a certain price for that. The relationship between price and how much of a good is supplied to the market is known as the supply relationship. Hence Price is a mirror image of supply and demand.
In market economy theories, demand and supply theory will distribute resources in the most effective way possible. Let’s understand this with the help of the law of demand and the law of supply.
1. The Law of Demand
The law of demand states that, if all other factors remain equal, the higher the price of a good, the less the people will demand that good. Hence the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded. The amount of a good that buyers acquire at a higher price is less. This is because as the price of a good goes up, so does the opportunity cost of buying that good.
2. The Law of Supply
The law of supply establishes the quantities that will be sold at a certain price. The supply relationship tends to show an upward slope. This ultimately means that the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. Producers supply more at a higher price. This is because selling a higher quantity at a higher price increases revenue.
4. Elasticity
Elasticity is the degree to which a demand or supply curve reacts to a change in price. It is also significant that the elasticity varies among products because some products may be more essential to the consumer than the other ones. A good or service is considered to be highly elastic when a slight change in its price leads to a sharp change in the quantity demanded or supplied. Whereas an inelastic good or service is one in which changes in price witness only slight changes in the quantity demanded or supplied.
The formula for determining the elasticity of the supply or demand curves is-
Elasticity = (% change in quantity / % change in price)
5. Utility
Total utility is the aggregate sum of contentment or benefit that an individual gains from consuming a given amount of goods or services. The amount of a person’s total utility matches the person’s level of consumption or utilization. The more the person consumes, the larger is his total utility. Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction, or amount of utility, gained from each extra unit of consumption.
6. Monopolies, Oligopolies, and Perfect Competition
A monopoly is a market structure where there is only one producer or a seller for a product. In other words, it is a single business industry. Entry into the monopoly market is difficult due to high costs or other obstructions, which may be economic, social or political. For example- in Saudi Arabia the government has control over the oil industry. Monopoly may also arise when a company has a copyright or patent which prevents others from entering the market.
In an oligopoly, there are only a few firms or players who form the industry. This select cluster of companies has control over the price. Also, oligopoly has high barriers to entry.
Perfect competition arises when there are many buyers and sellers, products that are similar in nature and as a result many substitutes are available for them. In perfect competition there are few barriers to entry and the prices are determined by supply and demand.
Important economic variables which help in Investing in the Stock Market
- Inflation
- Interest Rates
- Fiscal Policy
- Monetary Policy
1. Inflation
Inflation signifies a rise in the general level of prices. It refers to the rate of general price increase over a period of one year. For example, if the current inflation is 6%, it means the general price level has increased by 6% over the last one year.
To measure the rate of inflation, the following formula is used:
Rate of Inflation in year X=
[( Px – Px-1 ) / (Px-1 )] * 100Where:
Px = price index for the year X.
Px-1= price index of the preceding year.
2. Interest Rates
The amount lent or borrowed is called the principal. The interest rate is expressed in terms of percentage of the principal and in annualized terms. From a borrower’s perspective, the interest rate is the cost of capital.
Following factors affect the interest rates in an economy:
- Monetary Policy
- Growth in the economy
- Inflation
- Global liquidity
- Uncertainty
3. Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policies are the Government spending policies which can influence the macroeconomic conditions. Through this policy, the regulators try to improve unemployment rates, control inflation, stabilize business cycles and influence interest rates in an effort to control the economy.
4. Monetary Policy
Monetary policies include the actions of a central bank, currency board or any other regulatory committee. It determines the size and rate of growth of the money supply, which in turn affects interest rates. Monetary policies are maintained through actions such as increasing the interest rate, or changing the amount of money banks need to keep in the bank reserves.
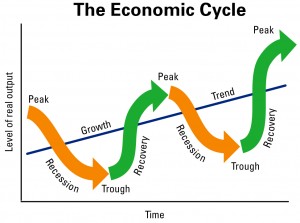
Business Cycle
Business cycle is the recurring and fluctuating levels of economic activity which an economy experiences over a long period of time. The basic 5 stages of the business cycle are-
- Growth or expansion
- Peak
- Recession or contraction
- Trough
- Recovery.